Aegidae
The Aegidae are a family of isopod crustaceans. The adults are temporary parasites of fish, feeding on their hosts' blood before dropping off to digest the meal.[1] They differ from members of the family Cirolanidae in having only three pairs of hook-like pereiopods, whereas in Cirolanidae all seven pairs of pereiopods are hooked.[2] The family was first described by Adam White in 1850.[3]
| Aegidae | |
|---|---|
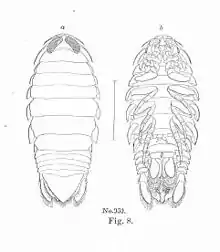 | |
| Aega psora | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Superorder: | Peracarida |
| Order: | Isopoda |
| Suborder: | Cymothoida |
| Superfamily: | Cymothooidea |
| Family: | Aegidae White, 1850 |
The family contains the following genera:[4]
References
- Richard C. Brusca, Vánia R. Coelho & Stefano Taiti (2007). "Isopoda". In Sol Felty Light; James T. Carlton (eds.). The Light and Smith Manual: Intertidal Invertebrates from Central California to Oregon (4th ed.). University of California Press. pp. 503–542. ISBN 9780520239395.
- Roger Tory Peterson; Kenneth L. Gosner (1999). A Field Guide to the Atlantic Seashore: from the Bay of Fundy to Cape Hatteras. Peterson Field Guide. Vol. 24. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 225. ISBN 9780618002092.
- White, A. (1850), List of the specimens of British animals in the collection of the British Museum (published 1845), doi:10.5962/BHL.TITLE.1582, Wikidata Q115584173
- Schotte M, Boyko CB, Bruce NL, Poore GC, Taiti S, Wilson GD, eds. (2011). "Aegidae". World Marine, Freshwater and Terrestrial Isopod Crustaceans database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved January 12, 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.