533rd Training Squadron
The 533rd Training Squadron (533 TRS) is a United States Space Force unit. It is assigned to the Space Training and Readiness Command, California, where it trains Space Force personnel on space systems. It was activated in this role in 1994.
| 533rd Training Squadron | |
|---|---|
 Squadron emblem | |
| Active | 1942–1945; 1962–1986; 1994–present |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Squadron |
| Role | Undergraduate space training |
| Part of | Space Delta 1 |
| Headquarters | Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, U.S. |
| Nickname(s) | Centurions[1] |
| Engagements | European Theater of Operations[2] |
| Decorations | Distinguished Unit Citation[2] Air Force Outstanding Unit Award |
| Commanders | |
| Commander | Lt Col Jonathan Arehart |
| Insignia | |
| World War II fuselage code[3] | VP |
The squadron was first activated in 1942 as the 533d Bombardment Squadron. It moved to England in 1943 and served in combat until 1945, earning two Distinguished Unit Citations for its actions in combat. Following V-E Day, the squadron returned to the United States, where it was inactivated.
In 1962, the squadron became the 533d Strategic Missile Squadron. It was equipped with LGM-25C Titan II missiles and stood alert during the Cold War until inactivating in 1986. In 1978, one of its sites was destroyed, when one of its missiles exploded.
Mission
The mission of the unit is to conduct technical training for the nation's space operators going into the United States Space Force. It provides a pipeline into three Space Force Warfighter shredouts- Orbital Warfare, Space Battle Management, and Electronic Warfare.
History
Training in the United States

The squadron was first activated on 3 November 1942 at Gowen Field, Idaho as the 533d Bombardment Squadron, one of the four original squadrons of the 381st Bombardment Group. It gathered its initial cadre at Gowen, but only began training for combat with the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress after moving to Pyote Army Air Field, Texas at the end of the year. On 8 May 1943, the ground echelon began moving to the port of embarkation at Camp Kilmer, New Jersey, and boarded the RMS Queen Elizabeth for the European Theater of Operations on 27 May. The air echelon marshalled at Salinas Army Air Field, Kansas, and began movement by the North Atlantic Ferry Route on 15 May.[2][4][5]
Combat in the European Theater

The air echelon of the squadron arrived at RAF Bovingdon in late May 1943. The following month, the squadron was reunited at RAF Ridgewell, which was to be its combat station for the rest of the war. The squadron entered the strategic bombing campaign against Germany, when it flew its first mission on 21 June, a diversionary attack against Antwerp.[5][6] Its targets in France included an aircraft assembly plant near Villacoublay, and an engine plant at Le Mans , locks at Saint-Nazaire, and Amiens – Glisy Aerodrome. It also attacked an aircraft plant in Brussels, Belgium. During Blitz Week, it bombed nitrate factories in Heroya, Norway, stopping production for over three months.[4][7]
The squadron also flew deeper penetration missions into Germany. It hit oil refineries at Gelsenkirchen, submarine pens at Kiel, aircraft plants at Kassel and Leipzig, industrial targets in Münster, marshalling yards at Offenberg, and the ball bearing plants at Schweinfurt. On 8 October 1943, despite heavy enemy interceptor opposition, it accurately struck shipyards at Bremen, for which it was awarded the Distinguished Unit Citation (DUC).[4] All squadron bombers that returned from this mission[note 2] received battle damage.[8] It received a second DUC for attacks on aircraft plants in Germany on 11 January 1944. In late February 1944, the unit participated in Big Week, the intensive attacks on the German aircraft industry.[4]
The squadron was occasionally taken off strategic operations to perform air support and interdiction missions. It bombed bridges and airfields near the beachhead to support Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy, in June 1944. The following month, it attacked positions of enemy forces opposing Operation Cobra, the breakout at Saint Lo. It supported Operation Market Garden, the airborne attacks in the Netherlands near Arnhem, in the fall. From December 1944, through January 1945, it attacked lines of communications and airfields near the battle zone during the Battle of the Bulge. It also supported the Allied crossing of the Rhine and push through central Germany in March 1945.[4]
Return to the United States and inactivation
The squadron flew its last mission on 26 April 1945 and the majority of the unit's aircraft departed the theater on 24 May 1945. Ground personnel sailed on the RMS Queen Elizabeth on 24 June, arriving in the US by the end of the month. The squadron was located at Sioux Falls Army Air Field, South Dakota a few days later and was inactivated on 24 August 1945.[2][5][4]
Strategic Air Command missile operations
.jpg.webp)

The unit was redesigned the 533d Strategic Missile Squadron and organized at McConnell Air Force Base, Kansas on 1 August 1962 as a part of the 381st Strategic Missile Wing. The squadron began training in preparation for LGM-25C Titan II, and the 381st Wing put its first Titans on alert in July 1963.[9] It operated nine Titan II underground silos constructed beginning in 1960; the first site going operationally ready in October 1963 The nine missiles remained on alert for over 20 years during the Cold War. On 24 August 1978, an accident at Site 533-7 involving an oxidizer leak killed two Air Force personnel, and caused the temporary evacuation of local communities. The damage to the site was determined to be unrepairable and the silo was permanently closed.
