Akashi, Hyōgo
Akashi (明石市, Akashi-shi) is a city in southern Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 May 2022, the city had an estimated population of 304,274 in 135,323 households and a population density of 6,200 people per km².[1] The total area of the city is 49.42 square kilometres (19.08 sq mi).
Akashi
明石市 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
 Flag  Emblem | |||||||
Location of Akashi in Hyōgo Prefecture | |||||||
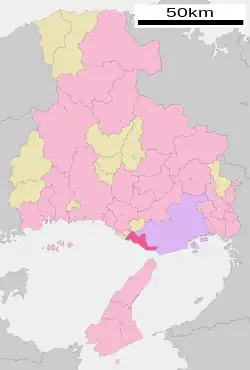 | |||||||
 Akashi Location in Japan | |||||||
| Coordinates: 34°39′N 135°0′E | |||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||
| Region | Kansai | ||||||
| Prefecture | Hyōgo | ||||||
| Government | |||||||
| • Mayor | Fusaho Izumi (from May 2011) | ||||||
| Area | |||||||
| • Total | 49.42 km2 (19.08 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population (May 1, 2022) | |||||||
| • Total | 304,274 | ||||||
| • Density | 6,200/km2 (16,000/sq mi) | ||||||
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) | ||||||
| City hall address | 1-5-1 Nakasaki, Akashi-shi, Hyōgo-ken 673-8686 | ||||||
| Climate | Cfa | ||||||
| Website | Official website | ||||||
| Symbols | |||||||
| Flower | Chrysanthemums | ||||||
| Tree | Sweet Osmanthus | ||||||
| Akashi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 明石市 | ||||
| Hiragana | あかしし | ||||
| |||||


Geography
Akashi is located in southern Hyōgo prefecture, and is a long and narrow municipality along the Seto Inland Sea. It is separated from Awaji Island by Harima Bay; however, the terminus of the Akashi Kaikyō Bridge, which connects Honshu to Awaji Island and to Shikoku, is not in Akashi but in Tarumi-ku, Kōbe. The 135th meridian east line that determines Japan Standard Time passes through the city.
Climate
Akashi has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot summers and cool to cold winters. Precipitation is significantly higher in summer than in winter, though on the whole lower than in most parts of Honshū, and there is no significant snowfall. The average annual temperature in Akashi is 15.9 °C (60.6 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,156.6 mm (45.54 in) with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.7 °C (81.9 °F), and lowest in January, at around 5.2 °C (41.4 °F).[2] The highest temperature ever recorded in Akashi was 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) on 13 August 2019; the coldest temperature ever recorded was −4.3 °C (24.3 °F) on 30 January 2003.[3]
| Climate data for Akashi (1992−2020 normals, extremes 1992−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.5 (61.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
29.4 (84.9) |
33.4 (92.1) |
36.3 (97.3) |
37.2 (99.0) |
34.9 (94.8) |
30.7 (87.3) |
25.2 (77.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
37.2 (99.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.1 (48.4) |
9.5 (49.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
17.4 (63.3) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.5 (88.7) |
28.3 (82.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.2 (41.4) |
5.6 (42.1) |
8.5 (47.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
12.9 (55.2) |
7.7 (45.9) |
15.8 (60.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
1.7 (35.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
9.3 (48.7) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
23.4 (74.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
20.8 (69.4) |
14.6 (58.3) |
8.7 (47.7) |
3.7 (38.7) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.3 (24.3) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
0.4 (32.7) |
6.5 (43.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
17.7 (63.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
11.3 (52.3) |
5.8 (42.4) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 35.1 (1.38) |
50.7 (2.00) |
83.6 (3.29) |
89.5 (3.52) |
115.4 (4.54) |
150.5 (5.93) |
152.3 (6.00) |
86.2 (3.39) |
162.6 (6.40) |
118.1 (4.65) |
59.2 (2.33) |
48.7 (1.92) |
1,156.6 (45.54) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5.0 | 6.5 | 8.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 10.7 | 9.7 | 5.9 | 9.2 | 7.6 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 93.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 168.0 | 153.9 | 186.3 | 196.9 | 205.1 | 154.2 | 186.0 | 239.7 | 169.3 | 176.5 | 161.8 | 165.4 | 2,160.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[3][2] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 58,087 | — |
| 1925 | 63,665 | +9.6% |
| 1930 | 66,872 | +5.0% |
| 1935 | 72,397 | +8.3% |
| 1940 | 84,835 | +17.2% |
| 1945 | 101,583 | +19.7% |
| 1950 | 112,011 | +10.3% |
| 1955 | 120,200 | +7.3% |
| 1960 | 129,780 | +8.0% |
| 1965 | 159,299 | +22.7% |
| 1970 | 206,532 | +29.7% |
| 1975 | 234,905 | +13.7% |
| 1980 | 254,869 | +8.5% |
| 1985 | 263,363 | +3.3% |
| 1990 | 270,722 | +2.8% |
| 1995 | 287,606 | +6.2% |
| 2000 | 293,117 | +1.9% |
| 2005 | 291,027 | −0.7% |
| 2010 | 290,993 | −0.0% |
| 2015 | 293,409 | +0.8% |
| 2020 | 303,601 | +3.5% |
| Akashi population statistics[4] | ||
History
Akashi is mentioned in a waka (five-line, 31-syllable poem) written by Kakinomoto no Hitomaro in the 7th century and it is the setting for one of the chapters of the 11th-century novel The Tale of Genji. It developed as the castle town of Akashi Domain during the Edo Period, from 1617 to 1871 due to its location dominating the San'yōdō highway connecting the Kinai region with western Japan. The famous swordsman Miyamoto Musashi is claimed to have laid out the design of the castle town. The town of Akashi was established on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system. It was raised to city status on November 1, 1919. The city annexed the neighboring villages of Hayashizaki on February 11, 1942 and Okubo, Uozumi and Futami on January 10, 1951 to reach its present dimensions. A proposal to merge with the city of Kobe was rejected by a referendum in 1955. The city suffered from the Great Hanshin earthquake of 1995 with 4,839 houses were completely or partially destroyed and nine fatalities.
