Câlnic Fortress
The Câlnic Fortress (Romanian: Cetatea Câlnic; German: Burg Kelling, pronunciation: [ˈkɨlnik]) is a fortress located in Câlnic, Alba County, in the Transylvania region of Romania. It was built by a nobleman whose family later sold it to the local ethnic German Transylvanian Saxon community at a time when the area belonged to the Kingdom of Hungary. When still used for defensive purposes, the double walls encompassed a residential keep, storerooms and a Roman Catholic chapel that became Lutheran following the Reformation. Together with the surrounding village, the fortress forms part of the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania UNESCO World Heritage Site.
| Câlnic Fortress | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General information | |
| Town or city | Câlnic, Alba County |
| Country | |
| Coordinates | 45.8891°N 23.6604°E |
Description
Background and construction

The Mongol invasion of 1241 prompted a surge in military construction in Transylvania, with wood and earthen defenses abandoned in favor of stone, assembled in haste and without much initial attention to artistic detail.[1] At Câlnic, the fortress began as a residence for a Graf (count), one of the last such to be built in Transylvania. Around 1270, the nobleman Chyl of Kelling, whose family gave the village its German name, built a keep for his residence.[2] The strong parallelepiped structure, with a ground floor and three floors for living space, came to be known as the Siegfried tower.[3] Frequent Ottoman attacks led the keep to be fortified with a defensive level and surrounded by a massive wall.[2] The oval precinct around the keep was fitted with a guard tower to the south and a gate tower to the north.[1][3] The structure was surrounded by a water-filled moat, with access only by drawbridge. The noble owners never went along very well with the local notables, and in 1430, the final Graf sold the fortress to the villagers and moved out.[2]
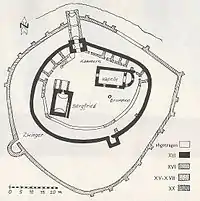
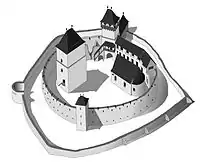
Once the Saxon community took ownership, they extended it by building a second fortification wall and a tower in the southern part, using the structure for refuge during Ottoman raids. Within were built storerooms and living quarters for withstanding sieges; these have not survived.[2] After the second wall was finished in the 16th century, two levels were added to the keep (which reached over 20 m in height) so that defenders could fire guns outside the precinct walls.[4]
At the end of the 15th century, a small hall church-type chapel with an apse was built for the fort[2] on the site of an earlier, ruined sacral building. The chapel interior features fresco fragments from the beginning of the 16th century. Its western side has a wooden platform decorated with panels painted in 1733 in a floral, folk-Renaissance style.[4] In the mid-16th century, the moat was filled and the drawbridge replaced by a gatehouse fitted with a portcullis. The Ottomans destroyed the village in 1658, but failed to take the fortress.[2]
Surroundings and recognition
Restoration work was done between 1961 and 1964. Since 1995,[4] the site has been administered by a foundation of Babeș-Bolyai University in Cluj-Napoca. The tower hosts a museum detailing the local Saxons' lifestyle and traditions,[2] while the chapel hosts lectures. Nearby, there is a former Lutheran parish house built in the 16th century and enlarged in 1779.[1]
Further out, there is a church on a hill towering over the village, surrounded by a cemetery.[1] Villagers built the church in the 15th century, although it was much altered in the 19th century and now has a Gothic Revival style. Its two tabernacles and the sacristy portal are original carved Gothic items, while two Baroque pulpits are from the second part of the 18th century.[4]
In 1999, Câlnic, together with five other places, was added to the already-listed Biertan to form the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania UNESCO World Heritage Site.[5] Additionally, the fortress is listed as a historic monument by Romania's Ministry of Culture and Religious Affairs, the following considered separate monuments: the keep, the chapel, the inner wall, the outer wall, the church and the parish house.[6]
 Double walls, exterior
Double walls, exterior Path to interior beneath barbican
Path to interior beneath barbican Walls from interior
Walls from interior Siegfried tower
Siegfried tower Courtyard
Courtyard Chapel
Chapel Chapel interior
Chapel interior Altar
Altar Floral decor in chapel
Floral decor in chapel Bells
Bells Well
Well.JPG.webp) Museum room
Museum room
Notes
- (in Romanian) Câlnic/Kelling at biserici-fortificate.com
- (in Romanian) Câlnic/Kelling Archived 2014-05-03 at the Wayback Machine at biserici-fortificate.org
- Dan Ghinea, Enciclopedia geografică a României, p.390. Editura Enciclopedică, Bucharest, 2000. ISBN 978-97345-014-8-9
- (in Romanian) Marius Porumb, Ciprian Firea, Cetatea Câlnic Archived 2014-05-03 at archive.today at the Alba County Cultural Affairs Office site
- "World Heritage Committee Inscribes 48 New Sites on Heritage List" at the UNESCO site
- (in Romanian) Lista Monumentelor Istorice 2010: Judeţul Alba
