21st Ohio Infantry Regiment
The 21st Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Mostly an all-volunteer unit, with the exception of a few draftees, the 21st Ohio served for both ninety-day and three-year enlistments and fought exclusively in the Western Theater. It saw action in some of the war's bloodiest battles including Stones River, Chickamauga, the Atlanta Campaign, and Sherman's March to the Sea.
| 21st Ohio Infantry Regiment | |
|---|---|
 Ohio state flag | |
| Active | April 1861– July 1865 |
| Country | United States of America |
| Allegiance | Union |
| Branch | Infantry |
| Type | Regiment |
| Engagements | Battle of Scary Creek Battle of Ivy Mountain Stones River Chickamauga Atlanta Campaign Sherman's March to the Sea Carolinas Campaign Bentonville |
Three-months regiment
On April 27, 1861, volunteers from throughout northwestern Ohio were organized into the 21st Ohio Infantry Regiment at Camp Taylor, near Cleveland, Ohio.[1] The recruits hailed from the counties of Hancock, Defiance, Wood, Ottawa, Sandusky and Putnam.[2] Many were farmers and farmers' sons who had spent years taming the Great Black Swamp, a huge, black, liquid mire that still blanketed a good portion of the region, in order to cultivate the rich soil beneath it. Other early volunteers were merchants, lawyers, school teachers, blacksmiths, politicians and a county sheriff who was a veteran of the Mexican–American War. Of the soldiers in the regiment, Captain, Americus V. Rice, would become a brigadier general by the end of the war.[3] In addition, among the privates, Thomas W. Custer and Edward S. Godfrey, both would later win the Medal of Honor (Custer won two). Both later fought with the Seventh Cavalry at the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Godfrey survived and eventually retired as a brigadier general.
On May 23, the new regiment under the command of Colonel Jesse S. Norton, and marched to Gallipolis, Ohio, where it went into camp along the banks of the Ohio River at Camp Carrington.[4] Two months later, the regiment crossed the river into western Virginia as a part of the force under George B. McClellan and entered into its first engagement at the Battle of Scary Creek, July 17, 1861. During the five-hour battle, the regiment lost nine men killed and seventeen wounded. Colonel Norton was wounded and captured, but later was paroled and exchanged.
When its three-month term of enlistment expired, the 21st Ohio Infantry marched to Columbus, where it was mustered out of service on August 12, 1861.
Three-years regiment
Reorganized at Camp Vance in Findlay, Ohio, the 21st Ohio Infantry reenlisted for three-years service on September 19, 1861.[5] On September 26, the regiment left Camp Vance and headed to Camp Dennison in Cincinnati, where it received arms and equipment. It then proceeded to Kentucky, where it saw action at the Battle of Ivy Mountain in early November.
Tennessee and the Andrews' Raid
Campaigning into Tennessee in early 1862 as part of the Army of the Ohio, the regiment was one of a number of Union regiments instrumental in capturing the capital of Nashville in February. From there, the regiment moved toward Murfreesboro, Tennessee, and then to Confederate-held Huntsville, Alabama, in early April.
Concurrent with the move toward Huntsville in April 1862, nine men of the regiment volunteered to participate in a secret mission known as Andrews' Raid. The men, along with two civilians and thirteen soldiers from two other Ohio regiments, dressed in civilian clothes and slipped behind enemy lines. They hijacked the Confederate locomotive The General. The mission was a failure, and all of the raiders were captured. Eight men, including Private John M. Scott of Co. F, 21st Ohio Infantry, were hanged. Another eight, including privates Wilson W. Brown, William J. Knight, John R. Porter, Mark Wood, and John A. Wilson, escaped from captivity. The remaining raiders, among them Private William Bensinger, Private Robert Buffum, and Sergeant Elihu H. Mason of the regiment, were released in a prisoner exchange the next year. In recognition of their actions, Congress awarded most of the raiders, including all nine from the 21st Ohio Infantry the newly created Medal of Honor. Bensinger, Buffum, and Mason were three of the first six men ever to receive the medal.[6]
Near La Vergne on October 7, the regiment captured a part of the 3rd Alabama Rifle Regiment, along with its colors and fifty-four horses. The regiment participated in the Siege of Nashville from September 12 to November 7.
By December, the regiment was in the vicinity of Murfreesboro, Tennessee, and on December 30 – January 2, 1863, participated in the Battle of Stones River.
