C7orf25
C7orf25 protein UPF0415 (UPF0415) is a protein encoded on chromosome 7, in open reading frame 25 (C7orf25) and are located at domain of unknown function 1308. C7orf25 is located at the minus strand and encodes 12 proteins, one of them being UPF0415. This protein is believed to be active in the proteosome pathway. C7orf25 protein UPF0415 is not a transmembrane protein and has no signal peptide. UPF0415 has two isoforms, Q9BPX7-1 and Q9BPX7-2. Both consists of two exons that are both highly conserved among vertebrates.
| C7orf25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | C7orf25, C7orf25 protein UPF0415, chromosome 7 open reading frame 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2145422 HomoloGene: 11439 GeneCards: C7orf25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Background information
| Gene Size | Protein Size | # of exons | Promoter Sequence | Signal Peptide | Molecular Weight | Chromosome position | Protein Isoelectric point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1844 bp | 421 aa | 2 | ~600bp | No | 46.45 kDa [5] | 7p14 | 5.76 [5] |
Gene neighborhood
C7orf25 is an open reading frame that encodes 12 proteins. Most of these are of unknown function. One of these proteins is UPF0415 and another is PSMA2 which is also functional in the proteosome pathway.[6] Other genes located near C7orf25 protein UPF0415 are TCP1P1, HECW1, MIR3943 and MRPL32.
Predicted mRNA features
Promoter
The promoter for the C7orf25 protein UPF0415 gene spans 600 base pairs from 42,951,804 to 42,952,404 with a predicted transcriptional start site that encodes a sequence of 1844 base pairs. The sequence spans from 42,908,726 to 42,912,090.[7] The promoter region and beginning of the C7orf25 gene (20,008,263 to 20,009,250) is not conserved past primates. This region was used to determine transcription factor interactions.
Transcription factors
Some of the main transcription factors that bind to the promoter are listed below.[8]
| Reference | Detailed Family Information | Start (nucleotide) | End (nucleotide) | Strand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XCPE | Activator-, mediator- and TBP-dependent core promoter element for RNA polymerase II transcription from TATA-less promoters | 360 | 370 | - |
| MIZ1 | Myc-interacting Zn finger protein 1 | 120 | 130 | - |
| PLAG1 | Pleomorphic adenoma gene | 160 | 182 | - |
| FOX proteins | Fork head domain factors | 35 | 51 | + |
| E2FF | E2F-myc activator/cell cycle regulator | 357 | 373 | - |
| MZF1 | Myeloid zinc finger 1 factors | 497 | 507 | + |
| HAND | Twist subfamily of class B bHLH transcription factors | 335 | 355 | - |
| RU49 | Zinc finger transcription factor RU49, zinc finger proliferation 1 - Zipro1 | 651 | 657 | - |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B/c-rel | 219 | 233 | - |
| E2FF | E2F-myc activator/cell cycle regulator | 492 | 508 | + |
| SP1F | GC-Box factors SP1/GC | 490 | 506 | + |
| IKRS | Ikaros zinc finger family | 64 | 76 | + |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription | 409 | 427 | - |
| RBP2 | Retinoblastoma-binding proteins with demethylase activity | 538 | 546 | - |
| YY1F | Activator/repressor binding to transcription initiation site | 553 | 575 | - |
| SP1F | GC-Box factors SP1/GC | 359 | 375 | - |
| HSF | Heat shock factors | 240 | 264 | - |
| BPTF | Bromodomain and PHD domain transcription factors | 423 | 433 | + |
| ZNF35 | Zinc finger protein ZNF35 | 309 | 321 | + |
| ETSF | Human and murine ETS1 factors | 235 | 255 | + |
Function and expression
C7orf25 protein UPF0415 is believed to be active in ATP dependent protein breakdown in the proteosome pathway. It is expressed ubiquitously in humans.[9]
Homology
UPF0415 protein C7orf25 has one paralog which is FLJ18411.[10] UPF0415 is also highly conserved in vertebrates. The following table shows a small selection of orthologs found using BLAST and BLAT and their identity to C7orf25 protein UPF0415.
| Genus and species | Accession number | Similarity (aa) |
|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | NM_001099858 | - |
| Bos taurus (Cow) | NM_001076140.1 | 95% |
| Falco cherrug (Falcon) | XM_005446213.1 | 78% |
| Xenopus laevis (Frog) | XM_005014944.1 | 73% |
Predicted protein features
Post Translational Modifications
UPF0415 protein C7orf25 is not a transmembrane protein as it has no transmembrane domains. C7orf25 protein UPF0415 has multiple phosphorylation which are believed to be responsible in protein activation.[11]
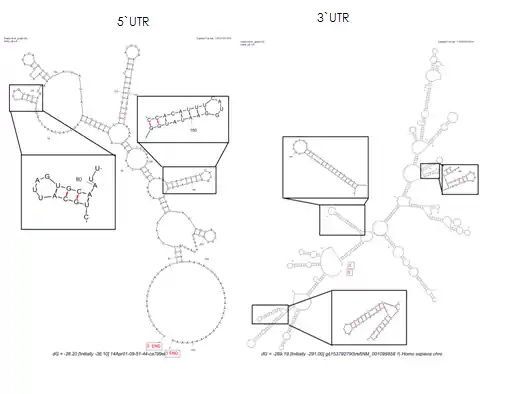
Multiple stem loops have been predicted in both 3` and 5`UTR and these are believed to be functional in gene transcription.[12]
Interactions
Other proteins that are known to interact with UPF0415 protein C7orf25 are FRA10AC1, FLJ23825 and TUBB (tubulin, beta class I) and only TUBB is associated with proteosome activity.
Conceptual presentation
All post transnational modifications, genetic or proteomic factors that are relevant for UPF0415 protein C7orf25 transcription and regulation, mentioned above, are annotated in the conceptual translation.

C7orf25
C7orf25 encodes 12 different transcripts. Two of these transcripts are (PSMA2 and UPF0415). No specific phenotypes or polymorphisms are yet to be related to mutations in C7orf25. This suggests that this reading frame is important for survival in vertebrates. The picture below shows all predicted transcripts encoded in C7orf25.[13]

References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136197 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000039182 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Kozlowski LP (October 2016). "IPC - Isoelectric Point Calculator". Biology Direct. 11 (1): 55. doi:10.1186/s13062-016-0159-9. PMC 5075173. PMID 27769290. Archived from the original on 2013-04-29. Retrieved 2019-06-19.
- "Gene_neighborhood".
- "El Durado (Genomatix)".
- "Genomatrix_tool_Eldorado".
- Gazitua R, Wilson K, Bistrian BR, Blackburn GL (August 1979). "Factors determining peripheral vein tolerance to amino acid infusions". Archives of Surgery. 114 (8): 897–900. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370320029005. PMID 111645.
- "FLJ18411". 12 January 2008.
- Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (December 1999). "Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites". Journal of Molecular Biology. 294 (5): 1351–62. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3310. PMID 10600390. Archived from the original on 2021-07-09. Retrieved 2014-05-10.
- Zuker, M. (1 July 2003). "Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction". Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (13): 3406–3415. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.138.4837. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg595. PMC 169194. PMID 12824337.
- Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J (2006). "AceView: a comprehensive cDNA-supported gene and transcripts annotation". Genome Biology. 7 Suppl 1: S12.1–14. doi:10.1186/gb-2006-7-s1-s12. PMC 1810549. PMID 16925834.