Cambay State
Cambay, Kambay, or Khambhat was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The City of Khambat (Cambay) in present-day Gujarat was its capital. The state was bounded in the north by the Kaira district and in the south by the Gulf of Cambay.
| Cambay State ખંભાત | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of Mughal India British Raj | |||||||||
| 1730–1948 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||
 Cambay State in modern state of Gujarat | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1901 | 906 km2 (350 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1901 | 75,122 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Motto | "Dar Babi Farhat" ("This Is the Gate of Joy") | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1730 | ||||||||
| 1948 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Cambay". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. | |||||||||
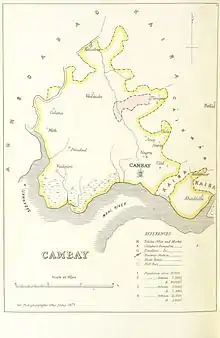

Cambay was the only state in the Kaira Agency of the Gujarat division of the Bombay Presidency, which merged into the Baroda and Gujarat States Agency in 1937.
History
Cambay was founded as a state in 1730 by the penultimate Mughal governor of Gujarat, Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I, the last of the Mughal governors of Gujarat, at the time of the dismemberment of Mughal rule in India. In 1742 Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I defeated his brother-in-law Nizam Khan, governor of Khambhat, and established himself in his place.
In 1780, Cambay was taken by the British Army, led by General Goddard Richards, but it was restored to the Marathas in 1783. Finally it was ceded to the British by the Peshwa after the Treaty of Bassein in 1803.[1] Cambay became a British protectorate in 1817. The state was provided with a railway in 1901.[2] Cambay's last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 10 June 1948.[3]
Hub of mercantile activity
The traders and the merchants reached here from across the world. Cambay was known for its cotton and silk cloths. Cambay was one of India's most active trade center since the 14th century (Source: Ibn Battuta). After 200 years, Duarte Barbosa described Cambay as an important commercial center with carpets, and other textile goods in Mughal established industries.[4]
Rulers
The rulers of the state bore the title of 'Nawab' and had the privilege of an 11-gun salute.[5]
Nawabs
- 1730 – 1742 Mirza Jaffar Mumin Khan I, penultimate Mughal governor of Gujarat
- 1742 – 1743 Nur-ud-din Muftakher Khan
- 1743 – 1784 Najm ad-Dawla Ja`far Mu´min Khan II
- 1784 – 1790 Mohammad Qoli Khan (d. 1790)
- 1790 – 28 October 1823 Fath `Ali Khan (d. 1823)
- 1823 – 15 March 1841 Banda `Ali Khan (d. 1841)
- 1841 – Apr 1880 Husayn Yawar Khan I (d. 1880)
- 11 Jun 1880 – 21 January 1915 Najib ad-Dawla Mumtaz al-Molk Ja`far `Ali Khan (b. 1848 – d. 1915)
- 21 Jan 1915 – 1930 .... -Regent
- 21 Jan 1915 – 15 Aug 1947/10 June 1948 Nizam ad-Dawla Najm ad-Dawla Mumtaz al-Molk Husayn Yawar Khan II (b. 1911 – d. ....)
List of Nawabs of Cambay state
- Mirza JA'AFAR MU'MIN KHAN I 1730/1742, last Muslim Governor of Gujarat
- Nawab NURADDIN MUFTAKHAR KHAN 1742/1743
- Nawab JA'AFAR MU'MIN KHAN II 1743/1784
- Nawab MUHAMMED QULI KHAN 1784/1790, son of Najam Khan (poisoned 1748), married and had issue. He died 1790.
- Nawab FATH ALI KHAN (qv)
- Nawab FATH ALI KHAN 1790/1823, eldest of three sons, he received the title Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung, and the rank of a commander of six thousand as Nawab of Cambay.
- Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Momin Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung Nawab BANDA ALI KHAN 1823/1841
- Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Momin Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung Nawab HUSAIN YAWAR KHAN I 1841/1880
- Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Momin Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung Nawab JA'AFAR ALI KHAN Bahadur 1880/1915, born 1848, succeeded 11 June 1880 (#1), married 1stly, 1876, Bibi Gauhar Khanum Saheb, married 2ndly, 1882, Bibi Khurshid Jahan Begum. He died 21 January 1915.
- HH Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Momin Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung Nawab Mirza HUSAIN YAWAR KHAN II Bahadur 1915/- , born 16 May 1911, educated at Rajkumar College, Rajkot; married January 1936, Nawabzadi Safia Sultan Qizilbash, daughter of Nawab Sir Fateh Ali Khan Qizilbash of Lahore (see Nawabganj), and had issue.
- HH Najum-ud-Daulah Mumtaz-ul-Mulk Momin Khan Bahadur Dilawar Jung Nawab Mirza MUHAMMED JA'AFAR ALI KHAN
References
- Great Britain India Office. The Imperial Gazetteer of India. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1908.
- Princely States of India
- "Cambay State – Princely State (11 gun salute)". Archived from the original on 17 July 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- Walker, Daniel (1997). Flowers Underfoot: Indian Carpets of the Mughal Era. p. 5.
- G. B. Malleson, An historical sketch of the native states of India. London 1875. Reprint Delhi 1984
- Cahoon, Ben. "Indian Princely States K-Z". www.worldstatesmen.org. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "Indian states before 1947 K-W". www.rulers.org. Retrieved 25 August 2019.