1995 Lombard regional election
The 1995 Lombard regional election took place on 23 April 1995. The 6th term of the Regional Council was chosen.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
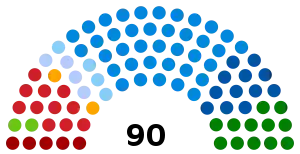
All 90[1] seats to the Regional Council of Lombardy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 84.24% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
For the first time the President of the Region was directly elected by the people, although the election was not yet binding and the President-elect could have been replaced during the term.
Roberto Formigoni (member of the right-wing of the Italian People's Party, on the list of Forza Italia) was elected President of the Region, defeating Diego Masi (Segni Pact) and Francesco Speroni (Northern League).
Electoral system
Lombardy used for the first time the national Tatarella Law to elect its Council. Sixty-four councillors are elected in provincial constituencies by proportional representation using the largest remainder method with a Droop quota and open lists; remained seats and votes are grouped at regional level where a Hare quota is used, and then distributed to provincial party lists.
Sixteen councillors are elected at-large using a general ticket: parties are grouped in alliances, and the alliance which receives a plurality of votes elects all its candidates, its leader becoming the President of Lombardy. If an alliance wins more than 60% of votes, only 8 candidates from the regional list will be chosen and the number of those elected in provincial constituencies will be 72; if the winning alliance receives less than 50% of votes, special seats are added to the Council to ensure a large majority for the President's coalition.
Council apportionment
According to the official 1991 Italian census, the 64 Council seats which must be covered by proportional representation were so distributed between Lombard provinces.
| BG | BS | CO | CR | LC | LO | MN | MI | PV | SO | VA | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 27 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 64 |
The allocation is not fixed. Remaining seats and votes after proportional distribution, are all grouped at regional level and divided by party lists. The consequent division of these seats at provincial level usually change the original apportionment. Only 41 seats were directly assigned at provincial level, and the final distribution between provinces changed in this way.
| BG | BS | CO | CR | LC | LO | MN | MI | PV | SO | VA | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +3 | +3 | +1 | = | = | = | -1 | +1 | +2 | = | +1 | +10 |
As it can be seen, the simple plurality victory of the Pole of Freedoms caused the distribution of ten more seats to the President's majority at provincial level. Brescia and Como and Pavia received two new seats, Bergamo and Lodi and Milan and Varese one each.
Parties and candidates
| Political party or alliance | Constituent lists | Previous result | Candidate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes (%) | Seats | |||||
| Centre-left coalition | Populars | 28.6 | 25 | Diego Masi | ||
| Democratic Party of the Left | 18.8 | 15 | ||||
| Federation of the Greens | 5.2 | 3 | ||||
| Pact of Democrats | — | — | ||||
| Labour Federation | — | — | ||||
| Populars and Democrats | — | — | ||||
| Northern League – Lombard League | 18.9 | 15 | Francesco Speroni | |||
| Centre-right coalition | National Alliance | 2.5 | 2 | Roberto Formigoni | ||
| Forza Italia – The People's Pole | — | — | ||||
| Christian Democratic Centre | — | — | ||||
| Pensioners of Sun | — | — | ||||
| Pensioners' Party | 1.8 | 1 | Carlo Fatuzzo | |||
| Pannella's coalition | Pannella List | 1.0 | 1 | Marco Pannella | ||
| Autonomist Front | — | — | ||||
| Communist Refoundation Party | — | — | Giuseppe Torri | |||
Results
In the context of the profound political changes that invested Italy between 1992 and 1994, Italian Parliament changed the regional electoral law, adapting them to new majoritarian principle now in vogue in the country, trim and tend bipolar politics. The new political geography, however, did not fit properly to Lombardy where, besides a garrison of far-left, assumed significant importance the presence of Umberto Bossi's Northern League, during the previous five years had not made any secret to aim the conquest of the Regional Presidency as a key step for a transformation of Italy in a federal state. In addition to the League, however, another major innovation had originated in Lombardy in 1994: the descent into the political field of Silvio Berlusconi, who by its movement Forza Italia had collected anti-Communist orphans of deceased traditional parties.
The central political alliances had not been followed up at Lombardy, with the League in sharp contrast with Forza Italia, not only for connecting the latter with the newly formed training nationalist and post-fascist of National Alliance, but mainly because the entrance into the political arena of Forza Italia, accused by the League to be the trojan horse for the recycling of the old political class, had led to the arrest of the Northern League's electoral steady ascent - which had previously yielded the capture of the City of Milan in 1993 - if not also a marked reflux into the consent of the federalist party.
The election on 23 April saw the success of the broad coalition of Berlusconi, grouping ex-Christian Democrats, ex-Socialists, Liberals and post-fascist, and led to presidency Communion and Liberation's Roberto Formigoni that, with the majority premium, was able to give life to the first government in the history of the region that managed to last the entire legislature.
