Cytidine diphosphate
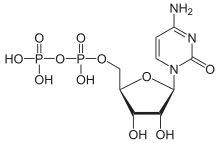
Cytidine diphosphate, abbreviated CDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside cytidine. CDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase cytosine.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cytidine 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.507 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H15N3O11P2 | |
| Molar mass | 403.176422 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
In Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, CDP-activated glycerol and ribitol are necessary to build wall teichoic acid.[1]
See also
References
- Pereira, Mark P.; Brown, Eric D. (2010-01-01), Holst, Otto; Brennan, Patrick J.; Itzstein, Mark von; Moran, Anthony P. (eds.), "Chapter 19 - Biosynthesis of cell wall teichoic acid polymers", Microbial Glycobiology, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 337–350, ISBN 978-0-12-374546-0, retrieved 2021-12-08
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.