Bradley railway station
Bradley railway station served the district of Bradley, West Yorkshire, England until closure in 1950.
Bradley | |
|---|---|
 Site of Bradley Station View NE, towards Bradley Wood Junction and Brighouse (left), Heaton Lodge Junction and Mirfield (also Spen Valley loop) (right) | |
| General information | |
| Location | Bradley, Kirklees England |
| Coordinates | 53.676190°N 1.740900°W |
| Grid reference | SE172200 |
| Other information | |
| Status | Disused |
| History | |
| Original company | Huddersfield and Manchester Railway |
| Pre-grouping | London and North Western Railway |
| Post-grouping | London, Midland and Scottish Railway |
| Key dates | |
| 3 August 1847 | opened |
| July 1849 | resited |
| 6 March 1950 | closed |
History
Bradley station was opened in 1847 along with Huddersfield railway station, as the first section completed of the new Huddersfield and Manchester Railway.[1]
Previously, Huddersfield had been by-passed by the existing east–west route, the Manchester and Leeds Railway which had opened in 1840.[2] That line instead had closely followed the even gradients of the River Calder, which left Huddersfield to be served with a station at Cooper Bridge about 4 miles (6.4 km) distant. The new line ran through the town itself, with Bradley station to the east of it, where the line divided to meet the existing Manchester and Leeds route in a triangular junction, allowing trains to continue on eastwards via Mirfield towards Dewsbury, Wakefield and Leeds, or westwards via Brighouse up the Calder valley.[3]
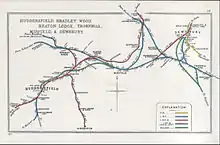
The Manchester and Leeds Railway (from 1847 the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway) had been closely involved with the Huddersfield and Manchester Railway; but in 1848 it was the London and North Western Railway that took over the line and completed its connection from Manchester to Huddersfield via Stalybridge and the Standedge tunnel and its new line through to Leeds through the centre of Dewsbury. The LNWR still had to work together with the L&Y, however, as the LNWR depended on running powers over L&Y rails from Manchester Victoria to Stalybridge and between Bradley and Dewsbury, over the former Manchester and Leeds section of track. The L&Y, in turn, used the LNWR track through Bradley to run trains onwards via Huddersfield onto a new line it constructed via Penistone, where it met the MS&LR line south via Barnsley to Sheffield.
Additional nearby destinations opened up when the L&Y opened its Pickle Bridge Line in 1881 to Bradford via Clifton Road; and when LNWR opened a new line in 1900 to Leeds up the Spen valley, to reduce congestion on the shared L&Y section of track. These routes survived the 1923 amalgamation, when all became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. However, under British Railways both were subsequently closed in the 1950s, and Bradley station itself closed in 1950.[4] However, the track through it remains an important link in the Huddersfield Line, and since the year 2000 also the Caldervale Line.
This real station should not be confused with the fictional station featured in the TV series How We Used To Live, which served the equally fictional town of Bradley (though also located in West Yorkshire) and was depicted as part of the LMS.
References
- Bairstow 1984, p. 15.
- Joy, David (1984). A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain, Volume 8: South and West Yorkshire (2 ed.). Newton Abbot: David & Charles. p. 253. ISBN 0-946537-11-9.
- Bairstow 1984, p. 9.
- Bairstow 1984, p. 72.
Sources
- Bairstow, Martin (1984). The Leeds, Huddersfield and Manchester Railway. Pudsey: Bairstow. ISBN 0-90243830-1.
External links
Kirklees South Lines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preceding station | Historical railways | Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huddersfield Line and station open |
Manchester and Leeds line LNWR/L&YR |
Mirfield Line and station open | ||
| Calder Valley line L&YR |
Brighouse Line and station open | |||
| Disused railways | ||||
| Huddersfield Line and station open |
Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway Pickle Bridge Line |
Clifton Road Line and station closed | ||
| London and North Western Railway Leeds New Line |
Battyeford Line and station closed | |||