 | |||||||||
| Candidates | Votes | % | Seats | Parties | Votes | % | Seat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roberto Formigoni | 2,386,732 | 41.07 | 16 | ||||||
| Forza Italia – The People's Pole | 1,455,706 | 29.24 | 28 | ||||||
| National Alliance | 496,939 | 9.98 | 8 | ||||||
| Christian Democratic Centre | 110,058 | 2.21 | 2 | ||||||
| Pensioners of Sun | 14,518 | 0.29 | – | ||||||
| Total | 2,077,221 | 41.72 | 38 | ||||||
| Diego Masi | 1,591,417 | 27.39 | – | ||||||
| Democratic Party of the Left | 821,280 | 16.50 | 11 | ||||||
| Italian People's Party | 321,314 | 6.45 | 4 | ||||||
| Federation of the Greens | 154,624 | 3.11 | 2 | ||||||
| Pact of Democrats | 146,293 | 2.94 | 2 | ||||||
| Labour Federation | 18,682 | 0.38 | – | ||||||
| Populars and Democrats | 11,146 | 0.22 | – | ||||||
| Total | 1,473,339 | 29.59 | 19 | ||||||
| Francesco Speroni | 1,087,128 | 18.71 | – | Northern League – Lombard League | 879,139 | 17.66 | 12 | ||
| Giuseppe Torri | 459,051 | 7.90 | – | Communist Refoundation Party | 381,221 | 7.66 | 5 | ||
| Marco Pannella | 165,838 | 2.85 | – | ||||||
| Pannella List | 90,445 | 1.82 | – | ||||||
| Autonomist Front | 5.596 | 0.11 | – | ||||||
| Total | 96,041 | 1.93 | – | ||||||
| Carlo Fatuzzo | 120,665 | 2.08 | – | Pensioners' Party | 71,608 | 1.44 | – | ||
| Total candidates | 5,810,831 | 100.00 | 16 | Total parties | 4,978,569 | 100.00 | 74 | ||
| Source: Ministry of the Interior – Historical Archive of Elections | |||||||||
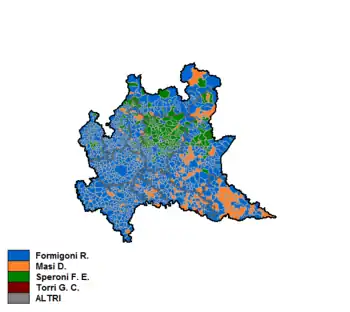
Results by province
| Province | Roberto Formigoni | Diego Masi | Francesco Speroni | Giuseppe Torri | Turnout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milan | 1,055,959 (44.04%) | 686,933 (28.65%) | 308,557 (12.87%) |
219,034 (9.14%) |
81.15% |
| Brescia | 261,475 (37.18%) | 206,475 (29.36%) | 161,185 (22.92%) |
43,162 (6.14%) |
88.07% |
| Bergamo | 217,679 (34.90%) | 141,144 (22.63%) | 188,726 (30.26%) | 35,518 (5.69%) |
87.70% |
| Varese | 207,136 (40.91%) | 110,368 (21.80%) | 136,866 (27.03%) | 33,079 (6.53%) |
82.79% |
| Como | 151,132 (44.32%) | 73,498 (21.55%) |
80,339 (23.56%) |
21,126 (6.19%) |
84.77% |
| Pavia | 146,761 (44.74%) | 86,502 (26.37%) |
47,626 (14.52%) |
31,512 (9.61%) |
85.90% |
| Mantua | 88,822 (35.44%) |
95,032 (37.92%) | 36,581 (14.60%) |
23,035 (9.19%) |
87.04% |
| Cremona | 89,472 (39.35%) |
70,704 (31.09%) |
33,182 (14.59%) |
21,589 (9.49%) |
89.81% |
| Lecco | 72,633 (36.72%) | 58,694 (29.68%) |
46,622 (23.57%) |
12,263 (6.20%) |
87.32% |
| Lodi | 52,052 (41.28%) |
39,594 (31.40%) |
15,858 (12.58%) |
12,021 (9.53%) |
89.04% |
| Sondrio | 43,611 (40.00%) |
22,473 (20.61%) |
31,586 (28.97%) |
6,712 (6.16%) |
82.75% |
Results by capital city
| City | Roberto Formigoni | Diego Masi | Francesco Speroni | Giuseppe Torri | Turnout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milan | 406,163 (48.34%) |
236,249 (28.12%) |
77,362 (9.21%) |
73,409 (8.74%) |
75.87% |
| Brescia | 52,920 (39.95%) |
43,844 (33.10%) |
20,869 (15.76%) |
8,802 (6.65%) |
85.27% |
| Bergamo | 33,591 (41.07%) |
22,373 (27.35%) |
15,659 (19.14%) |
4,701 (5.75%) |
85.83% |
| Como | 27,783 (49.60%) |
13,027 (23.26%) |
8,882 (15.86%) |
3,801 (6.79%) |
80.89% |
| Varese | 22,923 (43.52%) |
12,103 (22.98%) |
12,746 (24.20%) |
2,761 (2.46%) |
78.94% |
| Pavia | 22,637 (44.32%) |
14,708 (28.80%) |
6,701 (13.12%) |
4,170 (8.16%) |
84.99% |
| Cremona | 20,190 (38.31%) |
17,838 (33.85%) |
6,353 (12.06%) |
5,289 (10.04%) |
88.68% |
| Mantua | 12,463 (35.19%) |
14,359 (40.54%) | 4,015 (11.34%) |
3,337 (9.42%) |
83.36% |
| Lecco | 12,200 (40.09%) |
9,668 (31.77%) |
5,555 (18.26%) |
1,826 (6.00%) |
84.27% |
| Lodi | 12,424 (42.80%) |
9,087 (31.31%) |
3,574 (12.31%) |
2,235 (7.70%) |
85.19% |
| Sondrio | 5,938 (42.67%) |
3,287 (23.62%) |
2,944 (21.16%) |
1,103 (7.93%) |
77.88% |
References
- Ten overhang seats added according to new electoral law.


