Buick XP-300
The Buick XP-300 (initially designated the XP-9) is a concept car created by General Motors in 1951. It is a counterpart to GM's Le Sabre, with which it shares many common mechanical components, including its 335-horsepower (250 kW) supercharged V8 engine, which could run on either gasoline or methanol. Representative of GM's "long and low" design philosophy in the 1950s, the XP-300 measures over 16 feet (4,900 mm) in total length but is only 39.1 inches (990 mm) in height. It includes numerous features ranging from push-button power windows and seats to hydraulic jacks and de Dion axles.
| Buick XP-300 | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Buick XP-300 at the Alfred P. Sloan Museum in Flint, Michigan | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | General Motors |
| Production | 1951 |
| Designer | Charles Chayne Ned F. Nickles |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Concept car |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 335-horsepower (250 kW) supercharged V8 engine |
| Transmission | Dynaflow automatic transmission |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 116 inches (2,900 mm) |
| Length | 16 feet (4,900 mm) |
| Width | 80 inches (2,000 mm) |
| Height | 39.1 inches (990 mm) |
| Curb weight | 3,125 pounds (1,417 kg) |
Claimed to have attained a top speed of 140 miles per hour (230 km/h) during testing, the XP-300 was displayed at auto shows across the United States, including the Chicago Auto Show in February 1951 and GM's 1953 Motorama tour. Together with the Le Sabre, the XP-300 pioneered the wraparound windshield, although it ultimately had much less influence on future car design than its counterpart. In 1966, the XP-300 was refurbished and donated to the Alfred P. Sloan Museum in Flint, Michigan, where it remains as of 2018.
Background
The XP-300, which was initially designated the XP-9,[1][2] was designed by General Motors (GM) vice president of engineering Charles Chayne,[2][3] along with Ned F. Nickles.[1] Chayne had previously assisted Harley Earl in designing the 1938-39 Buick Y-Job, often regarded as the first concept car.[1] In May 1951, Chayne granted approval for construction of the XP-300 along with a counterpart GM concept car, the Le Sabre.[1][2]
Design
The XP-300 features a wraparound windshield, three tailfins, and a grille that resembles an electric razor.[1] It also includes push-button power windows and seats.[1] Although somewhat similar in appearance to the Le Sabre, the XP-300's styling was noticeably cleaner than the more futuristic, rocket-inspired lines of its counterpart.[1] Furthermore, while the Le Sabre generally reflected Earl's design philosophy, the XP-300 was more in line with Chayne's conception of the future of Buick production cars, and its front end design ultimately foreshadowed the 1954 Buick line.[1] The car's name reflects the fact that it produced over 300 horsepower (220 kW) and was an experimental (XP) vehicle in nature.[3]
Body
.jpg.webp)
The XP-300's body and frame were welded together into a single unit.[1][3][4] It shares many common mechanical components with the Le Sabre.[1] Representative of GM's "long and low" design philosophy in the 1950s, the XP-300 measures over 16 feet (4,900 mm) in total length and has a 116-inch (2,900 mm) wheelbase with just 6.5 inches (170 mm) of ground clearance.[1][3][5] The car is only 39.1 inches (990 mm) in height and 80 inches (2,000 mm) in width.[6] Weighing in at 3,125 pounds (1,417 kg),[4] the total weight of the car was reduced by its use of heat-treated, aluminum body panels.[1][3]
The car also features relatively heavy and wide drum brakes that necessitated two sets of brake shoes for each wheel.[1][3] In addition, it boasts hydraulic steel bars that made it more rigid while being driven, helping form a framework somewhat similar to a roll cage;[1][4] similarly, four hydraulic jacks that could raise either the driver or passenger side of the car facilitated easier tire changes.[1][7] The XP-300 also has de Dion axles based on a Daimler-Benz design used for Grand Prix race cars.[8] It additionally features four coil springs and a hydraulic system more complex than that of the Le Sabre, which operates the car's cowl vents, door-locking devices, hood, jacks, seats, and windows.[9]
The car was painted "Venus White".[9] It has functional chrome louvers running down its rocker panels; the forward-mounted louvers served to vent heat from the engine, while the aft ones allowed air to enter the passenger compartment.[10][9] Similarly, a chrome fin runs through the center of the car's trunk, hiding hinges for the twin deck lids, while a floodlight-style, sealed-beam backup lamp was mounted in the central fixture, which imitates the exhaust of a jet engine.[9] The car was originally built with both a folding convertible top and a hardtop that were interchangeable, although the hardware to mount the latter has been removed and the hardtop can no longer be used.[9]
