Cleveland Night Express
The Cleveland Night Express was an American named train of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) on its route between Baltimore, Maryland, and Cleveland, Ohio, with major station stops in Washington, D.C., and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The B&O inaugurated the Cleveland Night Express in 1915. Its discontinuation in 1962 marked the end of B&O passenger service to Cleveland.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Service type | Inter-city rail |
| Status | Discontinued |
| Locale | Mid-West/Mid-Atlantic |
| First service | 1915 |
| Last service | 1962 |
| Former operator(s) | Baltimore and Ohio Railroad |
| Route | |
| Termini | Baltimore, Maryland Cleveland, Ohio |
| Distance travelled | 194.2 miles (312.5 km) (1960) |
| Service frequency | Daily |
| Train number(s) | 17 (westbound) 18 (eastbound) |
| On-board services | |
| Seating arrangements | Reclining seat coach |
| Sleeping arrangements | Roomettes, double bedrooms (1960) |
| Catering facilities | Lounge car |
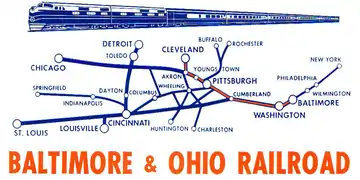
History
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was chartered in 1827 and grew to be one of the largest passenger railways in the United States, often by acquiring other, smaller railroads. In Cleveland the B&O purchased two local companies, the Cleveland Lorain & Wheeling Railroad and the Cleveland, Terminal & Valley Railway in 1915.[1]
From 1915 until 1962 the B&O provided overnight sleeping car service between Baltimore and Cleveland on the Cleveland Night Express. After June 1934, the Cleveland Night Express used Cleveland's Union Terminal as its passenger station. At times in this period, the train was called the Baltimore-Washington-Cleveland Express westbound and Cleveland-Washington-Baltimore Express.[2]
On February 7, 1956, the train had four passenger cars overturn in a sudden rockslide near McKeesport, Pennsylvania, no deaths occurred with only one injured.[3]
Decline and end of the train
In 1962, as railroad passenger traffic was declining nationwide, the B&O discontinued the Cleveland Night Express on December 7, 1962, which ended all B&O passenger service to Ohio's largest city, Cleveland.[1]
Stations
| Station | State |
|---|---|
| Washington (Union Station) | District of Columbia |
| Harpers Ferry (B&O station) | West Virginia |
| Martinsburg | |
| Cumberland | Maryland |
| Connellsville | Pennsylvania |
| Pittsburgh (P&L.E. Station) | |
| New Castle | |
| Youngstown (B&O Station) | Ohio |
| Akron (Union Station) | |
| Cleveland (Cleveland Union Terminal) |
Schedule and equipment
In 1961, the westbound Cleveland Night Express departed Union Station (Washington, D.C.) at 9:20 p.m. daily as train No. 17, arriving in Cleveland the following morning at 8:45 a.m., equipped with a Pullman sleeping car, coaches, and a lounge car having a snack bar serving what B&O described in its timetable as a "light breakfast" prior to arrival.[4]
The westbound Cleveland Night Express train No. 17 made the following principal station stops, with a connecting Budd Rail Diesel Car departing at 8:10 p.m. from Baltimore, Maryland:
| City | Departure time |
|---|---|
| Washington, D.C. (Union Station) | 9:20 p.m. |
| Silver Spring, Maryland (B&O station) | 9:35 p.m. |
| Harpers Ferry, West Virginia | 10:29 p.m. |
| Martinsburg, West Virginia | 11:20 p.m. |
| Cumberland, Maryland | 1:05 a.m. |
| Connellsville, Pennsylvania | 3:35 a.m. |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (P&L.E. Station) | 5:15 a.m. |
| New Castle, Pa. | 6:28 a.m. |
| Youngstown, Ohio (B&O Station) | 6:43 a.m. |
| Akron, Ohio (Union Station) | 7:45 a.m. |
| Cleveland, Ohio (Cleveland Union Terminal) | 8:45 a.m. |
| source: B&O timetable, October 29, 1961[4] | |
References
- Vantassel, David D.; John J. Grabowski. "The BALTIMORE & OHIO RAILROAD". The Encyclopedia of Cleveland History. Archived from the original on 2006-09-08. Retrieved 2007-11-19.
- Official Guide of the Railways, May 1946, Baltimore & Ohio section
- Place, John (Feb 7, 1981). "It Happened Feb. 7". The Pittsburgh Press. p. A-2.
- Baltimore & Ohio Railroad — Passenger Train Schedules, October 29, 1961.