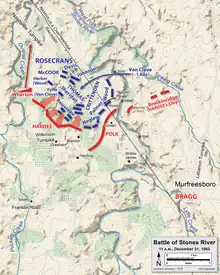
For the battle, the 21st Ohio was with the 74th Ohio, the 37th Indiana, and the 78th Indiana in Colonel John F. Miller's brigade of James S. Negley's division. By 10:00 on December 31, the regiment held the brigade left by a rail fence at the eastern edge of the cedar forest. The left of the regiment was attacked by James R. Chalmers' Mississippi brigade, which retreated in disorder in the face of volleys from the regiment and canister shot from the supporting Battery B, 1st Kentucky Light Artillery. Lieutenant Colonel James Neibling ordered a charge, exhorting the regiment to "Give 'em hell by the acre," hastening the flight of Chalmers' brigade. However, his flank exposed by the collapse of Philip Sheridan's division on the right, Negley soon ordered his division to withdraw, despite Miller's attempt to hold the brigade's positions. With the brigade, the 21st Ohio retreated into the cedar forest.[7]
On January 2, the regiment was ordered to charge across the frigid water of Stones River, where it captured a Confederate artillery battery of four guns. The regiment suffered 159 casualties, and Private Wilson Vance of Company B was awarded the Medal of Honor for saving a fellow soldier from capture.
Tullahoma and Chickamauga campaigns
Following the Battle of Stones River, the 21st remained in camp until June 1863. In the Army of the Cumberland's camp, Rosecrans wrote to the Union General-in-Chief Major General Henry Wager Halleck and Secretary Edwin Stanton that he felt that he needed to outfit all of his cavalry with repeating weapons. In a dispatch from 2 February, he explained his reasons to Secretary Stanton:
I telegraphed the General-in-Chief that 2,000 carbines or revolving rifles were required to arm our cavalry.
He replied as though he thought it a complaint. One rebel cavalryman takes on an average three of our infantry to watch our communications, while our progress is made slow and cautious, and we command the forage of the country only be sending large train guards.
It is of prime necessity, in every point of view, to master their cavalry. I propose to do this, first, by so arming our cavalry as to give it its maximum strength. Second, by having animals and saddles temporarily to mount infantry brigades for marches and enterprises.[8]
This eagerness to embrace new repeating technology manifested itself in many units in the army receiving repeating firearms. While Wilder's famed Lightning Brigade received Spencers and other units got Henry rifles, the 21st Ohio opted for the five-shot Colt Revolving Rifles. While there were not enough for all companies, six of the eight received the Colts.[9]
The regiment first found how well their new weapons would perform when it embarked on the Tullahoma Campaign. Marching and skirmishing through Tennessee and northern Georgia during the campaign, the regiment crossed over Lookout Mountain in late August and arrived in the vicinity of Chickamauga Creek on September 19. Fully engaged in the Battle of Chickamauga, the regiment, under the command of Lt. Colonel Dwella M. Stoughton, deployed into line of battle and opened a brisk fire upon the enemy, which continued until night. The next morning, September 20, the regiment, then occupying a reserve position, witnessed the Confederate breakthrough. Lt. Colonel Stoughton immediately moved to the right and occupied the crest of a ridge, known as Snodgrass Hill, in an attempt to stem the Confederate onslaught.
The Confederates made their first assault on the regiment around 11 a.m. They continued to attack throughout the morning and afternoon, but each attack was repulsed by a murderous fire from the regiment's five-shot Colt Revolving Rifles. So heavy was the volume of fire that the Confederates were convinced that they were attacking an entire division, not just a single regiment. At around 3:30 p.m., Lt. Colonel Stoughton, seated on his horse at the rear of the regiment, was fired upon by a rebel sharpshooter. Ignoring the warning, Stoughton dismounted and walked to the front of the line, where another shot rang out and the colonel, struck through the left arm, fell to the ground severely wounded. Command of the regiment passed to Major Arnold McMahan. Stoughton would die on November 19 from an illness that set in during his convalescence.[10]
By late afternoon, the 21st was desperately low on ammunition. Soldiers plundered the cartridge boxes of the dead and wounded in a frantic attempt to procure Colt's ammunition. When this reserve was depleted, a runner was sent to the rear to search the ordnance trains, but quickly discovered that they had left with the rest of the retreating Union army for Chattanooga. At dusk, having exhausted all of their ammunition, the 21st retired to the rear of the ridge, having expended 43,550 rounds of ammunition.
The 21st was ordered to fix bayonets and occupy the extreme right flank. They managed to procure one last round of ammunition for each man. After each firing their round, the men, remaining in their position, were surrounded and quietly captured. Major Arnold McMahan, 120 soldiers and the colors of the regiment were now in the hands of the enemy.
In six hours of fighting, the 21st Ohio, numbering about 540 men, lost 265 killed, wounded or captured. 46 men would eventually be sent to Andersonville prison. Only ten of the prisoners would survive.
