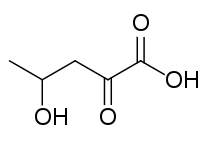
4-Hydroxy-2-oxopentanoic acid
4-Hydroxy-2-oxopentanoaic acid, also known as 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate, is formed by the decarboxylation of 4-oxalocrotonate by 4-oxalocrotonate decarboxylase, is degraded by 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase, forming acetaldehyde and pyruvate and is reversibly dehydrated by 2-oxopent-4-enoate hydratase to 2-oxopent-4-enoate.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Hydroxy-2-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Other names
4-Hydroxy-2-ketopentanoic acid; 4-Hydroxy-2-ketovaleric acid; 4-Hydroxy-2-oxovaleric acid; 4-Hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate; 4-Hydroxy-2-ketopentanoate; 4-Hydroxy-2-ketovalerate; 4-Hydroxy-2-oxovalerate; HKP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 132.115 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Kunz DA, Ribbons DW, Chapman PJ (1981). "Metabolism of allylglycine and cis-crotylglycine by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2 harboring a TOL plasmid". J. Bacteriol. 148 (1): 72–82. doi:10.1128/JB.148.1.72-82.1981. PMC 216168. PMID 7287632.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.