Ü
Ü (lowercase ü) is a Latin script character composed of the letter U and the diaeresis diacritical mark. In some alphabets such as those of a number of Romance languages or Guarani it denotes an instance of regular U to be construed in isolation from adjacent characters with which it would usually form a larger unit; other alphabets like the Azerbaijani, Estonian, German, Hungarian and Turkish ones treat it as a letter in its own right. In those cases it typically represents a close front rounded vowel [y] ⓘ.
| U with umlaut/diaresis | |
|---|---|
| Ü ü | |
| V, UE, II | |
 | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | alphabetic |
| Phonetic usage | [ɨ] |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Variations | V, UE, II |
| Other | |
Although not a part of their alphabet, Ü also appears in languages such as Finnish and Swedish when retained in foreign proper names like München ("Munich"). A small number of Dutch and Afrikaans words employ the character to mark vowel hiatus (e.g. reünie /reːyˈni/ ("reunion"), a loanword marked with diaeresis to suppress the native reading of eu as a digraph pronounced /øː/).
U-umlaut
A glyph, U with umlaut, appears in the German alphabet. It represents the umlauted form of u, which results in [yː] when long and [ʏ] when short. The letter is collated together with U, or as UE. In languages that have adopted German names or spellings, such as Swedish, the letter also occurs. It is however not a part of these languages' alphabets. In Swedish the letter is called tyskt y which means German y.
Though not a part of the Slovene alphabet, ü is often used in eastern Styrian dialects, especially around Ptuj[1] as well as in the Resian dialect with the same pronouncation as in German.
In other languages that do not have the letter as part of the regular alphabet or in limited character sets such as ASCII, U-umlaut is frequently replaced with the two-letter combination "ue". Software for optical character recognition sometimes sees it falsely as ii.
Letter Ü
The letter Ü is present in the Hungarian, Turkish, Uyghur Latin, Estonian, Azeri, Turkmen, Crimean Tatar, Kazakh Latin and Tatar Latin alphabets, where it represents a close front rounded vowel [y]. It is considered a distinct letter, collated separately, not a simple modification of U or Y, and is distinct from UE.
Wayuu represents the close central unrounded vowel [ɨ] using this letter.
In the Swedish and Finnish alphabets ü is alphabetized as y.
It is not present in the Basque alphabet but the Souletin dialect uses it for [y].
This same letter appears in the Chinese Romanisations pinyin, Wade–Giles, and the German-based Lessing-Othmer, where it represents the same sound [y]: 綠/lǜ (green) or 女/nǚ (female). Standard Mandarin Chinese pronunciation has both the sounds [y] and [u]. Pinyin only uses "Ü" to represent [y] after the letters "L" or "N" to avoid confusion with words such as 路/lù (road) and 怒/nù (anger). Words such as 玉/yù (jade) or 句/jù (sentence) are pronounced with [y], but are not spelled with "Ü", although Wade–Giles and Lessing use "Ü" in all situations. As the letter "Ü" is missing on most keyboards and the letter "V" is not present in standard Mandarin pinyin, the letter "V" is used on most computer Chinese input methods to enter the letter "Ü". As a result, romanisation of Chinese with the letter "V" representing the Ü sound is sometimes found. However, Ü sound should be officially represented by "yu" in Pinyin when it is difficult to enter Ü. For example, the surname Lü (吕) would be written as "Lyu" in passports.[2] Four extra tones for the letter "ü", which are "ǖ, ǘ, ǚ, ǜ", is added in Unicode as per GB/T 2312.
U-diaeresis
Several languages use diaeresis over the letter U to show that the letter is pronounced in its regular way, without dropping out or building diphthongs with neighbouring letters.
In Spanish, it is used to distinguish between "gue"/"güe" [ɡe]/[ɡwe] and "gui"/"güi" [ɡi]/[ɡwi]: nicaragüense ("Nicaraguan"), pingüino ("penguin").
Similarly in Catalan, "gue~güe" are [ɡe]~[ɡwe], "gui~güi" are [ɡi]~[ɡwi], "que~qüe" are [ke]~[kwe] and "qui~qüi" are [ki]~[kwi], as in aigües, pingüins, qüestió, adeqüi. Also, ü is used to mark that vowel pairs that normally would form a diphthong must be pronounced as separate syllables, examples: Raül, diürn.
In French, the diaeresis appears over the "u" only very rarely, in some uncommon words, capharnaüm [-aɔm] ('shambles'), Capharnaüm/Capernaüm [-aɔm] or Emmaüs [-ays]. After the 1990 spelling reforms, it is applied to a few more words, like aigüe (formerly aiguë), ambigüe (formerly ambiguë) and argüer [aʁɡɥe] (formerly without the diaeresis).
Usage in phonetic alphabets
In the Rheinische Dokumenta, a phonetic alphabet for many West Central German, Low Rhenish, and related vernacular languages, "ü" represents a range from [y] to [ʏ].
Typography
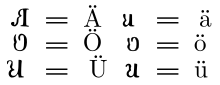
Historically the unique letter Ü and U-diaeresis were written as a U with two dots above the letter.
U-umlaut was written as a U with a small e written above (Uͤ uͤ): this minute e degenerated to two vertical bars in medieval handwritings. In most later handwritings these bars in turn nearly became dots.
