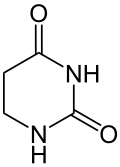
Dihydrouracil
Dihydrouracil is an intermediate in the catabolism of uracil.[1] It is the base present in the nucleoside dihydrouridine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Diazinane-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
Dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.257 |
| MeSH | Dihydrouracil |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.10264 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.