Chamba State
Chamba State[3] was one of the oldest princely states in present-day Republic of India, having been founded during the late 6th century. It was part of the States of the Punjab Hills of the Punjab Province in India from 1859 to 1947. Its last ruler signed the instrument of accession to the Indian Union of 15 April 1948.
Chamba State चम्बा रियासत | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~550[1]–1948 | |||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||
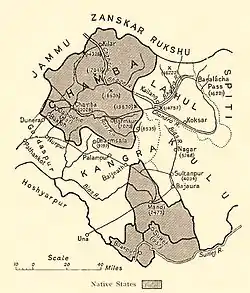 1911 map of the Princely States of the Shimla Hills showing the boundaries of Chamba State. | |||||||
| Capital | Chamba | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | ~550[2] | ||||||
| 1948 | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
| 1892 | 8,329 km2 (3,216 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1892 | 115,773 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Himachal Pradesh, India | ||||||

..jpg.webp)
Geography
Chamba is situated in the bosom of the Himalaya Mountains, and its boundaries are on the northwest, west, and northeast by Kishtwar and Doda district of Jammu region; on the east, Lahaul; and on the southeast and south, the districts of Kangra and Gurdaspur.
The Ravi River flows through this district, and many hydroelectric generating stations have been developed here.
History
According to tradition, the ancient name of Chamba was Champa, and its predecessor state was known as Brahmpur. This site later became Bharmour around 550 AD when Raja Maru Verman came from Kalpagram to the Chamba Hills. In the 900s, the capital was shifted from Bharmour to present day Chamba Town. The rulers of Chamba State patronized artists of the Pahari painting style.[4] Between 1809 and 1846 Chamba was tributary to Jammu. In 1821, Chamba annexed Bhadrawah State. On 9 Mar 1846, Chamba State became a British protectorate.[5]
Rulers
The rulers of Chamba princely state belonged to the Suryavanshi Mushana(मूषाण) Rajput Dynasty.[6]
Rajas
Raja Sahil Verman Around 920AD shifted His Capital From Bharmaur to Present Day Chamba Town. It is believed that King Shail Varman ruled until 940 AD. From then onwards the state of Chamba continued to be ruled by different kings of the Mushana Rajput Dynasty from their capital at Champavati, which later came to be Known as Chamba. Following are some of more famous kings of Chamba in Himachal Pradesh:
.jpg.webp)
- Raja Yugakar Verman
- Raja Vidagdha Verman
- Raja Dodaka Verman
- Raja Vichitra Verman
- Raja Dhariya Verman
- Raja Salavahana Verman
- Raja Soma Varman
- Raja Asata Varman
- Raja Jasata Verman
- Raja Dhala Verman
- Raja Udayan Varman
- Raja Anand Verman
- Raja Ganesa Verman
- Raja Pratap Singh Verman, (from 1559 to 1586)
- Raja Vir Vahnu Verman (1586 to 1589)
- Raja Balbhadra Verman (1589 to 1641) as Chamba.
- 1690 - 1720 Udai Singh (b. ... - d. 1720)
- 1720 - 1735 Ugar Singh
- 1735 - 1794 Raj Singh (b. 1735 - d. 1794)
- 1794 - 1808 Jit Singh (b. 1775 - d. 1808)
- 1808 - 1844 Charhat Singh (b. 1803 - d. 1844)
- 1844 - 1870 Shri Singh (b. 1839 - d. 1870)
- 1870 - Apr 1873 Gopal Singh (b. 18... - d. 1893)
- 17 Apr 1873 – 22 Jan 1904 Sham Singh (b. 1866 - d. 1905)
- 22 Jan 1904 – 22 Sep 1919 Bhuri Singh (b. 1869 - d. 1919)
- 22 Sep 1919 - 7 Dec 1935 Ram Singh (b. 1890 - d. 1935)
- 7 Dec 1935 – 15 Aug 1947 Tikka Lakshman Singh (b. 1924 - d. 1971)[7]
Demographics
Religion
| Religion | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Hinduism |
155,028 | 91.78% |
| Islam |
12,318 | 7.29% |
| Christianity |
150 | 0.09% |
| Sikhism |
107 | 0.06% |
| Others[lower-alpha 2] | 1,305 | 0.77% |
| Total Population | 168,908 | 100% |
Further reading
- The Princely and Noble Families of the Former Indian Empire: Himachal Pradesh V. 1, by Mark Brentnall. Published by Indus Publishing, 2006. ISBN 81-7387-163-9.
Notes
- Including Ad-Dharmis
- Including Jainism, Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Tribals, others, or not stated
References
- or "6th century" https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V10_136.gif
- or "6th century" https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V10_136.gif
- "Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 10, page 130 -- Imperial Gazetteer of India -- Digital South Asia Library". Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- Hindu Hill Kingdoms Archived 30 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine V&A Museum.
- "Indian Princely States A-J". Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- Abhinay Rathore. "Chamba". Rajput Provinces of India. Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- "Indian states before 1947 A-J". Retrieved 11 March 2016.
- "CENSUS OF INDIA, 1941 VOLUME VI PUNJAB PROVINCE". Retrieved 16 January 2023.
External links
 Media related to Chamba State at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chamba State at Wikimedia Commons- . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.