Circular rampart
A circular rampart (German: Ringwall)[1] is an embankment built in the shape of a circle that was used as part of the defences for a military fortification, hill fort or refuge, or was built for religious purposes or as a place of gathering.
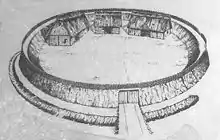
The period during which these structures were built ranged from the Neolithic to the Middle Ages.
Construction
The key feature of a circular rampart is that the embankment formed the primary element of the defensive fortification.[2] It can be constructed in various ways: as a simple earth embankment, as a wood and earth structure, or as a wall. Circular ramparts usually have a moat or ditch in front of them; the embankment can be enhanced with a wooden palisade. They are mostly found on lowlands, but sometimes encircle the summit of a hill.[2] Often several concentric rings were built, which produced a more effective defensive position against attackers.[2] The interior of such sites often shows evidence of buildings such as halls, barns, and other secondary structures.
Locations


Circular ramparts are found in north and western Europe, for example, in Denmark, Estonia, Sweden, Germany, Great Britain, Belgium and the Netherlands; in central Europe, in Austria and Switzerland; in southeastern Europe in Romania, Moldova and Ukraine;[3] and also in the United States.[4] They are often hidden in woods and discovered by aerial photography. Archaeological profiles through the defences and excavations of the interior enable analysis of the period the site was occupied, the pottery used and the type of food consumed.
Notable circular ramparts

- Aggersborg, near Aggersund, Denmark
- Circular rampart of Burg, near Celle, Lower Saxony, Germany
- The Donnersberg, near Rockenhausen, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany
- Castle Dore, Cornwall, England
- Fyrkat, Denmark
- Gråborg, built in stages between years 500–1100, Öland, Sweden
- The Heidenmauer near Bad Dürkheim, Germany
- Nanih Waiya, a Choctaw mound, Winston County, USA
- The circular rampart at Old Basing, Hampshire, England
- Celtic circular wall of Otzenhausen, Saarland, Germany
- Saxon rampart on the Marienberg near Nordstemmen, Germany
- Varbola Stronghold largest circular rampart fortress built in Estonia (10th – 12th century)
- Viking ring fortress of Trelleborg, Sweden
See also
- Ringfort – Circular fortified settlements found in Northern Europe
- Ringwork – Form of fortified defensive structure
- Viking ring fortress – Type of circular fort built in Scandinavia in the Viking Age
References
- Comité International d'Histoire de l'Art (1996) Burgen und Feste Plätze/Chateaux-forts et places fortes/Castles and Fortified Places, Munich: De Gruyter, p. 236.
- Radig (1935), pp. 9–10.
- Gimbutas, Marija (1982), "Old Europe in the Fifth Millennium B.C.: The European Situation on the Arrival of Indo-Europeans", in Edgar C. Polomé (ed.), The Indo-Europeans in the Fourth and Third Millennia, Ann Arbor, USA: Karoma Publishers, pp. 1–60, ISBN 0-89720-041-1
- Shoemaker, Nancy, American Indians, WileyBlackwell, 1 October 2000, ISBN 0-631-21995-1
Literature
- Radig, Dr. Werner (1935). "Die Burgwälle Ostthüringens" in Die Fundpflege. Yr 3, Issue 2/3 (June 1935), pp. 9–15.
- Orser, Charles E., Encyclopedia of historical archaeology, Routledge, 11 April 2002, ISBN 0-415-21544-7
