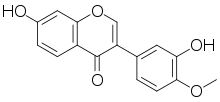
Calycosin
Calycosin is an O-methylated isoflavone. It can be isolated from Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongholicus[1] and Trifolium pratense L. (red clover).[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3′,7-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
7-Hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
7,3′-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone 3′-Hydroxyformononetin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.904 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 284.267 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Biosynthesis
Isoflavone 3′-hydroxylase uses formononetin, NADPH, H+ and O2 to produce calycosin, NADP+ and H2O.
References
- Ma, Xiaofeng; Zhang, Tianyou; Wei, Yun; Tu, Pengfei; Chen, Yingjie; Ito, Yoichiro (2002). "Preparative isolation and purification of calycosin from Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao by high-speed counter-current chromatography". Journal of Chromatography A. 962 (1–2): 243–7. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00535-6. PMID 12198969.
- Biggs, David R; Lane, Geoffrey A (1978). "Identification of isoflavones calycosin and pseudobaptigenin in Trifolium pratense". Phytochemistry. 17 (9): 1683. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)94679-X.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.