(7482) 1994 PC1
(7482) 1994 PC1 is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.1 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 August 1994, by astronomer Robert McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory in Coonabarabran, Australia.[2] With an observation arc of 47 years it has a very well known orbit and was observed by Goldstone radar in January 1997.[6] The 2022 approach has been observed every month since August 2021.[2]
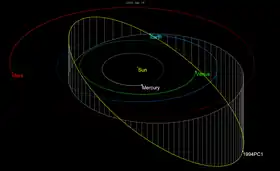 Orbit with positions Jan 2020 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | R. H. McNaught |
| Discovery site | Siding Spring Obs. |
| Discovery date | 9 August 1994 |
| Designations | |
| (7482) 1994 PC1 | |
| 1994 PC1 | |
| Apollo · NEO · PHA[1][2] | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 2022-Jan-21 (JD 2459600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 47.23 yr (17,251 days) |
| Earliest precovery date | 22 September 1974 |
| Aphelion | 1.7935 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.9042 AU |
| 1.3488 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3297 |
| 1.56 yr (572 days) | |
| 337.27° | |
| 0° 37m 51.6s / day | |
| Inclination | 33.479° |
| 117.88° | |
| 47.477° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00054 AU (0.21 LD) |
| Mars MOID | 0.139 AU (20.8 million km)[2] |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 1.052±0.303 km[3] 1.30 km (calculated)[4] |
| 2.5999 h[5] | |
| 0.277±0.185[3] 0.20 (assumed)[4] | |
| SMASS = S[1][4] | |
| 16.6[1][4] · 16.80±0.3[3] | |
Orbit and classification
1994 PC1 orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.9–1.8 AU once every 1 years and 7 months (572 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.33 and an inclination of 33° with respect to the ecliptic.[1]
On 17 January 1933, it passed 811,350 km (504,150 mi) from the Moon and then about an hour later made its closest known approach to Earth of 1,125,400 km (699,300 mi).[1] On 18 January 2022, it passed about 1,981,468 km (1,231,227 mi) from Earth.[1]
| Date | JPL SBDB nominal geocentric distance |
uncertainty region (3-sigma) |
|---|---|---|
| 1933-01-17 | 1125383 km | ± 65 km[lower-alpha 1] |
| 2022-01-18 | 1981468 km | ± 47 km[7] |
| 2105-01-18 | 2328125 km | ± 1069 km[8] |
Physical characteristics
In the SMASS classification, 1994 PC1 is a common stony S-type asteroid.[1][4]
Rotation period
In 1998, a rotational lightcurve of 1994 PC1 was obtained from photometric observations by Petr Pravec. Lightcurve analysis gave a well-defined rotation period of 2.5999 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.29 magnitude (U=3).[5]
Diameter and albedo
According to the survey carried out by the NEOWISE mission of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, 1994 PC1 measures 1.052 kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo of 0.277.[3] The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link assumes an albedo of 0.20 and calculates a diameter of 1.30 kilometers based on an absolute magnitude of 16.8.[4]
2022 flyby
At 18 January 2022 21:51 UTC, 1994 PC1 passed 5.15 lunar distances from Earth[1] and had a 3-sigma uncertainty region of less than ± 50 km.[7] It peaked at an apparent magnitude of about 10[9] placing it just outside the reach of common 7×50 binoculars. The nearly Full moon being about 100 degrees from the asteroid during closest approach may have made it more difficult to observe with smaller telescopes.
| Date & Time | Approach to |
Nominal distance |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-18 18:58 | Moon | 2085780 km[10] |
| 2022-01-18 21:51 | Earth | 1981468 km[1] |

Sun · Earth · 1994 PC1
 |
| PHA | Date | Approach distance (lunar dist.) | Abs. mag (H) |
Diameter (C) (m) |
Ref (D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nomi- nal(B) |
Mini- mum |
Maxi- mum | |||||
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 1908-12-16 | 3.542 | 3.537 | 3.547 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (458732) 2011 MD5 | 1918-09-17 | 0.911 | 0.909 | 0.913 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (7482) 1994 PC1 | 1933-01-17 | 2.927 | 2.927 | 2.928 | 16.8 | 749–1357 | data |
| 69230 Hermes | 1937-10-30 | 1.926 | 1.926 | 1.927 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| 69230 Hermes | 1942-04-26 | 1.651 | 1.651 | 1.651 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| (137108) 1999 AN10 | 1946-08-07 | 2.432 | 2.429 | 2.435 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 1956-12-16 | 3.523 | 3.523 | 3.523 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (163243) 2002 FB3 | 1961-04-12 | 4.903 | 4.900 | 4.906 | 16.4 | 1669–1695 | data |
| (192642) 1999 RD32 | 1969-08-27 | 3.627 | 3.625 | 3.630 | 16.3 | 1161–3750 | data |
