Chemin du Roy
The Chemin du Roy (pronounced [ʃəmẽ d͡zʏ ʁwɑ]; French for "King's Highway" or "King's Road") is a historic road along the north shore of the St. Lawrence River in Quebec. The road begins in Repentigny and extends almost 280 kilometres (170 mi) eastward towards Quebec City, its eastern terminus. Most of the Chemin du Roy today follows along the present-day Quebec Route 138. The modern expressway that replaces both Route 138 and the Chemin du Roy through most of its course is Quebec Autoroute 40.
_2020_03_06_018.jpg.webp)

History

In 1706, the Conseil supérieur (Grand Council) of New France decreed that a road be built to connect the houses along the north shore of the St. Lawrence River, between Quebec City and Montreal.[1] Work began in 1731, under the supervision of Grand Voyer (senior road surveyor) Eustache Lanouiller de Boisclerc, and was completed in 1737. Upon completion, the Chemin du Roy was 7.4 metres (24 ft) wide, over 280 kilometres (170 mi) long, and crossed 37 seignories. The Chemin du Roy was the longest road in existence at the time in North America north of Mexico.
In 1910, the portion of the Chemin du Roy on Montreal Island was renamed by the District and County of Montreal as Gouin Boulevard.[1] It is no longer considered part of the historic route and does not feature the "Chemin du Roy" route markers that the tourist route now is signed with.
Gallery photos
Road
Est to West, at the foot of the Laurentians, an eye on the St. Lawrence River
 Route marker, Quebec City
Route marker, Quebec City Neuville, Autun harvest
Neuville, Autun harvest Rivière du Moulin and Vieux moulin Hamelin, Grondines
Rivière du Moulin and Vieux moulin Hamelin, Grondines Ste-Anne-de-la-Perade, spring flood
Ste-Anne-de-la-Perade, spring flood Batiscan, sunrise
Batiscan, sunrise_-_Rue_Notre_Dame_016.jpg.webp) Champlain, Crossroads
Champlain, Crossroads Trois-Rivières, 1993
Trois-Rivières, 1993
Flora
Wild plants in ditches and roadsides
 Cichorium intybus L. ― Chicory.
Cichorium intybus L. ― Chicory. Typha latifolia L. — Broad-leaved cattail.
Typha latifolia L. — Broad-leaved cattail. Melilotus alba Desr. — White sweet-clover.
Melilotus alba Desr. — White sweet-clover. Trifolium arvense L. — Trèfle des champs.
Trifolium arvense L. — Trèfle des champs. Iris versicolor L. — Iris versicolore.
Iris versicolor L. — Iris versicolore.
Communities
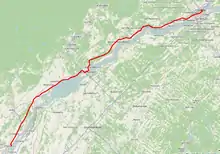
- Modern signed route
- Repentigny (western terminus)
- Saint-Sulpice
- L'Assomption
- Lavaltrie
- Lanoraie
- Sainte-Geneviève-de-Berthier
- Berthierville
- Saint-Cuthbert
- Saint-Barthélemy
- Maskinongé
- Louiseville
- Yamachiche
- Trois-Rivières
- Champlain
- Batiscan
- Sainte-Anne-de-la-Pérade
- Deschambault-Grondines
- Portneuf
- Cap-Santé
- Donnacona
- Neuville
- Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures
- Quebec City (eastern terminus)
References
- Roger Lagacé (16 December 2014). "Du chemin du Roy au boulevard Gouin". Le Guide de Montréal-Nord (in French). Journal Métro de Montréal ("Metro").