On July 21, 2001, 11 people were killed and 247 were injured during a stampede after a fireworks show. Five city officials were subsequently convicted of negligence in connection with the incident.[5]
Akashi became a Core city on April 1, 2018 with increased local autonomy.
Government
Akashi has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 30 members. Akashi contributes four members to the Hyogo Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Hyōgo 9th district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan. Akashi is governed by Mayor Fusaho Izumi, an independent.
Economy
Akashi is located within the Hanshin Industrial Area and Harima Seaside Industrial Area and has succeeded in attracting many companies to its Futami Seaside Industrial Park. the city has long been noted for aviation-related instrumentation manufacturers and electronic component manufacturers. Yamato Scale, a leading global manufacturer of commercial weighing and packaging equipment, is headquartered in the city.[6] Due to its transportation connections and location, numerous bedroom communities have developed for commuters to Kobe and Osaka, which is estimated to exceed 30% of the working population. The city has also been noted since the Edo Period for its production of sake.
Education
Akashi has 28 public elementary schools, 13 public middle schools and one public high school operated by the city government and seven public high schools operated by the Hyōgo Prefectural Department of Education. There is also one national elementary school. The city also operates one special education school for the handicapped. The nursing school of University of Hyogo is located in Akashi.
The city also has the National Institute of Technology Akashi College (NITAC( (国立明石工業高等専門学校).[7]
The city once had a North Korean school, Akashi Korean Elementary School (明石朝鮮初級学校)[8] and Akashi Junior College (明石短期大学).
Transportation
Highways
 Daini-Shinmei Road
Daini-Shinmei Road National Route 2 (Kobe, Okayama, Hiroshima, Shimonoseki)
National Route 2 (Kobe, Okayama, Hiroshima, Shimonoseki) National Route 28 (Kobe, Tokushima)
National Route 28 (Kobe, Tokushima) National Route 175 (Maizuru)
National Route 175 (Maizuru) National Route 250 (Kobe, Okayama)
National Route 250 (Kobe, Okayama) National Route 427 (Maizuru)
National Route 427 (Maizuru) National Route 250 (Nishiwaki, Asago)
National Route 250 (Nishiwaki, Asago)
Ferries
- Akashi Awaji Ferry and Awaji Jenova Line to Awaji Island
International relations
Local attractions
- Akashi Castle, National Historic Site
- Akashi Municipal Planetarium, which stands on the meridian of 135 degrees east longitude, which is used to determine Japan Standard Time.
- Akashi Park Stadium is a track and field stadium that can hold 20,000 spectators.
- Kakinomoto Shrine
- Uonotana (Uo-no-Tana, 魚の棚, literally "fish-shelf"), a market where local fishermen display an array of fresh seafood caught in the Akashi Strait.
 Port of Akashi
Port of Akashi
 Old town area
Old town area Uontana
Uontana Akashi Municipal Planetarium
Akashi Municipal Planetarium
Culture
Akashi is known for Akashiyaki, a kind of takoyaki particular to the region. Small pieces of octopus (tako) are placed inside a ball-shaped mold containing a mixture of flour and eggs, and this is then fried. Akashiyaki is often eaten by dipping in a thin soup. People who live in Akashi call it "tamagoyaki"(tamago, 玉子 or 卵, literally "egg").
Noted people from Akashi
- Yumi Kokamo, long-distance runner
- Mami Kingetsu, voice actress
- Airi Taira, actress
References
- "Akashi city official statistics". city.akashi.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- "Hyōgo (Japan): Prefecture, Cities, Towns and Villages - Population Statistics, Charts and Map". www.citypopulation.de.
- Kyodo News, "Ex-Cop Pleads Not Guilty in Fatal '01 Akashi Crush Archived 21 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine", Japan Times, 20 January 2012, p. 1.
- "Yamato Scale corporate profile". Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- "Akashi City website". Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ウリハッキョ一覧. Chongryon. 6 November 2005. Archived from the original on 6 November 2005. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- "Vallejo Sister City". Vallejo Sister City Association. Archived from the original on 11 September 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2013.
- 明石市. "姉妹都市提携50周年記念事業". 明石市 (in Japanese). Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- 明石市. "友好都市・無錫市の紹介". 明石市 (in Japanese). Retrieved 11 August 2021.
External links
- Akashi City official website
 Geographic data related to Akashi, Hyōgo at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Akashi, Hyōgo at OpenStreetMap



