BLS AG
BLS AG is a Swiss railway company created by the 2006 merger of BLS Lötschbergbahn and Regionalverkehr Mittelland AG. 55.8% of it is owned by the canton of Berne, and 21.7% by the Swiss Confederation. It has two main business fields: passenger traffic and infrastructure.
BLS has a subsidiary—BLS Cargo—which is responsible for all freight operations. BLS Cargo works in cooperation with the freight subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn, Railion. However, the staff, apart from management and sales, is employed by BLS AG. Part of the BLS locomotive fleet is owned by BLS Cargo.
Another subsidiary, BLS Fernverkehr AG, is responsible for long-distance passenger transport. BLS Fernverkehr AG is wholly owned by BLS AG.
Infrastructure
In 2007 the new, 34.6-kilometre-long (21.5 mi), Lötschberg Base Tunnel opened, which is part of the 449 km of infrastructure owned and operated by BLS AG. The Lötschberg base tunnel was built by a wholly owned subsidiary, BLS AlpTransit AG. By mid-2007 this company handed over the base tunnel to BLS AG. In 2009 this company was renamed BLS Netz AG and the entire BLS infrastructure passed over to this company which is mainly owned by the Swiss Confederation, which has paid for most of the recent investments.
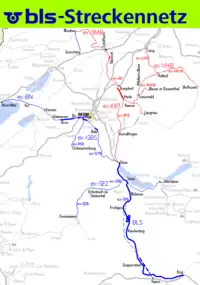
BLS AG owns or operates on the following railway lines:
Rolling stock
Also see Bern–Lötschberg–Simplon railway#Locomotives and multiple units


- 3 x BLS Re 420
- 33 x BLS Re 425
- 18 x BLS Re 465
- 28 x BLS RABe 515
- 36 x BLS RABe 525
- 13 x BLS RABe 526
- 30 x BLS RABe 528 (+ 28 under delivery)
- 25 x BLS RABe 535
- 21 x BLS RBDe 565
- 13 x BLS RBDe 566
BLS Cargo has the following rolling stock.
- 4 x BLS Re 425
- 2 x BLS Re 456
- 10 x BLS Re 465
- 15 x BLS Re 475
- 20 x BLS Re 485
- 10 x BLS Re 486
- 1 x BLS Am 845
In 2010, 28 Stadler KISS EMUs were ordered; the first was delivered in March 2012. As of 2012, BLS was planning to spend around 1·2bn SFr on new rolling stock by 2025, building a more standardised fleet with fewer different types of train.[1] In 2017, 58 Stadler FLIRT EMUs were ordered, expected to enter service between 2021 and 2026.[2]
Passenger train services
Since the merger, BLS has been the exclusive operator of the standard gauge part of the S-Bahn Bern. This includes open access services over Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) and STB Sensetalbahn tracks. Since December 2007 BLS offers a new RegioExpress service over the old Lötschberg route while most SBB and Cisalpino, InterCity, and EuroCity trains use the new Lötschberg tunnel. Here is a full list of regular BLS train services:
- S1 Fribourg-Bern-Münsingen-Thun
- S2 Laupen-Bern-Konolfingen-Langnau
- S3 Biel/Bienne-Lyss-Bern-Belp
- S31 (Biel/Bienne-)Münchenbuchsee-Bern-Belp-Thun
- S4 Thun-Belp-Bern-Burgdorf-Langnau
- S44 Thun-Belp-Bern-Burgdorf-Solothurn/Sumiswald-Grünen
- S5 Bern-Kerzers-Neuenburg/Murten(-Payerne)
- S51 Bern-Stöckacker-Bern Brünnen Westside
- S52 Bern-Bern Brünnen Westside-Kerzers
- S6 Bern-Köniz-Schwarzenburg
- S6 Langnau-Wolhusen-Malters-Luzern
- S7 Langenthal-Huttwil-Willisau-Wolhusen-Luzern (coupled with the RE Bern-Luzern between Wolhusen and Luzern)
- RegioExpress (RE)
- RE Bern-Langnau-Luzern
- RE Bern-Neuchâtel-La Chaux-de-Fonds
- RE Bern-Münsingen-Spiez-Brig/Zweisimmen
- Regional trains (R)
- R Interlaken Ost-Spiez-Wiessenbach-Zweisimmen
- R Spiez-Frutigen
- R Thun-Konolfingen-Hasle Rüegsau
- R Thun-Konolfingen-Burgdorf-Solothurn
- R Kerzers-Lyss
- R Lyss-Büren a. Aare
- InterRegio (IR)
- IR17 Bern-Olten
- IR65 Bern-Biel/Bienne
- IR66 Bern-Neuchâtel-La Chaux-de-Fonds
BLS Busland
BLS Busland operates a fleet of 36 buses over a network that complements the passenger train services. The bus fleet comprises:
BLS Navigation

BLS owns and operates steamers on Lake Brienz and Lake Thun under the BLS Navigation brand. These steamers utilise the Interlaken and Thun ship canals.
- Blümlisalp, paddle steamer built in 1906
References
- "Railway Gazette: First KISS for BLS". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 21 March 2012.
- "BLS selects Stadler for its largest rolling stock order". Railway Gazette International. 2 May 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2017.