Archisargoidea
Archisargoidea is an extinct superfamily of brachyceran flies known from the late Middle Jurassic (Callovian) to early Late Cretaceous (Turonian). Most flies in the superfamily have large eyes and an elongated abdomen, preserved females have a sharp, piercing oviscapt used for injecting eggs into host matter. Their relationships with other members of Brachycera is controversial, they are usually considered close relatives of either Stratiomyomorpha or Muscomorpha.[1][2] Internal relationships between the families are uncertain and the topology of the only cladistic analysis of the family was weakly supported, finding that Archisargidae was paraphyletic with respect to Eremochaetidae and miniaturized Tethepomyiidae.[3] The sharp piercing oviscaps possessed by the group had alternatively been suggested to represent evidence of being parasitoids, injecting their eggs into hosts similar to parasitic wasps, or to inject eggs into plant material like rotting wood or fruit, similar to members of Tephritoidea.[4]
| Archisargoidea Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
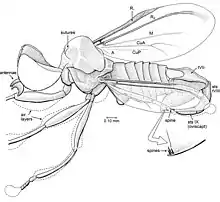 | |
| Zhenia xiai (Eremochaetidae, top) and Tethepomyia zigrasi (Tethepomyiidae, bottom} | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Suborder: | Brachycera |
| Superfamily: | †Archisargoidea Rohdendorf 1962 |
| Families | |
| |
References
- Grimaldi, David A. (2016-09-28). "Diverse Orthorrhaphan Flies (Insecta: Diptera: Brachycera) in Amber From the Cretaceous of Myanmar: Brachycera in Cretaceous Amber, Part VII". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 408: 1–131. doi:10.1206/0003-0090-408.1.1. ISSN 0003-0090. S2CID 89043544.
- Zhang, Qingqing; Zhang, Junfeng (2019-06-14). "Contribution to the knowledge of male and female eremochaetid flies in the late Cretaceous amber of Burma (Diptera, Brachycera, Eremochaetidae)". Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift. 66 (1): 75–83. doi:10.3897/dez.66.33914. ISSN 1860-1324.
- Grimaldi, David A.; Barden, Phillip (2016-09-29). "The Mesozoic Family Eremochaetidae (Diptera: Brachycera) in Burmese Amber and Relationships of Archisargoidea: Brachycera in Cretaceous Amber, Part VIII". American Museum Novitates. 3865 (3865): 1–29. doi:10.1206/3865.1. ISSN 0003-0082. S2CID 89602433.
- Zhang, Qingqing; Zhang, Junfeng (2019-06-14). "Contribution to the knowledge of male and female eremochaetid flies in the late Cretaceous amber of Burma (Diptera, Brachycera, Eremochaetidae)". Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift. 66 (1): 75–83. doi:10.3897/dez.66.33914. ISSN 1860-1324.