Tisopurine
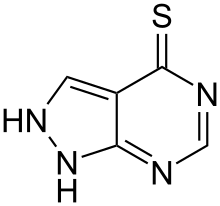
Tisopurine (or thiopurinol) is a drug used in the treatment of gout in some countries.[1] It reduces uric acid production through inhibiting an early stage in its production.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.865 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H4N4S |
| Molar mass | 152.18 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Dean BM, Perrett D, Simmonds HA, Grahame R (April 1974). "Thiopurinol: comparative enzyme inhibition and protein binding studies with allopurinol, oxipurinol and 6-mercaptopurine". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 1 (2): 119–27. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1974.tb00220.x. PMC 1402452. PMID 22454898.
- Jawad AS (June 1987). "Alternatives to allopurinol". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 46 (6): 493. doi:10.1136/ard.46.6.493-a. PMC 1002174. PMID 3632073.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.