Bothidae
Bothidae or lefteye flounders are a family of flounders. They are called "lefteye flounders" because most species lie on the sea bottom on their right sides, with both eyes on their left sides.[1] The family is also distinguished by the presence of spines on the snout and near the eyes.[2]
| Lefteye flounders | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scaldfish, Arnoglossus laterna | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Pleuronectiformes |
| Suborder: | Pleuronectoidei |
| Family: | Bothidae Smitt, 1892 |
| Type genus | |
| Bothus Rafinesque, 1810 | |
| Genera | |
|
Arnoglossus | |
Lefteye flounders vary considerably in size between the more than 160 species, ranging from 4.5 cm (1.8 in) to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length.[2]
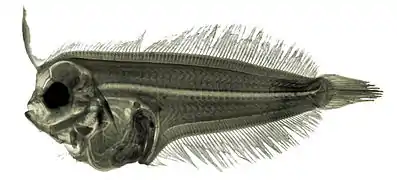 Scaldfish (Arnoglossus laterna) larva
Scaldfish (Arnoglossus laterna) larva Wide-eyed flounder, Bothus podas
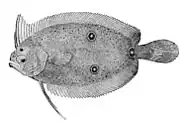
Wide-eyed flounder, Bothus podas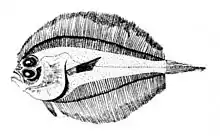 Laeops macrophthalmus
Laeops macrophthalmus Monolene atrimana
Monolene atrimana Deepwater flounder, Monolene sessilicauda
Deepwater flounder, Monolene sessilicauda Sash flounder, Trichopsetta ventralis
Sash flounder, Trichopsetta ventralis
See also
- Pleuronectidae, the righteye family of flounders
References
- Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2006). "Bothidae" in FishBase. February 2006 version.
- Chapleau, Francois & Amaoka, Kunio (1998). Paxton, J.R. & Eschmeyer, W.N. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Fishes. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 224–225. ISBN 0-12-547665-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.