The squadron operated the following missile sites:
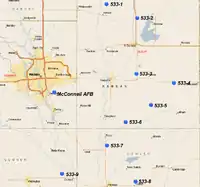
- 533-1 (27 Nov 1963-22 Aug 1985), 3.1 mi NNE of Potwin, KS 37°58′54″N 097°00′04″W
- 533-2 (16 Nov 1963-5 Jun 1985), 7.5 mi N of El Dorado, KS 37°55′28″N 096°50′37″W
- 533-3 (7 Nov 1963-3 Oct 1985), 3.7 mi W of Leon, KS 37°41′55″N 096°50′54″W
- 533-4 (4 Nov 1963-29 Jul 1985), 6.8 mi W of Beaumont, KS 37°39′41″N 096°39′25″W
- 533-5 (30 Oct 1963-14 Mar 1985), 7.7 mi WNW of Latham, KS 37°34′17″N 096°46′27″W
- 533-6 (14 Oct 1963-29 Apr 1985), 6.1 mi ESE of Douglass, KS 37°30′09″N 096°54′12″W
- 533-7 (20 Jul 1963-24 Aug 1978), 2.3 mi S of Rock, KS 37°24′28″N 096°59′57″W[note 3]
- 533-8 (5 Jul 1963-2 Jul 1984), 7.9 mi E of Winfield, KS 37°15′42″N 096°51′14″W
- 533-9 (21 Oct 1963-27 May 1986), 3.5 mi WNW of Oxford, KS 37°17′35″N 097°13′38″W
In October 1981, President Ronald Reagan announced that as part of the strategic modernization program, Titan II systems were to be retired by 1 October 1987. Inactivation of the sites began in September 1984, In November 1985, the squadron was inactivated and its remaining active missiles were transferred to the 532d Strategic Missile Squadron.[10]
After removal from service, the silos had reusable equipment removed by Air Force personnel, and contractors retrieved salvageable metals before destroying the silos with explosives and filling them in. Access to the vacated control centers was blocked off. Missile sites were later sold off to private ownership after demilitarization. Today the remains of the sites are still visible in aerial imagery, in various states of use or abandonment.
Space training
.png.webp)

Redesignated and activated on 30 September 1994 as the 533d Training Squadron, Air Education and Training Command the 533d provided initial qualification training for attack warning, space surveillance, and counterspace missions. Until 2003, The 534th Training Squadron trained crews in satellite command and control. That year, the 534th inactivated and the 533d assumed its training responsibilities.[10]
The 533d trains approximately 400 space professionals a years in both an officer and enlisted course. Beginning in October 2019 the 533d started its newest iteration of Space Training called UST Next. The UST Next course teaches topics in space law, history, orbital mechanics, rocketry, space systems, physics, RF technology, doctrine, and space capabilities.
On 1 September 2020 the 533d transitioned from the United States Air Force into the United States Space Force under Space Training and Readiness Delta (Provisional).
Structure
- Detachment 1, Goodfellow Air Force Base, Texas[11]
Lineage
- Constituted as the 533d Bombardment Squadron (Heavy) on 28 October 1942
- Activated on 3 November 1942
- Redesignated 533d Bombardment Squadron, Heavy on 20 August 1943
- Inactivated on 28 August 1945
- Redesignated 533rd Strategic Missile Squadron (ICBM-Titan) and activated on 26 February 1962 (not organized)
- Organized on 1 August 1962[12]
- Inactivated on 1 November 1985
- Redesignated as 533d Training Squadron on 4 August 1994
- Activated on 1 October 1994
- Inactivated as United States Air Force unit on 1 September 2020
- Activated as a United States Space Force unit on 1 September 2020
Assignments
- 381st Bombardment Group, 3 November 1942 – 28 August 1945
- Strategic Air Command, 26 February 1962
- 381st Strategic Missile Wing, 1 August 1962 – 1 November 1985[12]
- 381st Training Group, 1 October 1994 – 1 September 2020
- Space Training and Readiness Delta (Provisional), 1 September 2020 - 23 August 2021
- Space Training and Readiness Command, 23 August 2021 – present
Stations
- Gowen Field, Idaho, 3 Nov 1942
- Ephrata Army Air Base, Washington, 1 December 1942
- Pyote Army Air Field, Texas, 27 December 1942
- Pueblo Army Air Base, Colorado, 6 April–10 May 1943
- RAF Ridgewell (AAF-167),[13] England, 2 June 1943 – 24 June 1945
- Sioux Falls Army Air Field, South Dakota, 3 July–28 August 1945
- McConnell Air Force Base, Kansas, 1 August 1962[12] – 1 November 1985
- Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, 1 October 1994 – present
Aircraft and missiles
- Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, 1942–1945
- LGM-25C Titan II, 1962–1986[12]
Awards and campaigns
| Award streamer | Award | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distinguished Unit Citation | 8 October 1943 | Bremen, 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Distinguished Unit Citation | 11 January 1944 | Germany, 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 January 1966-30 June 1967 | 533d Strategic Missile Squadron[14] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 1971-30 June 1972 | 532d Strategic Missile Squadron[15] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 1974-30 June 1975 | 532d Strategic Missile Squadron[15] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 1981-30 June 1983 | 533d Strategic Missile Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 1984-1 November 1985 | 533d Strategic Missile Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 1997-30 June 1999 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2000-30 June 2001 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2005-30 June 2006 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2008-30 June 2010 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2010-30 June 2011 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2011-30 June 2013 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2013-30 June 2015 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2015-30 June 2017 | 533d Training Squadron[16] | |
| Air Force Outstanding Unit Award | 1 July 2017-30 June 2019 | 533d Training Squadron[16] |
| Campaign Streamer | Campaign | Dates | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Offensive, Europe | 2 June 1943 – 5 June 1944 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Air Combat, EAME Theater | 2 June 1943 – 11 May 1945 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Normandy | 6 June 1944 – 24 July 1944 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Northern France | 25 July 1944 – 14 September 1944 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Rhineland | 15 September 1944 – 21 March 1945 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Ardennes-Alsace | 16 December 1944 – 25 January 1945 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] | |
| Central Europe | 22 March 1944 – 21 May 1945 | 533d Bombardment Squadron[2] |
List of commanders
See also
References
- Notes
- In front is Boeing B-17G-20-BO Flying Fortress, serial 42-31443, "Friday the 13th". This aircraft was shot down by German fighters on mission to Oschersleben on 22 February 1944 and crashed near Bielefeld. Four of the crew became prisoners of war, six were killed. Missing Aircrew Report 2930.
