Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace.
Construction
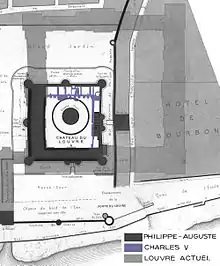
Between 1190 and 1215, Philip Augustus built the Wall of Philip II Augustus around Paris to protect the capital from the English. To reinforce this enclosure on the western side, he built the first incarnation of the Louvre, a large fortress with four high walls protected by a moat, towers, and a dungeon.
Under King Charles V of France (1364-1380), with the population of Paris increasing, Paris spread well beyond the Philip Augustus wall. The king built a new enclosure encompassing the new quarters. As the Louvre Castle was now inside the new city walls, it lost much of its military value. The king renovated the castle to make it more comfortable, installing numerous windows, adding chimneys, statues, turrets and gardens.
After returning from a two-year captivity in Italy and Spain following his defeat at Pavia in 1524, King Francis I of France wanted to transform the old castle of the Louvre into a Renaissance style palace, like those he encountered during his captivity. In 1528, he ordered the demolition of the Grosse Tour (Great Tower), which had served as a keep. This took four months and the tower was replaced by a moat serving the main court of the castle. In 1546, the King asked architect Pierre Lescot and sculptor Jean Goujon to further renovate the castle.

After Francis I's death, his son Henri II (1547–1559) continued the work and oversaw demolition of the west wall, which he replaced with a Renaissance palace of the same length between December 1546 and March 1549. This area, the current Lescot Wing, hosted the Salle des Gardes (Hall of the Guards), today known as the Salle des Caryatides, a room for events which also serves as a ballroom. Many historical events took place there, such as the wedding of King Henri IV, an episode of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre, the funeral wake of Henry IV, and the first performance of a Molière play for King Louis XIV on October 16, 1658.

Henry II then demolished the southern wall to pave the way for the construction of the Pavillon du Roi from 1553 to 1556, located at the junction of the south and west wings. At this stage, the building was very heterogeneous since two wings were in the style of a Renaissance palace, while the other two remained in the style of a medieval castle with walls, battlements, and towers.
Construction on this court paused as Queen Catherine de' Medici focused on the Tuileries Palace, while Henry IV built the Grande Galerie along the River Seine, also known as the Grande Galerie du Bord de l'Eau (Grand Waterside Gallery), which linked the Louvre and the Tuileries. He also planned to quadruple the size of the courtyard of the Louvre Castle by demolishing the old walls and extending the existing Renaissance wings.

Louis XIII demolished the north wall of the castle in 1624. Since the Lescot Wing had been built for the small courtyard of the original castle, it was not easy to integrate it into a courtyard with sides twice as long. The new architect, Jacques Lemercier, duplicated this wing to the north, the present Lemercier Wing (1636), and installed a taller pavilion between the two, the Pavillon de l'Horloge.
Louis XIV had the east wall demolished and renovated by architect Louis Le Vau. These last two walls to be demolished (north and east) were simply razed and the ditches filled. Thus, their foundations remained intact and were rediscovered during excavations of the courtyard in 1866. During the construction of the Grand Louvre, basement-level galleries were created for exhibiting the artefacts and architectural remnants of the Medieval Louvre.

Louis XIV also had the length of the south wing doubled and built the north wing. Three sides of the courtyard were then in place. The yet to be built east wing was very important as it faced the city with other buildings nearby. This would be the new main entrance to the Louvre. After a contest launched by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, the king decided in 1665 to have the Louvre Colonnade built outside on the east by Claude Perrault and Louis le Vau. As the king did not have the power of expropriation, the work dragged on because it was necessary to buy the land and the houses in front of the future colonnade to clear the view. Moreover, the king's interest moved to the Palace of Versailles after 1674.
Louis XIV also decided to double the width of the south wing in 1668. This is why today we have two series of rooms: on the courtyard side, the rooms of the Charles X Museum; on the side near the river, the rooms of the Campana Gallery (for the display of Greek pottery). The river side of the south wing was not completed until a century later.
After the royal court moved to Versailles, the unfinished buildings hosted artists. Heterogeneous constructions were erected in the courtyard.
After its abandonment and degradation during the Revolution, Louis XVIII restored the Louvre and put his monogram (two L's of stick characters turning their backs) on the three exterior facades of the Cour Carrée (including the colonnade), despite only restoring them.
- The transformation steps :


Description

The buildings form a square of about 160 meters on each side. It consists of eight wings punctuated with eight pavilions. Starting at the northwest corner and going clockwise, the names of the eight pavilions are:
- Pavillon de Beauvais (at the northwest corner)
- Pavillon de Marengo (between the two north wings)
- Pavillon Nord-Est (at the northeast corner)
- Pavillon Central or Pavillon Saint-Germain l'Auxerrois (between the two east wings, with the Colonnade on the east side)
- Pavillon Sud-Est (at the southeast corner)
- Pavillon des Arts (between the two south wings)
- Pavillon du Roi or King's Pavilion (at the southwest corner)
- Pavillon Sully, also referred to as the Pavillon de l'Horloge (between the two west wings). It is recognisable by its clock, its four groups of monumental caryatids, its friezes of children, and its high domed roof, the prototype for all the domes of the Louvre, to maintain the harmony sought by successive architects of the Louvre.
The two wings on either side of the Sully Pavilion are named:
- Lescot Wing, built from 1546 to 1558, leading to the King's Pavilion to the south
- Lemercier Wing, built in 1639, leading to the Beauvais Pavilion to the north
At the center of the Cour Carrée, there is a fountain.
Although the buildings were built over a period of 250 years, they show great homogeneity. The ground floor and the two floors have successions of windows, bas-reliefs, and statues in niches. The French sovereigns left their monograms on the parts they built. Those of Henri II, Charles IX, Henri IV, Louis XIII and Louis XIV can easily be identified and they help track the history of construction.
The Republic did not want to be outdone and installed a rooster in the pediment of the west facade of the central pavilion of the east wing.

Example of sculptures
All the reliefs and statues in the Cour Carrée represent specific allegories or figures.
Here is the example of the first window on the left of the second floor of the Lemercier wing on the Pavillon de l'Horloge. Above the window, is an allegorical figure of Law. Then, at window level from left to right: Moses with the Ten Commandments; the Egyptian goddess Isis with a sistrum; the Inca emperor Manco Cápac with the sun representing his father, the sun god Inti; and Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome.
References
External links
- http://www.francebalade.com/paris/louvre.htm (in English and French)
- Base Mérimée: Palais du Louvre et jardin des Tuileries, Ministère français de la Culture. (in French)
- A virtual visit of the Louvre (in English)
- Panoramic view of the pyramid and the Cour Napoléon (in French)
