Codole Reservoir
Codole Reservoir (French: Réservoir de Codole, Lac de Codole) is a reservoir in the Haute-Corse department of France, on the island of Corsica. It supplies water for drinking and irrigation. The reservoir and its immediate surroundings are important as a biotope that offers habitat for many species of birds, reptiles and amphibians
| Codole Reservoir | |
|---|---|
 Lac de Codole viewed from Feliceto | |
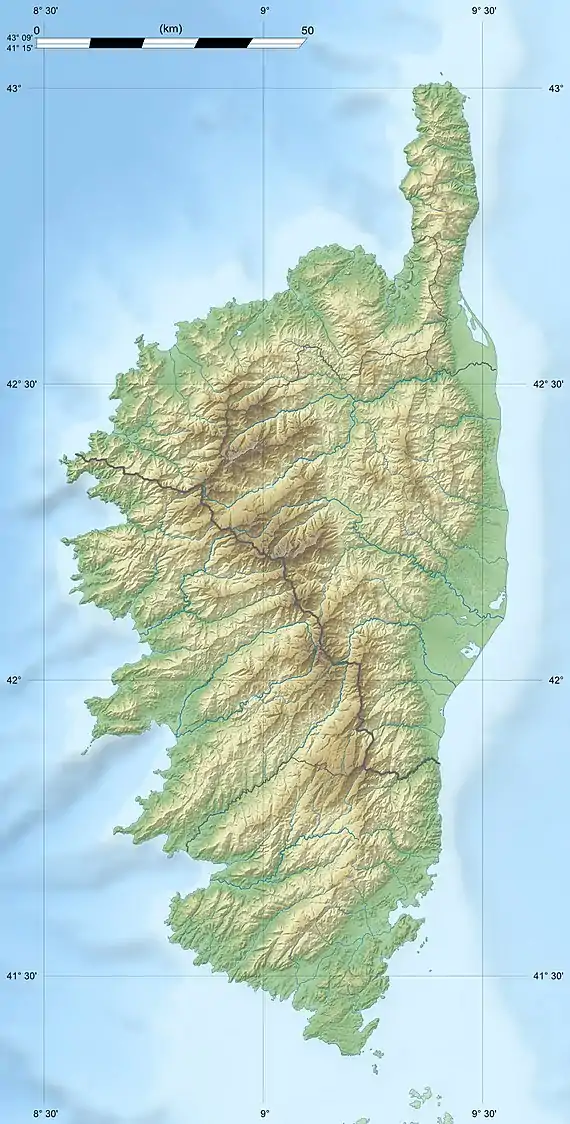 Codole Reservoir  Codole Reservoir | |
| Location | Corsica |
| Coordinates | 42°35′12″N 8°56′47″E |
| Type | Reservoir |
| Native name | Lac de Codole (French) |
| Basin countries | France |
| Surface area | 80 ha (200 acres) |
| Surface elevation | 108 m (354 ft) |
Location
The Codole Reservoir is formed by the Barrage de Codole, which dams the Fiume di Regino, a coastal river. The reservoir is to the south of L'Île-Rousse on the Mediterranean coast. The dam at the eastern end of the reservoir is in the commune of Speloncato. The southwest of the reservoir is in the commune of Feliceto, and the northwest of the reservoir is in the commune of Santa-Reparata-di-Balagna. The D113 road runs along the south shore.[1]
 Panorama from Regino
Panorama from Regino
Watershed
The reservoir is mainly fed by the 19.5 kilometres (12.1 mi) Reginu river, which rises at 1,680 metres (5,510 ft) in San Parteo, Feliceto, and has its mouth on the sea in Lozari, Belgodère. There are about 90 kilometres (56 mi) of streams in the Reginu watershed, which covers more than 110 square kilometres (42 sq mi).[2] The reservoir is supplied by a watershed of 39 square kilometres (15 sq mi).[3]
The Reginu valley has a Mediterranean climate, with little rain in the summer. It regularly has strong west or southwest winds. The landscape includes pastures, cultivated olive, almond and citrus groves, and abandoned scrub and forest.[4] Vegetation includes heather (Erica arborea), Arbutus unedo, oak forests (Quercus ilex, Quercus suber and some Quercus pubescens), lavender (Lavandula stoechas), rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis), Genista corsica and many Cistus species.[4]
Dam
The Codole dam (French: Barrage de Codole) was built in the early 1980s by the Société de Développement Agricole de la Corse (SOMIVAC) to supply water to the eastern part of the Balagne for drinking and irrigation.[5] It was commissioned in 1984. It is a rockfill dam with a height of 28 metres (92 ft) and crest length of 460 metres (1,510 ft). The crest elevation is 116 metres (381 ft). It contains 6,985,000 cubic metres (246,700,000 cu ft) of water.[3] In 1992 the Office d'Equipement Hydraulique de Corse (OEHC) took over management of water resources from SOMIVAC.[6]
_-_2021-09-07_-_3.jpg.webp) Causeway along the dam
Causeway along the dam_-_2021-09-07_-_6.jpg.webp) View from the dam
View from the dam
Lake
_-_2021-09-07_-_1.jpg.webp)
The perimeter of the lake is 5.75 kilometres (3.57 mi), with width and length of 1.2 kilometres (0.75 mi) and an area of 80 hectares (200 acres).[7] With a capacity of 6,600,000 cubic metres (230,000,000 cu ft) the reservoir is the second largest of ten on the island, apart from the Électricité de France dams. It is the largest body of water on the west coast.[5] The reservoir is full from January to May, gradually empties from June to October and then refills in November and December. Every ten years it is drained completely.[8] When fully filled the average depth is 8.1 metres (27 ft) and maximum depth is 23 metres (75 ft).[7]
Ecology
The lake is of high biological importance.[9] Its IUCN protection status is IV - Habitat or species management area, and V - Protected land or seascape.[10] It is eutrophic or hypertrophic, with a high nutrient content that favors a strong presence of cyanobacteria in the phytoplankton population.[11] The biotope offers habitat for many species of birds, reptiles and amphibians.[6] European pond turtles (Emys orbicularis) have been observed, and in 1999, an invasive turtle, the red-eared slider Trachemys scripta elegans was also discovered at the site.[12] In 1994 the Conservatoire des Espaces Naturels de Corse (CEN-Corse) and OEHC agreed to improve conditions for birds using the lake for wintering or as a stopover during migration. Actions included planting vegetation on the banks and placing artificial nests.[6]
Flora include:[13]
- bullrush (Scirpoides holoschoenus)
- common reed (Phragmites australis)
- cork oak (Quercus suber)
- downy oak (Quercus pubescens)
- Genêt de Corse (Genista corsica)
- holm oak (Quercus ilex)
- Montpellier cistus (Cistus monspeliensis)
- prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica)
- rose (Rubus) species
- Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis)
- Spanish lavender (Lavandula stoechas)
- strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo)
- tree heather (Erica arborea)
- yellow fleabane (Dittrichia viscosa)
Mammals include:[13]
- black rat (Rattus rattus)
- Etruscan shrew (Suncus etruscus)
- European hare (Lepus europaeus)
- European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)
- European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
- lesser white-toothed shrew (Crocidura suaveolens)
- house mouse (Mus musculus)
- least weasel (Mustela nivalis)
- long-fingered bat (Myotis capaccinii)
- red fox (Vulpes vulpes)
- wild boar (Sus scrofa)
Birds include:[14]
- barn swallow (Hirundo rustica)
- blue rock thrush (Monticola solitarius)
- carrion crow (Corvus corone cornix)
- Cetti's warbler (Cettia cetti)
- cirl bunting (Emberiza cirlus)
- common blackbird (Turdus merula)
- common buzzard (Buteo buteo)
- common chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs)
- common chiffchaff (Phylloscopus collybita)
- common cuckoo (Cuculus canorus)
- common linnet (Linaria cannabina)
- common nightingale (Luscinia megarhynchos)
- common raven (Corvus corax)
- common wood pigeon (Columba palumbus)
- corn bunting (Emberiza calandra)
- Corsican finch (Carduelis corsicana)
- Eurasian blackcap (Sylvia atricapilla)
- Eurasian blue tit (Cyanistes caeruleus)
- Eurasian collared dove (Streptopelia decaocto)
- Eurasian coot (Fulica atra)
- Eurasian hoopoe (Upupa epops)
- Eurasian jay (Garrulus glandarius)
- Eurasian scops owl (Otus scops)
- Eurasian wren (Troglodytes troglodytes)
- European goldfinch (Carduelis carduelis)
- European greenfinch (Chloris chloris)
- European nightjar (Caprimulgus europaeus)
- European robin (Erithacus rubecula)
- European stonechat (Saxicola rubicola)
- European turtle dove (Streptopelia turtur)
- great spotted woodpecker (Dendrocopos major)
- great tit (Parus major)
- grey wagtail (Motacilla cinerea)
- Italian sparrow (Passer italiae)
- little ringed plover (Charadrius dubius)
- long-tailed tit (Aegithalos caudatus)
- Marmora's warbler (Sylvia sarda)
- meadow pipit (Anthus pratensis)
- red kite (Milvus milvus)
- red-backed shrike (Lanius collurio)
- red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa)
- Sardinian warbler (Sylvia melanocephala)
- spotless starling (Sturnus unicolor)
- white wagtail (Motacilla alba)
- willow warbler (Phylloscopus trochilus)
- woodchat shrike (Lanius senator)
- woodlark (Lullula arborea)
- yellow-legged gull (Larus michahellis)
Reptiles include:[15]
- Barred grass snake (Natrix helvetica corsa)
- European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis)
- Green whip snake (Hierophis viridiflavus)
- Hermann's tortoise (Testudo hermanni)
- Red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans)
- Tyrrhenian wall lizard (Podarcis tiliguerta)
Amphibians include:[16]
- European green toad (Bufotes viridis)
- European tree frog (Hyla arborea)
- Pool frog (Pelophylax lessonae) bergeri
- Tyrrhenian painted frog (Discoglossus sardus)
Fish include:[16]
- Brown trout (Salmo trutta)
- Common roach (Rutilus rutilus)
- Common rudd (Scardinius erythrophthalmus)
- European eel (Anguilla anguilla)
- Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis)
Notes
- Way: Lac de Codole (28890019).
- Levadoux 2005, p. 6.
- Corse : Barrage de Codole, CFBR.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 7.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 2.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 3.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 9.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 10.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, p. 1.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, p. 2.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 11.
- Levadoux 2005, p. 5.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, p. 3.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, pp. 4–6.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, p. 6.
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole, p. 7.
Sources
- Corse : Barrage de Codole (in French), CFBR Comité Français des Barrages et Réservoirs, retrieved 2021-12-12
- FR834COR352 - Lac de barrage de Codole (in French), Initiative PIM, Office de l’Environnement de la Corse (OEC), 2019, retrieved 2021-12-31
- Levadoux, Damien (December 2005), Plan d'amenagement des berges du plan d'eau de Codole (in French), AAPNRC/CEN Corse, retrieved 2021-12-13
- "Way: Lac de Codole (28890019)", OpenStreetMap, retrieved 2021-12-12