In modern typography there was insufficient space on typewriters and later computer keyboards to allow for both a U-with-dots (also representing Ü) and a U-with-bars. Since they looked near-identical the two glyphs were combined, which was also done in computer character encodings such as ISO 8859-1. As a result, there was no way to differentiate between the three different characters. While the distinction can be recreated in modern Unicode using combining diacritics, modern typographic standards do not recommend doing so. In the Hungarian alphabet, double acute U (Ű) is a distinct letter representing a long Ü.
Computing codes
| Preview | Ü | ü | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS | LATIN SMALL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 220 | U+00DC | 252 | U+00FC |
| UTF-8 | 195 156 | C3 9C | 195 188 | C3 BC |
| GB 18030 | 129 48 137 53 | 81 30 89 35 | 168 185 | A8 B9 |
| Numeric character reference | Ü | Ü | ü | ü |
| Named character reference | Ü | ü | ||
| EBCDIC family | 252 | FC | 220 | DC |
| ISO 8859-1/2/3/4/9/10/14/15/16 | 220 | DC | 252 | FC |
| CP437 | 154 | 9A | 129 | 81 |
| Code page 10029 | 134 | 86 | 159 | 9F |
| GB/T 2312, GBK, GB 18030 | 168 185 | A8 B9 | ||
| HKSCS | 136 162 | 88 A2 | ||
Tonal marks for Hanyu Pinyin
| Preview | Ǖ | ǖ | Ǘ | ǘ | Ǚ | ǚ | Ǜ | ǜ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND MACRON | LATIN SMALL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND MACRON | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND ACUTE | LATIN SMALL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND ACUTE | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND CARON | LATIN SMALL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND CARON | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND GRAVE | LATIN SMALL LETTER U WITH DIAERESIS AND GRAVE | ||||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 469 | U+01D5 | 470 | U+01D6 | 471 | U+01D7 | 472 | U+01D8 | 473 | U+01D9 | 474 | U+01DA | 475 | U+01DB | 476 | U+01DC |
| UTF-8 | 199 149 | C7 95 | 199 150 | C7 96 | 199 151 | C7 97 | 199 152 | C7 98 | 199 153 | C7 99 | 199 154 | C7 9A | 199 155 | C7 9B | 199 156 | C7 9C |
| GB 18030 | 129 48 159 57 | 81 30 9F 39 | 168 181 | A8 B5 | 129 48 160 48 | 81 30 A0 30 | 168 182 | A8 B6 | 129 48 160 49 | 81 30 A0 31 | 168 183 | A8 B7 | 129 48 160 50 | 81 30 A0 32 | 168 184 | A8 B8 |
| Numeric character reference | Ǖ | Ǖ | ǖ | ǖ | Ǘ | Ǘ | ǘ | ǘ | Ǚ | Ǚ | ǚ | ǚ | Ǜ | Ǜ | ǜ | ǜ |
| GB/T 2312, GBK, GB 18030 | 168 181 | A8 B5 | 168 182 | A8 B6 | 168 183 | A8 B7 | 168 184 | A8 B8 | ||||||||
| HKSCS | 136 124 | 88 7C | 136 125 | 88 7D | 136 126 | 88 7E | 136 161 | 88 A1 | ||||||||
Uralic Phonetic Alphabet symbols related to Ü
| Preview | ᴞ | |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN SMALL LETTER SIDEWAYS DIAERESIZED U | |
| Encodings | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 7454 | U+1D1E |
| UTF-8 | 225 180 158 | E1 B4 9E |
| GB 18030 | 129 53 215 56 | 81 35 D7 38 |
| Numeric character reference | ᴞ | ᴞ |
Keyboarding
The methods available for entering ⟨Ü⟩ and ⟨ü⟩ from the keyboard depend on the operating system, the keyboard layout, and the application.
- Microsoft Windows – some keyboard layouts feature separate keys for ⟨Ü⟩
- Using the Swiss French keyboard, ⟨ü⟩ can be entered by typing ⇧ Shift+È
- Using the US International layout, ⟨ü⟩ can be entered by typing AltGR+Y
- Microsoft Windows: with the Number Lock on, hold down the Alt key while typing on the numeric keypad the decimal value of the code point from the active DOS/OEM code page without a leading zero, then release the Alt key; i.e. Alt+1+5+4 for ⟨Ü⟩ and Alt+1+2+9 for ⟨ü⟩
- Microsoft Windows: with the Number Lock on, hold down the Alt key while typing on the numeric keypad the decimal value of the code point from the active ANSI code page with a leading zero, then release the Alt key; i.e. Alt+0+2+2+0 for ⟨Ü⟩ and Alt+0+2+5+2 for ⟨ü⟩
- Microsoft Word for Windows: type Ctrl+: followed by ⇧ Shift+U for ⟨Ü⟩ or Ctrl+: then U for ⟨ü⟩
- macOS with an English keyboard layout (Australian, British, or U.S.): type ⌥ Option+U followed by ⇧ Shift+U for ⟨Ü⟩ or ⌥ Option+U and then U for ⟨ü⟩ or by keeping the U key pressed and then typing 2
- In Linux-based operating systems, this symbol may be typed by pressing the Compose key followed by u, ".
- In GTK-based GUI-Applications, Ctrl+⇧ Shift+U followed by the Hex-Code
See also
References
- "About Lük - Ptujski Lük".
- 新版护照“吕”姓改拼“LYU” 英文无ü被替代. Beijing Daily. 2012-10-11.