- Eight of the 17 bombers dispatched by the 381st Group were shot down on this mission. Freeman, p. 75.
- Site closed 24 Aug 1978 after an accident involving an oxidizer leak killed two Air Force personnel, caused the temporary evacuation of local communities, and damaged the site.
- Citations
- https://www.facebook.com/533TRS/posts/1277884989253471
- Maurer, Combat Squadrons, p. 640
- Freeman, p. 288
- Maurer, Combat Units, pp. 268-269
- Freeman, p. 253
- Freeman, p. 52
- Freeman, pp. 53, 63
- Freeman, p. 75
- Ravenstein, pp. 206-207
- "Vandenberg AFB Fact Sheets: 381st Training Group". 30th Space Wing Public Affairs. 6 December 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- "Space Force Det 1 activates on Goodfellow AFB".
- Lineage, including assignments stations, and aircraft/missiles, through 1963 in Maurer, Combat Squadrons, p. 640
- Station number in Anderson
- Air Force Pamphlet 900-2, 15 June 1971, p. 419
- Air Force Pamphlet 900-2, Vol. II, 30 Sep 1976, p. 79
- "Air Force Personnel Services: Unit Awards". Air Force Personnel Center. Retrieved 23 February 2020. (search)
- "Biography - Colonel Jason N. Schramm" (PDF). starcom.spaceforce.mil. United States Space Force. Retrieved 26 May 2022.
- "533d Training Squadron Student Welcome Packet" (PDF). 30 May 2019.
- https://www.facebook.com/533TRS/posts/1165593883815916
- Cashin, Kaitlin (22 December 2020). "533rd TRS transitions to STAR Delta Provisional". spoc.spaceforce.mil. Vandenberg Air Force Base, California.
- https://www.facebook.com/533TRS/videos/1052903445612618
Bibliography
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
- Anderson, Capt. Barry (1985). Army Air Forces Stations: A Guide to the Stations Where U.S. Army Air Forces Personnel Served in the United Kingdom During World War II (PDF). Maxwell AFB, AL yes: Research Division, USAF Historical Research Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 January 2016. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- Freeman, Roger A. (1970). The Mighty Eighth: Units, Men and Machines (A History of the US 8th Army Air Force). London, England, UK: Macdonald and Company. ISBN 978-0-87938-638-2.
- Knaack, Marcelle Size (1978). Encyclopedia of US Air Force Aircraft and Missile Systems (PDF). Vol. 2, Post-World War II Bombers 1945-1973. Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-59-5. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- Maurer, Maurer, ed. (1983) [1961]. Air Force Combat Units of World War II (PDF) (reprint ed.). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-02-1. LCCN 61060979.
- Maurer, Maurer, ed. (1982) [1969]. Combat Squadrons of the Air Force, World War II (PDF) (reprint ed.). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-405-12194-6. LCCN 70605402. OCLC 72556.
- Ravenstein, Charles A. (1984). Air Force Combat Wings, Lineage & Honors Histories 1947-1977 (PDF). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-12-9. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "AF Pamphlet 900-2, Unit Decorations, Awards and Campaign Participation Credits" (PDF). Washington, DC: Department of the Air Force. 15 June 1971. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 August 2015. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
- "AF Pamphlet 900-2, Unit Decorations, Awards and Campaign Participation Credits, Vol II" (PDF). Washington, DC: Department of the Air Force. 30 September 1976. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 August 2015. Retrieved 11 August 2016.
External links
- Combat Crew: The Story of 25 Combat Missions Over Europe From the Daily Journal of a B-17 Gunner by John Comer 533d Squadron (8th Air Force, 1st Division, 381st Group)


