Asaka, Saitama
Asaka (朝霞市, Asaka-shi) is a city located in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 January 2021, the city had an estimated population of 143,195 and a population density of 7800 persons per km2.[1] The total area of the city is 18.34 square kilometres (7.08 sq mi).
Asaka
朝霞市 | |
|---|---|
 Asaka City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
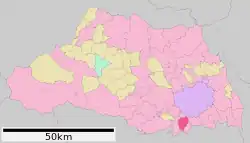 Location of Asaka in Saitama Prefecture | |
 Asaka | |
| Coordinates: 35°47′49.9″N 139°35′38″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Saitama |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18.34 km2 (7.08 sq mi) |
| Population (January 1, 2021) | |
| • Total | 143,195 |
| • Density | 7,800/km2 (20,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| - Tree | Zelkova serrata |
| - Flower | Azalea |
| Phone number | 048-463-1111 |
| Address | 1-1-1 Honcho, Asaka-shi, Saitama-ken 351-8501 |
| Website | Official website |


Geography
Located in far southern Saitama Prefecture, Asaka in the center of the Musashino Terrace on the central reaches of the Arakawa River, which runs along the city border with Saitama in the northeastern part of the city,
Surrounding municipalities
Climate
Asaka has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Ageo is 15.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1427 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.8 °C, and lowest in January, at around 4.4 °C.[2]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Asaka has grown roughly tenfold since the 1950s.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 14,685 | — |
| 1960 | 24,182 | +64.7% |
| 1970 | 67,938 | +180.9% |
| 1980 | 90,088 | +32.6% |
| 1990 | 103,617 | +15.0% |
| 2000 | 119,712 | +15.5% |
| 2010 | 129,691 | +8.3% |
| 2020 | 141,083 | +8.8% |
History
The area of modern Asaka developed as a series of four post stations on the Kawagoe Kaidō highway from the Muromachi period onwards. During the Edo Period, the area was noted as a center for copper crafts. Following the Meiji restoration, the village of Hizaori was created within Niikura District, Saitama with the establishment of the modern municipalities system on April 1, 1889. Niikura District was abolished in 1894 and became part of Kitaadachi District. It was raised to town status on May 1, 1921, and renamed Asaka after Prince Yasuhiko Asaka who was an honorary chairman of the Tokyo Golf Club, which relocated to the area at that time. On April 1, 1955, Asaka annexed the neighboring village of Uchimagi. At the 1964 Summer Olympics in neighboring Tokyo, the town hosted the riding part of the modern pentathlon event at Asaka Nezu Park. Asaka was elevated to city status on March 15, 1967. In 2005, a proposal to merge Asaka with Shiki, Wako, and Niiza to form a new city with a combined population sufficient to qualify for core city status was defeated in a referendum, largely due to opposition from Wako.
Government
Asaka has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 24 members. Asaka contributes two members to the Saitama Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Saitama 4th district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
Due to its location, Asaka is primarily a bedroom community with over 37% of its population commuting to the Tokyo metropolis for work. The area is also a distribution hub for northern Tokyo.
Education
Asaka has ten public elementary schools and five public middle schools operated by the city government, and two public high schools operated by the Saitama Prefectural Board of Education. Toyo University also has a campus in Asaka.
Transportation
Highway
Military facilities
- JGSDF Camp Asaka
Noted people from Asaka
- Daieishō Hayato, sumo wrestler
- Akira Nakamura, professional baseball player
- Shohei Takashima, professional baseball player
- Yuhi, professional wrestler
References
- "Asaka city official statistics" (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan.
- Asaka climate data
- Asaka population statistics
External links
- Official Website (in Japanese)