| (143651) 2003 QO104 | 1981-05-18 | 2.761 | 2.760 | 2.761 | 16.0 | 1333–4306 | data |
| 2017 CH1 | 1992-06-05 | 4.691 | 3.391 | 6.037 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (170086) 2002 XR14 | 1995-06-24 | 4.259 | 4.259 | 4.260 | 18.0 | 531–1714 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 2001-12-16 | 4.859 | 4.859 | 4.859 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| 4179 Toutatis | 2004-09-29 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 4.031 | 15.3 | 2440–2450 | data |
| 2014 JO25 | 2017-04-19 | 4.573 | 4.573 | 4.573 | 17.8 | 582–1879 | data |
| (137108) 1999 AN10 | 2027-08-07 | 1.014 | 1.010 | 1.019 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (35396) 1997 XF11 | 2028-10-26 | 2.417 | 2.417 | 2.418 | 16.9 | 881–2845 | data |
| (154276) 2002 SY50 | 2071-10-30 | 3.415 | 3.412 | 3.418 | 17.6 | 714–1406 | data |
| (164121) 2003 YT1 | 2073-04-29 | 4.409 | 4.409 | 4.409 | 16.2 | 1167–2267 | data |
| (385343) 2002 LV | 2076-08-04 | 4.184 | 4.183 | 4.185 | 16.6 | 1011–3266 | data |
| (52768) 1998 OR2 | 2079-04-16 | 4.611 | 4.611 | 4.612 | 15.8 | 1462–4721 | data |
| (33342) 1998 WT24 | 2099-12-18 | 4.919 | 4.919 | 4.919 | 17.9 | 556–1795 | data |
| (85182) 1991 AQ | 2130-01-27 | 4.140 | 4.139 | 4.141 | 17.1 | 1100 | data |
| 314082 Dryope | 2186-07-16 | 3.709 | 2.996 | 4.786 | 17.5 | 668–2158 | data |
| (137126) 1999 CF9 | 2192-08-21 | 4.970 | 4.967 | 4.973 | 18.0 | 531–1714 | data |
| (290772) 2005 VC | 2198-05-05 | 1.951 | 1.791 | 2.134 | 17.6 | 638–2061 | data |
| (A) List includes near-Earth approaches of less than 5 lunar distances (LD) of objects with H brighter than 18. (B) Nominal geocentric distance from the Earth's center to the object's center (Earth radius≈0.017 LD). (C) Diameter: estimated, theoretical mean-diameter based on H and albedo range between X and Y. (D) Reference: data source from the JPL SBDB, with AU converted into LD (1 AU≈390 LD) (E) Color codes: unobserved at close approach observed during close approach upcoming approaches | |||||||
Naming
As of 2022, this minor planet has not been named.[2]
See also
- List of asteroid close approaches to Earth in 2022
- 2014 JO25 – ~800 meters in diameter and passed 4.57 LD from Earth on 19 April 2017
- (153814) 2001 WN5 – ~900 meters in diameter and will pass 0.65 LD from Earth on 26 June 2028
Notes
- The 1933 approach is better constrained than the 2105 approach as a result of the 1974, 1977, 1980 precovery images of the asteroid.[lower-alpha 2]
References
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 7482 (1994 PC1)" (Under "Distance Units" select km for more sig figs). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- "7482 (1994 PC1)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- Mainzer, A.; Grav, T.; Masiero, J.; Bauer, J.; Cutri, R. M.; McMillan, R. S.; et al. (November 2012). "Physical Parameters of Asteroids Estimated from the WISE 3-Band Data and NEOWISE Post-Cryogenic Survey". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 760 (1): 6. arXiv:1210.0502. Bibcode:2012ApJ...760L..12M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/760/1/L12. S2CID 41459166.
- "LCDB Data for (7482)". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 2 November 2017.
- Pravec, Petr; Wolf, Marek; Sarounová, Lenka (November 1998). "Lightcurves of 26 Near-Earth Asteroids". Icarus. 136 (1): 124–153. Bibcode:1998Icar..136..124P. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.5993.
- "Asteroid Radar History". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- "Horizons Batch for 2022-Jan-18 21:51 UT". JPL Horizons. Archived from the original on 13 January 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2021.
- "Horizons Batch for 2105-Jan-18 12:28 UT". JPL Horizons. Archived from the original on 13 January 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2021.
- "Earth Approach Jan 2022". JPL Horizons. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- "Moon Horizons Batch for 2022-Jan-18 18:58 UT". JPL Horizons. Archived from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
External links
- A Giant Asteroid Bigger Than The Empire State Building Is About to Zip Past Earth (Fiona MacDonald 5 January 2022)
- Huge asteroid will pass Earth safely January 18 (Eddie Irizarry December 30, 2021)
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info Archived 16 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine)
- Sky and Telescope: The kilometer-wide, potentially hazardous asteroid 1994 PC1 will fly past Earth on January 18th.
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- (7482) 1994 PC1 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- (7482) 1994 PC1 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (7482) 1994 PC1 at the JPL Small-Body Database