Later campaigns
During the Battle of Chattanooga, the 21st was part of the assaulting column that carried the crest of Missionary Ridge. Colonel McMahan led the troops up the steep slopes into the enemy positions.
When the three-year term of enlistment expired, the majority of the men re-enlisted for the duration of the war. The reconstituted 21st OVI participated in the Atlanta Campaign under William T. Sherman. The regiment marched through Georgia to Savannah, Georgia, arriving on the coast at the end of the year. In early 1865, the 21st participated in the Carolinas Campaign, including the Battle of Bentonville.
Following the surrender of the opposing Confederate army at Bennett Place in April, the 21st marched to Washington, D.C., and participated in the Grand Review of the Armies. The soldiers were discharged from the army and paid on July 28, 1865, when the regiment mustered out in Louisville, Kentucky.
Postbellum
Many veterans of the 21st OVI joined the Grand Army of the Republic, and several posts were established throughout northwestern Ohio. Several towns erected statues and monuments to honor local soldiers. The 21st OVI was also remembered by the U.S. War Department, which erected a commemorative tablet in 1908 on the Chickamauga Battlefield.
Notable members
- William Bensinger – Awarded Medal of Honor for participation in the Anderson Raid, or Great Locomotive Chase.
- Wilson W. Brown – Anderson raider
- Robert Buffum – Anderson raider
- William James Knight – Anderson Raider
- Elihu H. Mason – Anderson Raider
- John Reed Porter – Anderson Raider
- John Morehead Scott – Anderson Raider. Hanged by the Confederates, June 18, 1862, and received award posthumously.
- John Alfred Wilson – Anderson Raider
- Mark Wood – Anderson Raider
Notes
- Ohio Roster Commission (1893), p. 425-442, vol.I.
- Reid (1868), pp. 148.
- Canfield (1893), p. 20.
- Dyer (1908), p. 1506.
- Ohio Roster Commission (1886), p. 3-39, vol.III.
- Pittenger (1887), p. 4.
- Daniel (2012), pp. 123, 128–129.
- Wilder's Brigade Mounted Infantry Living History Society (2007).
- Kepler (1967).
- Center for Archival Collections (2008).
References
- Canfield, Silas S. (1893). History of the 21st Regiment Ohio Volunteer Infantry in the War of the Rebellion. Toledo, OH: Vrooman, Anderson & Bateman Printers. p. 192. hdl:2027/yale.39002002964568. OCLC 749194471.
- Daniel, Larry J. (2012). Battle of Stones River: The Forgotten Conflict between the Confederate Army of Tennessee and the Union Army of the Cumberland. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8071-4516-6.
- Dyer, Frederick Henry (1908). A Compendium of the War of the Rebellion (PDF). Des Moines, IA: Dyer Pub. Co. pp. 31, 43, 206, 425, 426, 429, 431, 432, 440, 443. 444, 445, 1506. ASIN B01BUFJ76Q. LCCN 09005239. OCLC 8697590. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Ohio Roster Commission (1893). 1861 Three-Month Organizations — 1st–22nd Regiments, Etc. Official Roster of the Soldiers of the State of Ohio in the War on the Rebellion, 1861–1865. Vol. I. Akron, OH: The Werner Company. p. 810. hdl:2027/mdp.39015004198746. OCLC 633556.
- Ohio Roster Commission (1886). 21st–36th Regiments-Infantry. Official Roster of the Soldiers of the State of Ohio in the War on the Rebellion, 1861–1865. Vol. III. Cincinnati, OH: The Ohio Valley Pub. & Mfg. Co. p. 794. OCLC 181357575.
- Pittenger, William (1887). Daring and suffering: a history of the Andrews Railroad Raid into Georgia in 1862 ... New York: The War Publishing Co. p. A4. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- Reid, Whitelaw (1868). The History of Her Regiments, and Other Military Organizations. Ohio in the War: Her Statesmen, Her Generals, and Soldiers. Vol. II. Cincinnati, OH: Moore, Wilstach, & Baldwin. pp. 146–152. LCCN 02015300. OCLC 11632330.
- "Infantry Units: 21st Ohio Volunteer Infantry". www.bgsu.edu. Center for Archival Collections. 2019. Archived from the original on 2007-06-10. Retrieved 2008-03-20.
- Kepler, Virginia (1 January 1967). "Battle of Chickamauga: 21st Regiment, Ohio Volunteer Infantry and Their Colt's Revolving Rifles". www.historynet.com. Civil War Times Illustrated. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
The History Net
- "History". Wilder's Brigade Mounted Infantry Living History Society. Wilder's Brigade Mounted Infantry Living History Society. 2 January 2007. Retrieved 31 October 2009.