Andriake
Andriake or Andriaca (Ancient Greek: Ἀνδριάκη) was an ancient city and the port of the ancient town of Myra in Lycia. It is located in what is now the Demre district of Antalya.
Ἀνδριάκη | |
 Andriake Harbour area | |
 Shown within Turkey | |
| Location | Demre, Antalya Province, Turkey |
|---|---|
| Region | Lycia |
| Coordinates | 36°13′35″N 29°57′23″E |
| Type | Ancient Settlement and port |
The site[1] has a museum.
History
Andriake is mentioned by Ptolemy; and Pliny has Andriaca civitas, Myra (v. 27).
Appian (B.C. iv. 82) says that in 42 BC Lentulus was sent by Brutus to collect money and broke through the chain which defended the entrance to the port, and went up the river to Myra.
Beaufort (Karamania, p. 26) gives the name Andráki to the river of Myra.
Andriake is clearly the port on the small river on which Myra stood, 20 stadia higher up. (Strab. p. 666.) It must have been at Andriake, as Cramer observes, that St. Paul and his companion prisoners were put on board the Alexandrian ship sailing for Italy. (Acts, xxvii. 5, 6.)
The Site
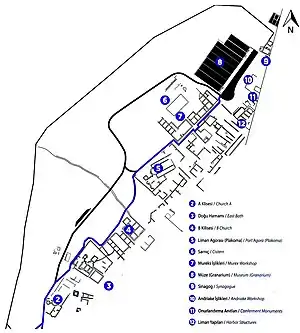
A notice on site (see picture Andriake Plan with text below) has: "Although it was an important harbour of the Lycian region in (the) Ancient Period, in part (because) of the alluvial silt transported by Kokarçay (Andriakos), the port ceased functioning and the ruins of the city Andriake, today engulfed by a swamp, are spread over the two shores of a small bay. Far from being an independent city in (the) Ancient Period, the city Andriake was a suburb and (the) port of Myra by (sic) its location. The inscription located in the city that covers trading laws of the Lycian state from (the) Emperor Nero period (54-68) exposes the importance of Andriake as a port during this period. Andriake lived its most prestigious period during Emperor Hadrian (117-138). The granarium/grain silo structure (Lycian Civilizations Museum) and the trade agora/plakoma structure on its eastern side were built in this period. Discovery of inscriptions written in the honour of Constantinus II, Julianus and Valens indicated that Andriake succeeded in maintaining its importance also in later periods (4th century AD)."
On the north side of the entrance are the remains of large Roman horrea with an inscription which states that they were Hadrian's: the date is Hadrian's third consulate, 119 AD.
Gallery
 Andriake Church
Andriake Church Andriake Church
Andriake Church Andriake Eastern Bath
Andriake Eastern Bath Andriake Harbour agora
Andriake Harbour agora Andriake Harbour agora cistern
Andriake Harbour agora cistern Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship
Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship
Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship
Andriake Harbour area Reconstructed ship Andriake Harbour area Conferment monument
Andriake Harbour area Conferment monument Andriake Plan with text
Andriake Plan with text Andriake Museum Votive stele 12 gods
Andriake Museum Votive stele 12 gods Andriake Museum General view
Andriake Museum General view Andriake Museum General view
Andriake Museum General view Andriake Museum Votive stele Kakasbos
Andriake Museum Votive stele Kakasbos
References
External links
 Media related to Andriake at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Andriake at Wikimedia Commons
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Andriaca". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Andriaca". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.