Bangalore–Chennai Expressway
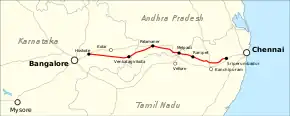
The Bangalore–Chennai Expressway, or National Expressway 7 (NE-7), is an under construction 258 km (160 mi) long, 4-lane wide[2] access-controlled expressway between the cities of Bangalore, the capital of Karnataka and Chennai, the capital of Tamil Nadu. It will run from Hoskote in Bangalore Metropolitan Region Development Authority to Sriperumbudur in Chennai Metropolitan Area. It is planned to allow vehicles to reach 120 km/h (75 mph).[3] This expressway was designated as a National Expressway on 1 January 2021.[4] The total project value is ₹ 17,930 crore.[5] It will be completed by March 2024.[6]
| Bengaluru – Chennai Expressway (National Expressway 7) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Route information | |
| Maintained by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) | |
| Length | 258 km (160 mi) |
| Existed | March 2024[1]–present |
| Major junctions | |
| West end | Hosakote, Bengaluru Rural district, Karnataka(Benagaluru Metropolitan Region) |
| East end | Sriperumbudur, Kanchipuram district, Tamil Nadu (Chennai Metropolitan Area) |
| Location | |
| Country | India |
| States | |
| Districts | |
| Towns |
|
| Highway system | |
Mepladi in Vellore district and Ponapanthangal in ranipet district will be major intersection points for transfers and real estate [7]
Prospects
The National Highways Development Project (NHDP) Phase-VI has been established, following expectations of the new government's involvement, and before the real estate prices begin to rise along the expressways, mainly near Ranipet -Ponnapanthangal-Arakkonam[8] (Tamil Nadu).[9]
Construction
The NHAI has divided the construction work of 258 km long Bangalore–Chennai Expressway into 3 Phases with a total of 10 construction packages. It which will be executed simultaneously by 6 construction companies.
Phase-1
| Sr. No | Package | Length in km | Contractor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hoskote–Malur | 18 | Dilip Buildcon[10] |
| 2. | Malur–Bangarapet | 27.1 | Dilip Buildcon[10] |
| 3. | Bangarapet–Bethamangala | 17.5 | KCC Buildcon |
Phase-2
| Sr. No | Package | Length in km | Contractor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bethamangala–Baireddipalle | 25.0 | Montecarlo Construction |
| 2. | Baireddipalle–Bangarupalem | 31.0 | Apco Infratech[11] |
| 3. | Bangarupalem–Gudipala | 29.0 | Dilip Buildcon |
Phase-3
| Sr. No | Package | Length in km | Contractor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Gudipala–Walajapettai | 24.0 | Montecarlo Construction |
| 2. | Walajapettai–Arakkonam | 24.5 | KCC Buildcon |
| 3. | Arakkonam–Kanchipuram | 25.5 | DP Jain & Co. |
| 4. | Kanchipuram–Sriperumbudur | 32.1 | Ramalingam Construction Co. |
Extension
The Indian National Expressway Network was proposed by the Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways (MoRTH). The Government of India envisioned a Bangalore–Mangalore Greenfield Expressway.[12] A Mangaluru–Chennai Expressway through Bangalore has also been proposed.[13]
Status updates
- Aug 2018: Land acquisition was announced to start soon.[14]
- Dec 2018: ₹1,370 crores were already spent by the Government of India on pre-construction activities of this ₹17,930 crores expressway.[15]
- Feb 2019: More than 60% of land required for 262 km expressway was now acquired. Work was announced to begin in six months. The deadline of the Expressway was set to 2023.[16]
- Nov 2020: Acquisition of required 2,650 hectares of land was nearly done. Tenders were invited for 3 out of total 10 packages.[17]
- Feb 2021: The expressway was later shortened to be 4 laned instead earlier planned 8 lanes.[18] Dilip Buildcon Ltd declared lowest bidder for Package 1 (Hoskote - Malur) and Package 2 (Malur - Bangarapet).
- Sep 2021: Dilip Buildcon Ltd receives Letter of Agreement (LoA) from National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) for construction of the expressway.
- Jan 2023: The expressway will have 8 lanes only, and will be completed by March 2024.[19]
- Jan 2023: As of 26 January, around 15% work has been completed on the expressway.[20]
See also
References
- Sharma, Anurakti (6 January 2023). "Bengaluru-Chennai Expressway to be completed by March 2024". Times Now. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- Sharma, Anurakti (6 January 2023). "Bengaluru-Chennai Expressway to be completed by March 2024". Times Now. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- "Project report on Chennai Expressway may get ready by March". The Hindu. 21 October 2011. Archived from the original on 2 May 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- Gazette notification dated 1 January 2021
- Akram Mohammed (18 December 2018). "Expressway to reduce travel time between Bengaluru, Chennai". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- Sharma, Anurakti (6 January 2023). "Bengaluru-Chennai Expressway to be completed by March 2024". Times Now. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- "Real Estate in Bangalore & Chennai to get elevated with the upcoming Bangalore-Chennai Expressway!". www.sulekha.com. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "Keezhveeranam - soul searchers - Maitreya - Dharmakshetra Real estate Project".
- "Karnataka / Bangalore News : Chennai Expressway to be ready in three years". The Hindu. 20 June 2010. Archived from the original on 24 June 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- "Dilip Buildcon declared L1 bidder for projects worth Rs 2,439 crores". Business Standard. 24 February 2021.
- "Apco will build NHAI's Bangalore-Chennai Expressway segment". Construction World. 18 March 2021.
- Project Report on Indian National Expressway Network
- "Greenfield express corridor from Mangalore to Chennai on the anvil - Times Of India". 8 July 2013. Archived from the original on 8 July 2013. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- "Notice issued to get land: Notice issued to get land for highway | Chennai News - Times of India".
- "Expressway to reduce travel time between Bengaluru, Chennai".
- "Chennai-Bangalore Expressway work to start in six months: Nirmala Sitharaman".
- "NHAI invites tenders for Bengaluru-Chennai Expressway".
- "Chennai-Bengaluru expressway downgraded due to traffic, alternative road".
- Sharma, Anurakti (6 January 2023). "Bengaluru-Chennai Expressway to be completed by March 2024". Times Now. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- Shivakumar, C. (26 January 2023). "Chennai-Bengaluru expressway: 14km road work complete". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 26 January 2023.