Concrete pump
A concrete pump is a machine used for transferring liquid concrete by pumping. There are different types of concrete pumps.


A common type of concrete pump for large scale construction projects is known as a boom concrete pump, because it uses a remote-controlled articulating robotic arm (called a boom) to place concrete accurately. It is attached to a truck or a semi-trailer. Boom pumps are capable of pumping at very high volumes and are less labor intensive to operate when compared to line or other types of concrete pumps.
The second main type of concrete pump, commonly referred to as a "line pump" or trailer-mounted concrete pump, is either mounted on a truck or placed on a trailer. This pump requires steel or flexible concrete placing hoses to be manually attached to the outlet of the machine and feed the concrete to the place of application. The length of the hoses varies, typical are 10’, 12.5’, 25’ and 50’ long hoses, depending on the diameter. Due to their lower pump volume, line pumps are used for smaller volume concrete placing applications such as swimming pools, sidewalks, single family home concrete slabs and most ground slabs.
There are also skid mounted and rail mounted concrete pumps, but these are uncommon and only used on specialized jobsites such as mines and tunnels.
History
Until the early 20th century, concrete was mixed on the job site and transported from the cement mixer to the formwork, either in wheelbarrows or in buckets lifted by cranes. This required a lot of time and labor. In 1927, the German engineers Max Giese and Fritz Hull came upon the idea of pumping concrete through pipes. They pumped concrete to a height of 38 meters (125 ft) and a distance of 120 meters (130 yd). Shortly after, a concrete pump was patented in Holland in 1932 by Jacob Cornelius Kweimn (Jacobus Cornelius Kooijman). This patent incorporated the developer's previous German patent.[1]
Mechanism
Concrete pump designers face many challenges because concrete is heavy, viscous, abrasive, contains pieces of hard rock, and solidifies if not kept moving.
Usually, piston pumps are used, because they can produce hundreds of atmospheres of pressure. Such piston-style pumps can push cylinders of heterogenous concrete mixes (aggregate + cement).[2] At present, double-piston pumps are predominantly used, which are hydraulically driven by electric or diesel engines using oil pumps.[3] The pressure pistons are hydraulically connected to each other through the drive cylinders and operate in a two-stroke mode.
For lower pressures peristaltic pumps are common.
How it works
The return pressure piston of one pressure cylinder creates a vacuum, the medium from the feed funnel is sucked into the cylinder. At the same time, the advancing delivery piston pushes the contents of the other delivery cylinder through the transfer tube into the delivery line. At the end of the stroke, the pump switches, i.e., the transfer tube turns in front of the other filled pressure cylinders, and the pressure pistons change their movement direction.[4]
Concrete pump drives are now exclusively hydraulic, so control options vary between individual manufacturers. Each system has certain advantages and disadvantages.[5]
Important performance factors are:
- discharge pressure;
- machine weight;
- price;
- system complexity.
For these reasons, many options have existed side by side for a long time. Nowadays, fluid pressures of up to 400 bar and flow rates of up to 200 m3/h can be achieved, while using piston-type pumps.
Example of pump performance
To illustrate, below are data on a typical concrete sample pump BRF 42.14 H:
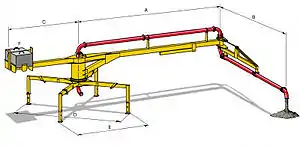
- Vertical reach of boom: 41.9 meters (137 ft).
- Horizontal reach of boom: 38.0 meters (124.7 ft)
- Pumping rate: 30 cubic meters per hour (39 cuyd/h).
- Concrete pressure: 112 bar (11,200 kPa; 1,624 psi).
- Cylinder length: 2,100 mm (82.677 in).
- Cylinder diameter: 210 mm (8.268 in).
- Number of substitutions of strokes per minute: 27.
- Number of outriggers legs: 4.
- Maximum Head: .
Gallery
 Construction site with concrete pump
Construction site with concrete pump A Putzmeister concrete pump in Germany in 1985
A Putzmeister concrete pump in Germany in 1985 Concrete pump folded for transport
Concrete pump folded for transport Boom concrete pump
Boom concrete pump.jpg.webp) Concrete pump
Concrete pump Putzmeister brand positive displacement mortar and plaster pump
Putzmeister brand positive displacement mortar and plaster pump Photo showing a concrete pump working a large foundation pour, showing deployed outriggers, rebar mats, and concrete mixer delivering concrete.
Photo showing a concrete pump working a large foundation pour, showing deployed outriggers, rebar mats, and concrete mixer delivering concrete..jpg.webp) Fully deployed concrete pump, showing outriggers and boom in use while receiving concrete.
Fully deployed concrete pump, showing outriggers and boom in use while receiving concrete.
See also
- High-density solids pump - concrete pump technology in general
- Concrete mixing transport truck
References
- Illingworth J.R. (1972). Movement and Distribution of Concrete. McGraw-Hill. p. 132. ISBN 978-0070942363. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- Intex Pool Pumps
- "How a gear pump works". web.mit.edu. Retrieved July 12, 2022.
- "Piston-type pumps". concretepumpingauckland.co.nz. Retrieved July 12, 2022.
- "Concrete pumping: advantages and disadvantages". hpdconsult.com. Retrieved July 12, 2022.