Central Bavarian
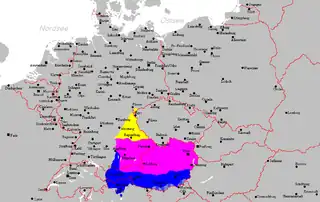
Central or Middle Bavarian form a subgroup of Bavarian dialects in large parts of Austria and the German state of Bavaria along the Danube river, on the northern side of the Eastern Alps. They are spoken in the 'Old Bavarian' regions of Upper Bavaria (with Munich (see Munich German)), Lower Bavaria and in the adjacent parts of the Upper Palatinate region around Regensburg, in Upper and Lower Austria, in Vienna (see Viennese German), in the state of Salzburg, as well as in the northern and eastern parts of Styria and Burgenland. Before 1945 and the expulsions of the Germans, it was also spoken in Hungary and southern Bohemia and Moravia.[2] It also influenced Austrian German.
| Central Bavarian | |
|---|---|
| Middle Bavarian; Mittelbairisch | |
| Native to | Germany (Upper and Lower Bavaria) Austria (Upper and Lower Austria, Salzburg, Styria, Burgenland) |
| Latin (German alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | cent1967 |
 | |
Differences
There are noticeable differences in the language within the group, but changes occur along a west-east dialect continuum on both sides of the historic border of the Bavarian stem duchy with the later Duchy of Austria. That means that the distinct languages of Vienna and Munich are very different from each other, but the dialects of any two neighbouring towns in between will be quite similar. However, due to influences of the corresponding political centres, discontinuous change is nowadays noticeable along the national border between Austria and Germany. Generally, Viennese has some characteristics differentiating it from other Bavarian dialects due to the influence of languages spoken by people moving to Vienna from many areas of Austria-Hungary during the 19th century.
Characteristics
A characteristic of Central Bavarian is the vocalization of l and r after e or i. E.g. the standard German viel becomes either vui (in Western Central Bavarian) or vüü (in Eastern Central Bavarian). The border between the western and eastern subgroups roughly coincides with the border between Bavaria and Austria.
In all subgroups, hard consonants such as p, t, k are softened to become b, d, g.
See also
References
- Ethnologue entry
- Kurt Gustav Goblirsch, Consonant Strength in Upper German Dialects, John Benjamins Publishing Company 2012 as NOWELE Supplement Series vol. 10 (originally Odense University Press 1994), p. 23