Botryococcus
Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.[2]
| Botryococcus Temporal range: Precambrian - Recent > | |
|---|---|
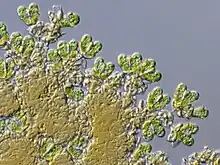 | |
| Botryococcus braunii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Trebouxiophyceae |
| Order: | Trebouxiales |
| Family: | Botryococcaceae |
| Genus: | Botryococcus Kützing, 1849 |
| Type species | |
| Botryococcus braunii | |
| Species[1] | |
|
See text | |
Taxonomy
The genus and its holotype were described in 1849 by Friedrich Traugott Kützing.[3]
Description
Appears as colonies of cells irregularly arranges cells in a folded mucilage. Cells spherical or oval, chloroplast net-like with a single pyrenoid.[4]
Ecology
The algae is frequently found in plankton in waters with differing characteristics and a wide geographic distribution. It is an important component of algal blooms and the discoloration of water.[5] It is known to reproduce asexually but zoospores and sexual reproduction are unknown.[1]
Species
There are 13 accepted species in the genus.[1]
- Botryococcus australis J.Komárek & P.Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus balkachicus Zalessky
- Botryococcus braunii Kützing 1849
- Botryococcus calcareus West 1892
- Botryococcus canadensis F.Hindák 1991
- Botryococcus comperei J.Komárek & P.Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus fernandoi J.Komárek & P.Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus neglectus (West & G.S.West) J.Komárek & P.Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus pila J.Komárek & P.Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus protuberans West & G.S.West 1905
- Botryococcus pusillus Goor 1924
- Botryococcus terribilis Komárek & Marvan 1992
- Botryococcus terricola Klebs 1883
References
- Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (20 December 2011). "Genus: Botryococcus taxonomy browser". AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- Tennant, Richard K.; Lux, Thomas M.; Sambles, Christine M.; Kuhn, Nikolaus J.; Petticrew, Ellen L.; Oldfield, Richard; Parker, David A.; Hatton, Jackie; Moore, Karen A.; Lee, Rob; Turney, Chris S. M. (2019-02-11). "Palaeogenomics of the Hydrocarbon Producing Microalga Botryococcus braunii". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 1776. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.1776T. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-38236-5. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6370823. PMID 30742038.
- Kützing, Friedrich Traugott (1849). Species Algarum. Brockhaus. p. 892.
- Guiry, M.D., John, D.M., Rindi, F. and McCarthy, T.K (Ed) 2007. New Survey of Clare Island Volume 6: The Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae. Royal Irish Academy. ISBN<978-1-904890-31-7
- Fanés Treviño, Ingrid; Sánchez Castillo, Pedro; Comas González, Augusto (2009). "Contribution to the taxonomic study of the family Botryococcaceae (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) in southern Spain" (PDF). Cryptogamie, Algologie. 30: 17–30. Retrieved 12 September 2023.