Wire obstacle
In the military science of fortification, wire obstacles are defensive obstacles made from barbed wire, barbed tape or concertina wire. They are designed to disrupt, delay and generally slow down an attacking enemy. During the time that the attackers are slowed by the wire obstacle (or possibly deliberately channelled into killing zones, or both) they are easy to target with machine gun and artillery fire. Depending on the requirements and available resources, wire obstacles may range from a simple barbed wire fence in front of a defensive position, to elaborate patterns of fences, concertinas, "dragon's teeth" (which serve a similar purpose as wire obstacles, but for combat vehicles instead) and minefields (both anti-personnel and anti-armor) hundreds of metres thick.

.jpg.webp)
One example is "low wire entanglement", which consists of irregularly placed stakes that have been driven into the ground with only some 15 cm (six inches) showing. The barbed wire is then wrapped and tightened on to these. An enemy combatant running through the barrier, which is difficult to see, is apt to trip and get caught.
History

Wire obstacles were used by Union Army general Ambrose Burnside during the Battle of Fort Sanders in the Knoxville campaign of the American Civil War, when telegraph wire was strung between tree stumps 30 to 80 yards in front of one part of the Union line. The Royal Danish Army also used wire fences in front of its Danevirke fortifications during the Second Schleswig War. They first saw significant military use by British forces during the Second Boer War, and reached the pinnacle of visibility during World War I where they indirectly, together with machine guns, were responsible for many (although not the majority of) casualties in the trench warfare that dominated that conflict. Wire obstacles served to magnify the substantial advantage that the repeating rifle and rapid-firing artillery, along with machine guns, had given to the defending side in the new era of warfare.
World War I entanglements could in some places be tens of metres thick and several metres deep, with the entire space filled with a random, tangled mass of barbed wire. Entanglements were often not created deliberately, but by pushing together the mess of wire formed when conventional barbed wire fences had been damaged by artillery shells. Whenever there was time and opportunity to plan and emplace wire obstacles during World War I, it was standard practice to deploy designs that would channel and concentrate attacking troops, through avenues of approach, herding them like cattle into designated killing zones i.e. fixing multiple screw pickets of wire running diagonally, away from the protected zone. This meant that a belt-fed machine-gun such as the Maschinengewehr 08 sited along that diagonal line had easy targets to enfilade when attacking troops were blocked from advancing by the wire and then massed together in a line.
Another method was to deliberately leave attractive-looking gaps in wire obstacles to give the appearance of a weak link in the defences. Such gaps were designed to act like a funnel, luring attacking troops through the opening and straight into the concentrated direct and enfilade fire of different machine gun emplacements. Because multiple water-cooled machine-guns such as the Vickers gun were used, continuous fire could be sustained for hours at a time if required. Methods for soldiers to face this threat were a small wheeled steel plate that was slowly pushed forward in front of the soldier to shield them from bullet fire as they crawled, shielded machine gun carts, the MacAdam Shield Shovel or systems like the mobile personnel shield among others. When the obstacle was reached, access holes in the shield allowed the attacking soldier to cut away at the wire obstacle with pliers from behind the protection of the armored shield.[1]
Stormtrooper platoons included ballistic shields in their equipment list, as infiltration was one of their specialities. Relatively elaborate obstacles were also used in some phases of the Korean War, and continue to be used on the Korean Demilitarized Zone, and a few other borders. However the more fluid nature of modern war means that most obstacles used today are relatively simple, temporary barriers. Tanks and light armored vehicles can generally flatten unmined wire obstacles, although the wire can become entangled in the tracks and immobilize the vehicle. This can also occur to wheeled vehicles once the wire becomes wrapped around the axle. Wire obstacles can also be breached by intense artillery shelling or Bangalore torpedoes.
Enhanced effectiveness
The effectiveness of any wire obstacle is greatly increased by planting anti-tank and blast antipersonnel mines in and around it. Additionally, connecting bounding anti-personnel mines (e.g. the PROM-1) to the obstacle with tripwires has the effect of booby-trapping the obstacle itself, hindering attempts to clear it. Dummy tripwires can be added to cause further confusion. If anti-personnel mines are unavailable, it is very easy to connect hand-grenades to the wire using trip-wires. If the use of lethal explosive devices is deemed to be unsuitable, it is easy to emplace tripflares in and around the wire obstacle in order to make night-time infiltration harder.
Gallery
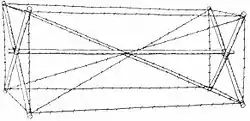 The "knife rest" or "Spanish rider" is a modern wire obstacle functionally similar to the cheval de frise, and sometimes called that.
The "knife rest" or "Spanish rider" is a modern wire obstacle functionally similar to the cheval de frise, and sometimes called that. Triple concertina wire fence.
Triple concertina wire fence. A complex obstacle belt of low wire entanglement backed by a double apron fence. Both obstacles have movable openings that can be blocked with knife rests.
A complex obstacle belt of low wire entanglement backed by a double apron fence. Both obstacles have movable openings that can be blocked with knife rests. The deadly result of enfilade fire during the Dieppe Raid of 1942: dead Canadian soldiers lie where they fell. Trapped between the beach and fortified sea wall (covered with barbed wire), they made easy targets for MG 34 machineguns in a German bunker. The bunker firing slit is visible in the distance, just above the German soldier's head.
The deadly result of enfilade fire during the Dieppe Raid of 1942: dead Canadian soldiers lie where they fell. Trapped between the beach and fortified sea wall (covered with barbed wire), they made easy targets for MG 34 machineguns in a German bunker. The bunker firing slit is visible in the distance, just above the German soldier's head.
References
- Popular Science. Bonnier Corporation.