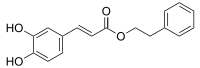
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a natural phenolic chemical compound. It is the ester of caffeic acid and phenethyl alcohol.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Phenylethyl (2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Phenylethyl caffeate; Phenethyl caffeate; Caffeic acid 2-phenylethyl ester; β-Phenylethyl caffeate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | CAPE |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.538 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 284.311 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Natural occurrences
CAPE is found in a variety of plants. It is also a component of propolis from honeybee hives.[1]
Potential pharmacology
A variety of in vitro pharmacology and effects in animal models have been reported for CAPE, but their clinical significance is unknown. It has antimitogenic, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties in vitro.[2] Another study also showed that CAPE suppresses acute immune and inflammatory responses in vitro.[3] This anti-cancer effect was also seen when mice skin was treated with bee propolis and exposed to TPA, a chemical that induced skin papillomas. CAPE significantly reduced the number of papillomas.[4][5]
References
- Demestre M, Messerli SM, Celli N, et al. (August 2008). "CAPE (caffeic acid phenethyl ester)-based propolis extract (Bio 30) suppresses the growth of human neurofibromatosis (NF) tumor xenografts in mice". Phytother Res. 23 (2): 226–30. doi:10.1002/ptr.2594. PMID 18726924. S2CID 21934712.
- Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR, Grunberger D, Aggarwal BB (August 1996). "Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (17): 9090–5. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.9090N. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.17.9090. PMC 38600. PMID 8799159.
- Orban Z, Mitsiades N, Burke TR, Tsokos M, Chrousos GP (2000). "Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces leukocyte apoptosis, modulates nuclear factor-kappa B and suppresses acute inflammation". Neuroimmunomodulation. 7 (2): 99–105. doi:10.1159/000026427. PMID 10686520. S2CID 31950905.
- Huang MT, Ma W, Yen P, et al. (April 1996). "Inhibitory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced tumor promotion in mouse skin and the synthesis of DNA, RNA and protein in HeLa cells". Carcinogenesis. 17 (4): 761–5. doi:10.1093/carcin/17.4.761. PMID 8625488.
- Huang MT, Smart RC, Wong CQ, Conney AH (November 1988). "Inhibitory effect of curcumin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and ferulic acid on tumor promotion in mouse skin by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate". Cancer Res. 48 (21): 5941–6. PMID 3139287.