Enprofylline
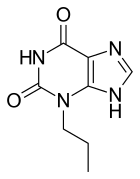
Enprofylline (3-propylxanthine) is a xanthine derivative used in the treatment of asthma, which acts as a bronchodilator. It acts primarily as a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor with relatively little activity as a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist.[1][2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.166 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.194 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Lunell E, Svedmyr N, Andersson KE, Persson CG (1982). "Effects of enprofylline, a xanthine lacking adenosine receptor antagonism, in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 22 (5): 395–402. doi:10.1007/bf00542541. PMID 6288396. S2CID 3240010.
- Laursen LC (December 1987). "Anti asthmatic effects and pharmacokinetics of enprofylline--a new xanthine derivate". Danish Medical Bulletin. 34 (6): 289–97. PMID 3325233.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.