California water resource region
The California water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey in the United States hydrologic unit system, which is used to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.[1][2]
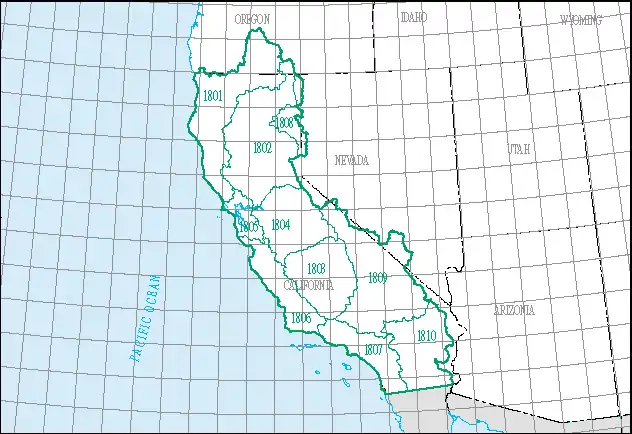
The California region, which is listed with a 2-digit hydrologic unit code (HUC) of 18, has an approximate size of 168,579 square miles (436,620 square kilometers), and consists of 10 subregions, which are listed with the 4-digit HUCs 1801 through 1810.[3]
This region includes the drainage within the United States that ultimately discharges into the Pacific Ocean within the state of California; and those parts of the Great Basin (or other closed basins) that discharge into the state of California. Includes parts of California, Nevada, and Oregon.[3]
List of California water resource subregions
| Subregion HUC[4] | Subregion Name[4] | Subregion Description[3] | Subregion Location[4] | Subregion Size[4] | Subregion Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1801 | Klamath–Northern California Coastal subregion | The drainage into the Pacific Ocean from and including the Smith River Basin to and including the Stemple Creek Basin | California, Oregon | 24,800 sq mi (64,000 km2) |  HUC1801 |
| 1802 | Sacramento subregion | The Sacramento River Basin and drainage into Goose Lake | California, Oregon | 27,600 sq mi (71,000 km2) |  HUC1802 |
| 1803 | Tulare–Buena Vista Lakes subregion | The drainage into the Tulare and Buena Vista Lake closed basins | California | 16,200 sq mi (42,000 km2) |  HUC1803 |
| 1804 | San Joaquin subregion | San Joaquin River Basin | California | 15,600 sq mi (40,000 km2) | 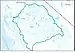 HUC1804 |
| 1805 | San Francisco Bay subregion | The drainage into the Pacific Ocean from the Stemple Creek Basin boundary to and including the Pescadero Creek Basin, excluding the Sacramento and San Joaquin River Basins | California | 4,470 sq mi (11,600 km2) | 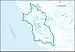 HUC1805 |
| 1806 | Central California Coastal subregion | The drainage into the Pacific Ocean from the Pescadero Creek Basin boundary to and including the Rincon Creek Basin | California | 11,400 sq mi (30,000 km2) | 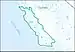 HUC1806 |
| 1807 | Southern California Coastal subregion | Drainage within the United States that discharges into the Pacific Ocean from the Rincon Creek Basin boundary to the California-Baja California international boundary | California | 11,100 sq mi (29,000 km2) | 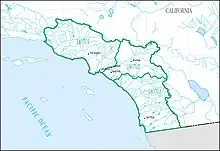 HUC1807 |
| 1808 | North Lahontan subregion | The drainage east of the Sierra Nevada and north of the Truckee River Basin, which includes the Lahonton closed basins that discharge into California | California, Nevada | 4,480 sq mi (11,600 km2) | 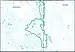 HUC1808 |
| 1809 | Northern Mojave–Mono Lake subregion | The Closed Desert Basins that discharge into South Central California, including Mono Lake, Owens Lake, Death Valley, and the Upper Mojave Desert | California, Nevada | 28,000 sq mi (73,000 km2) | 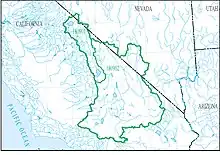 HUC1809 |
| 1810 | Southern Mojave–Salton Sea subregion | The closed desert basins in southeastern California, including the Lower Mojave Desert and the Salton Sea | California | 16,000 sq mi (41,000 km2) | 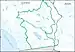 HUC1810 |
Additional images
 Region (2-digit code)
Region (2-digit code)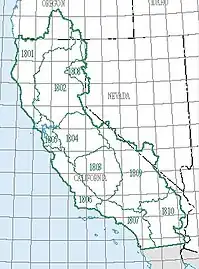 Subregions (4-digit codes)
Subregions (4-digit codes)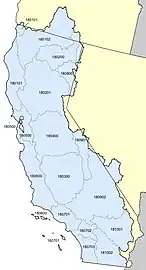 Basins (6-digit codes)
Basins (6-digit codes)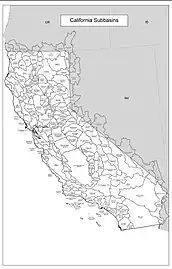 Subbasins (8-digit codes)
Subbasins (8-digit codes)
See also
References
- "Science in Your Watershed - Locate Your Watershed". USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Hydrologic Unit Maps". USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units". water.usgs.gov. USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - McManamay RA, Bevelhimer MS, Kao SC, Yaxing W, Martinez-Gonzalez M, Samu N (2013). "National Hydropower Asset Assessment Environmental Attribution". USGS-Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.