Cholesterolosis of gallbladder
In surgical pathology, strawberry gallbladder, more formally cholesterolosis of the gallbladder and gallbladder cholesterolosis, is a change in the gallbladder wall due to excess cholesterol.[1]
| Cholesterolosis of gallbladder | |
|---|---|
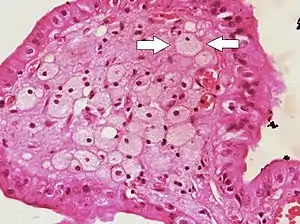 | |
| Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder, with an annotated foam cell. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
The name strawberry gallbladder comes from the typically stippled appearance of the mucosal surface on gross examination, which resembles a strawberry. Cholesterolosis results from abnormal deposits of cholesterol esters in macrophages within the lamina propria (foam cells) and in mucosal epithelium. The gallbladder may be affected in a patchy localized form or in a diffuse form. The diffuse form macroscopically appears as a bright red mucosa with yellow mottling (due to lipid), hence the term strawberry gallbladder. It is not tied to cholelithiasis (gallstones) or cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder).[2]
Additional images
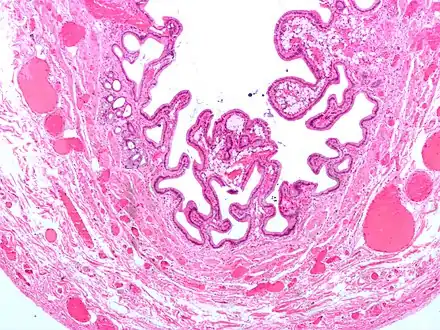 Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder
Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder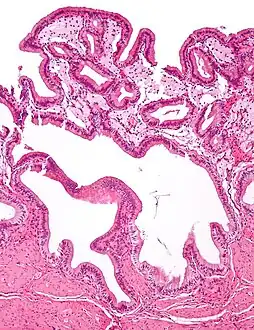 Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder
Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder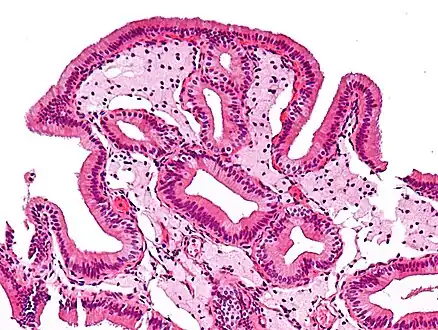 Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder
Micrograph of cholesterolosis of the gallbladder
References
- Strawberry gallbladder - cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk.
- "Cholesterolosis of the Gall Bladder".