The interior of the XP-300 features pleated blue-leather bucket seats with adjustable inflatable air bladders and a center console.[9] The car also has a telescoping steering wheel and an instrument panel displaying a prominently mounted combined speedometer/tachometer as well as a fuel gauge.[9] It also boasted numerous technologies considered safety features in 1951, including its dual brakes, adjustable seats, and adjustable steering wheel in addition to seat belts.[6][10]
Engine
The XP-300 was powered by a supercharged V8 engine made of aluminum that weighed just 550 pounds (250 kg) yet produced 335 horsepower (250 kW).[1][11] This engine is 250 pounds (110 kg) lighter than the engine used in the contemporary production Buick Roadmaster, but is twice as powerful.[7] The XP-300's engine could run on either gasoline or methanol, and the car featured two separate fuel fillers and fuel tanks, one for each fuel.[12] The engine was fitted with a Bendix-Eclipse two-barrel carburetor,[12] with one using gasoline and the other methanol.[7] The methanol carburetor automatically cut in once the gasoline carburetor reached 40% throttle,[7] in order to prevent engine knocking during rapid acceleration.[6]
With a displacement of just 215.7 cubic inches (3.535 L), the engine, which also powered the Le Sabre, had an impressive power-to-size ratio for the era.[13] It also boasted a chain-driven camshaft and hemispherical combustion chambers,[13] the latter of which allowed it to achieve an air-to-fuel-mixture ratio of 10.0:1, also considerable for 1951.[14] The engine features rocker arms that were mounted transversely on its intake valves but in a fore/aft position for the exhaust valves, which made it more compact and allowed easier installation into the car.[12] It is mated to a custom Dynaflow automatic transmission.[6]
Testing and touring
During testing, Chayne claimed that the XP-300 achieved a top speed of 140 miles per hour (230 km/h) in the hands of Buick general manager Ivan Wiles.[1][3][4] Chayne also used the car personally, and reached at least 110 mph (180 km/h) in it himself.[1]
The XP-300 was displayed at auto shows across the United States, where it became a popular fixture with attendees as well as the press.[1] It was displayed at the Chicago Auto Show in February 1951, despite not yet being completely finished.[4] Later that year, it was displayed at the GM Proving Grounds alongside the Le Sabre.[4] The two cars were then displayed together during GM's 1953 Motorama tour.[4] During its unveiling in Santa Ana, California, Chayne called the car "undoubtedly the safest, most comfortable, high-performance car on the road today".[6] The XP-300 accumulated nearly 10,400 miles (16,700 km) of driving, although it did not drive as far as the more publicized Le Sabre.[4] The XP-300 was also insured for $1 million.[7]
Legacy
Together with the Le Sabre, the XP-300 pioneered the wraparound windshield.[1][12] While the XP-300 inspired the design of the front and upper quarter panels of 1953 and 1954 Buicks,[15] and the headlight styling, wraparound windshield, and adjustable front seats of the 1954 Buick line,[16] it ultimately had much less influence on future car design than the Le Sabre.[15] The Le Sabre, on the other hand, inspired the tailfins on 1953 and 1954 Pontiacs as well as 1957 Cadillacs, the gull-wing bumpers on various Cadillacs, and even European designs such as the Spohn-bodied Veritas and the ZIS-112.[15]
In 1966, the XP-300 was refurbished and donated to the Alfred P. Sloan Museum in Flint, Michigan.[15] In 1985, it was at the Sloan Museum alongside the 1956 Buick Centurion, Buick Wildcat II, Buick Y-Job, Cadillac Cyclone, and General Motors Le Sabre.[17] In 1991, it was exhibited at the Museum of Transportation in Brookline, Massachusetts, along with four other GM cars.[10] As of 2018, it was on display at the Sloan Museum, along with four other Buick concept cars.[1][3]
References
- Gunnell, John (October 21, 2014). "Car of the Week: 1951 Buick XP-300 concept". Old Cars Weekly.
- Temple 2015, p. 16.
- "1951 Buick XP-300". Flint Cultural Center Corporation. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- Temple 2015, p. 22.
- Temple 2015, pp. 21–22.
- Schrader, Del (November 11, 1951). "Buick's XP-300 Boasts Many Safety Features". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved May 15, 2018 – via Newspapers.com
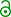 .
. - Kuebler, Joseph E. (April 18, 1952). "Engineers See GM's Super Buick". Akron Beacon Journal. Retrieved May 15, 2018 – via Newspapers.com
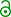 .
. - Temple 2015, pp. 20–21.
- Temple 2015, p. 21.
- "Historic GM concept cars on exhibit at museum". Green Bay Press-Gazette. April 17, 1991. Retrieved May 15, 2018 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Lentinello, Richard (May 10, 2017). "General Motors Concept Ad". Hemmings Motor News. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- Temple 2015, p. 18.
- Temple 2015, p. 17.
- Temple 2015, pp. 17–18.
- Temple 2015, p. 23.
- "Buick: Borrows Ideas From Its 'Dream' Cars". Democrat and Chronicle. Rochester, New York. March 14, 1954. Retrieved May 15, 2018 – via Newspapers.com
 .
. - Lamm, Michael (April 1985). "Yesterday's Dream Cars". Popular Mechanics. 162: 179 – via Google Books.
Sources
- Temple, David W. (2015). Motorama: GM's Legendary Show & Concept Cars. CarTech, Inc. ISBN 978-1-61325-159-1.
