التيس (نجم)
نجم التيس ، الاسم الإنكليزي Delta Draconis والاسم التقليدي له هو Altais مشتق من الاسم العربي. وهو نجم في كوكبة التنين .
| التيس | |
|---|---|
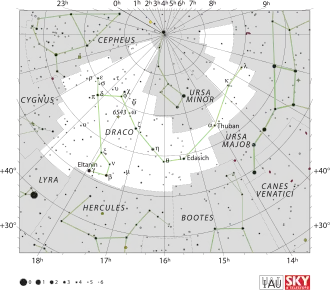
مكان نجم التيس (في الدائرة الحمراء) | |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 | |
| كوكبة | التنين |
| مطلع مستقيم | 19س 12د 33.30197ث[1] |
| الميل | ° +67 ′39 ″41.5456[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 3.07[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | G9 III[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +0.78[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +1.00[2] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +24.8[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | +95.74[1]+91.92[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 33.48 ± 0.10 د.ق |
| البعد | 97٫4 ± 0٫3 س.ض (29٫87 ± 0٫09 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | +0.62[5] |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 2.32[5] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 11[6] نق☉ |
| ضياء | 59[5] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 2.98[7] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 4,820[7] ك |
| معدنية (فلك) [Fe/H] | –0.27[7] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 8[8] كم/ثا |
| عمر | 0.8[5] ج.سنة |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Aldib, Altais,[9] Nodus Secundus,[10] HR 7310, BD+67 1129, HD 180711, SAO 18222, FK5 723, هيباركوس 94376.[11] | |
هو نجم عملاق من الصنف G9III ويبعد حوالي 100 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض وله قدر ظاهري +3.0 ويبلغ التزيح 32.54 دقيقة قوسية يتوافق هذا مع نصف قر يعادل 11 ضعف من قطر الشمس.
انظر أيضا
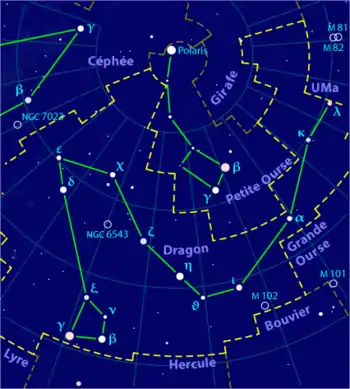
كوكبة التنين ، وبها نجم التيس (δ Draconis).
مراجع
- van Leeuwen, F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474، ص. 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- Johnson, H. L.؛ Mitchell؛ Iriarte؛ Wisniewski (1966)، "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars"، Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory، 4 (99): 99، Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- Roman, Nancy G. (يوليو 1952)، "The Spectra of the Bright Stars of Types F5-K5"، Astrophysical Journal، 116: 122، Bibcode:1952ApJ...116..122R، doi:10.1086/145598.
- Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953)، General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities، Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington، Bibcode:1953QB901.W495......
- Takeda, Yoichi؛ وآخرون (أغسطس 2008)، "Stellar Parameters and Elemental Abundances of Late-G Giants"، Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan، ج. 60، ص. 781–802، arXiv:0805.2434، Bibcode:2008PASJ...60..781T، doi:10.1093/pasj/60.4.781
- The Sun has a radius of 0.004652 AU. Thus:
- Stellar diameter = 1 AU × angular diameter/parallax = 3.37/32.54 AU = 0.10 AU = قالب:Solar radius.
- McWilliam, Andrew (ديسمبر 1990)، "High-resolution spectroscopic survey of 671 GK giants. I - Stellar atmosphere parameters and abundances"، Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series، 74: 1075–1128، Bibcode:1990ApJS...74.1075M، doi:10.1086/191527.
- Bernacca, P. L.؛ Perinotto, M. (1970)، "A catalogue of stellar rotational velocities"، Contributi Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova in Asiago، 239 (1): 1، Bibcode:1970CoAsi.239....1B.
- Bakich, Michael E. (1995)، The Cambridge guide to the constellations، Cambridge University Press، ص. 184، ISBN 0-521-44921-9.
{{استشهاد بكتاب}}: صيانة CS1: التاريخ والسنة (link) - Kaler, James B.، "Nodus Secundus"، STARS، University of Illinois، مؤرشف من الأصل في 07 أكتوبر 2018، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 06 أبريل 2010.
- "del Dra -- Star in double system"، SIMBAD، Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg، مؤرشف من الأصل في 07 نوفمبر 2017، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 06 أبريل 2010.
- بوابة نجوم
- بوابة علم الفلك
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.