1937 Romanian general election
General elections were held in Romania in December 1937.[1] The Chamber of Deputies was elected on 20 December, whilst the Senate was elected in three stages on 22, 28 and 30 December.[1] Voting was by universal male vote,[2] making them the last elections held before female suffrage was introduced.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 387 seats in the Chamber of Deputies All 113 seats in the Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 66.07% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
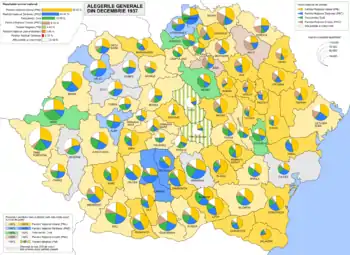
The National Liberal Party remained the largest party, winning 152 of the 387 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 97 of the 112 the Senate seats. However, unlike all previous elections organised by partisan governments, the results did not give the governing party a majority. The National Liberals' unexpectedly poor showing prevented it from creating a government on its own (obtaining 40% of the vote would have automatically awarded them a large parliamentary majority). They ruled out a coalition with their arch-rivals, the second-placed National Peasants' Party, or with the third-placed Iron Guard's Everything for the Country Party. King Carol II invited the fascist Octavian Goga to form a government, though his National Christian Party finished fourth and had an avowedly anti-Semitic platform. Goga's government was formed on 29 December 1937.[3]
Electoral system
The members of the Chamber of Deputies were elected from multi-member constituencies with between two and twenty seats. Seats were allocated on a proportional basis, unless a party received over 40% of the vote nationally. If this happened, the party in question was awarded half of the seats in each constituency, with the other half divided proportionally amongst the all parties (including the victorious one), with an electoral threshold of 2%.[4]
The Senate was elected on a plurality basis. Voters had to be at least 21 to vote in the Chamber elections and 25 to vote in Senate elections. Candidates for both bodies had to be at least 40 years old.[4]
Campaign
The campaign was marred by violent clashes between the two fascist groups, the National Christian Party's Lăncieri and the Iron Guard.[5] During the first round, clashes occurred at Orhei and Târgu Mureş, when four were killed and which led to 300 arrests.
After the vote, the Electoral Commission surprised observers by deciding, in its allocation of seats by proportional representation, to count the entire country as one district, rather than use smaller districts, as had been the norm.
Results
Chamber of Deputies
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Liberal Party | 1,103,353 | 36.46 | 152 | –148 | |
| National Peasants' Party | 626,612 | 20.71 | 86 | +57 | |
| Everything for the Country Party | 478,378 | 15.81 | 66 | New | |
| National Christian Party | 281,167 | 9.29 | 39 | +21 | |
| Magyar Party | 136,139 | 4.50 | 19 | +11 | |
| National Liberal Party–Brătianu | 119,361 | 3.94 | 16 | +6 | |
| Radical Peasants' Party | 69,198 | 2.29 | 9 | +3 | |
| Agrarian Union Party | 52,101 | 1.72 | 0 | –5 | |
| Jewish Party | 43,681 | 1.44 | 0 | 0 | |
| German Party | 43,612 | 1.44 | 0 | New | |
| Social Democratic Party | 28,840 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | |
| People's Party | 25,567 | 0.84 | 0 | 0 | |
| Traders Council | 1,219 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | |
| Other parties | 16,912 | 0.56 | 0 | – | |
| Total | 3,026,140 | 100.00 | 387 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 3,026,140 | 98.52 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 45,555 | 1.48 | |||
| Total votes | 3,071,695 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,649,163 | 66.07 | |||
| Source: Sternberger et al.,[6] Nohlen & Stöver | |||||
Senate
| Party | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Liberal Party | 97 | –8 | |
| National Peasants' Party | 10 | +10 | |
| Everything for the Country Party | 4 | New | |
| Magyar Party | 2 | –1 | |
| Total | 113 | +5 | |
| Source: Nohlen & Stöver | |||
Aftermath
The elections were the last elections held under the nominally democratic 1923 constitution. On 18 January 1938, less than a month after the elections, Goga asked Carol to dissolve Parliament. Carol granted the request, with a view toward holding fresh elections that winter. However, Carol became alarmed with overtures being made by the National Christian Party towards the Iron Guard,[7] and on 10 February 1938 he sacked Goga after only 45 days in office, suspended the constitution, cancelled the elections, and seized emergency powers. Later that year Carol pushed through a new constitution that concentrated all power in his hands, effectively codifying his emergency powers and turning his government into a royal dictatorship.
As a result, the elections were the last free multi-party elections until 1990.[8] Elections held in 1939 featured a single list from Carol's National Renaissance Front. By the time of the first elections after World War II in 1946, the country had passed through two more dictatorships and a fourth, Communist one was rapidly consolidating.
References
- Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p1591 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- Nohlen & Stöver, p1610-1611
- Brustein, William (2010). Roots of Hate: Anti-Semitism in Europe Before the Holocaust. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-52177-478-9.
- Nohlen & Stöver, p1582
- Background and Precursors to the Holocaust, p. 26
- Dolf Sternberger, Bernhard Vogel, Dieter Nohlen & Klaus Landfried (1978) Die Wahl der Parlamente: Band I: Europa, Zweiter Halbband, pp1062–1064
- Michael Mann, Fascists, Cambridge University Press, 2004, pp. 288-289
- Reaves, Joseph A. Romanians Hope Free Elections Mark Revolution's Next Stage. Chicago Tribune, 1990-03-30.
- Kurt W. Treptow (1996) "Alegerile din decembrie 1937 şi instaurarea dictaturii regale" in Romania and World War II, Centrul de Studii Româneşti, Iaşi (in Romanian)
- "4 Die as Rumania Votes", The New York Times, 21 December 1937, p18
- "Cabinet Aims to Rule Rumania", The New York Times, 24 December 1937, p4



