Cravens
Cravens Railway Carriage and Wagon Company Limited was a railway rolling stock builder in the Darnall district of Sheffield, England. Founded by brothers named Craven and known as Craven Brothers, later Cravens Limited, it remained a family business until John Brown & Company acquired a controlling shareholding in 1919. Its name was changed back to Cravens Limited in 1954 when it finally became a wholly owned subsidiary of John Brown.[1]
 | |
| Type | Private |
|---|---|
| Industry | Railway Engineering |
| Founded | pre 1900 |
| Defunct | 1966 |
| Fate | Acquired |
| Successor | Metropolitan-Cammell |
| Headquarters | Sheffield, England, UK |
| Products | carriages , locomotives |
Ownership
Craven Brothers was a British engineering firm started in 1853 by brothers William and John Craven that built large machine tools for railway and engineering workshops and later workshop and railway cranes. Two Sheffield-raised Craven brothers, sons of a Wakefield mason and builders themselves began to make railway wagons in 1866[2] when railway companies also pulled wagons, particularly purpose-built wagons, for other owners. A third brother, previously an architect and timber merchant, soon joined them.[note 1]
John Brown & Company acquired a substantial interest in Craven's in 1919 "not only as in itself a sound investment but as a means of ensuring a friendly customer for much of the company's product in railway material".[3][4] By 1965 John Brown found that Craven's major home customer, British Rail, was also its competitor both at home and in export markets and elected to withdraw.[5]
In 1928, Craven Brothers acquired the machine tool interests of Armstrong Whitworth, Joshua Buckton & Co and Thomas Shanks & Co. The crane division was sold to Herbert Morris of Loughborough in 1928, with the crane work being transferred to Loughborough in 1931. In 1939, the company purchased the Victoria Works in Saxon Street, Denton from Knight & Hale.
The Machine tool division at Reddish remained in business until 1966. In 1966 Metropolitan-Cammell absorbed the railway rolling stock business of Cravens. In 1967 the remaining rolling stock business switched to making shipping containers under the name Cravens Homalloy. The engineering division became Bone-Cravens and made plastic extrusion and plastic moulding machines.[6]
Premises
Their first factory was known as the Vauxhall Works, Salford. In 1857, they moved to larger premises in Osborne Street. By 1900 they required larger premises and expanded into the new Vauxhall Works in Greg Street, Reddish. Difficult trading lead to the closure of the Osborne Street site in 1920.
Products
During the 1880s London's The Times newspaper made regular reports on the state of trade throughout England and Scotland. From taking a low place in reports on Sheffield by 1890 Cravens were near the top of those reports. Published successes were: In 1883 Great Northern Company ordered 400 sets of wheels and axles.[7] In 1885 Messrs Craven Brothers of Darnall Carriage Works have completed and delivered to the Cheshire Lines Connittee 40 composite carriages for use in the Manchester expresses.[8] Cravens have built several fine dining saloons for express service and other railway carriages, wagons etc.[9] North British Railway have placed an order for 500 sets of wheels and axles.[10] The South Eastern railway have placed an order for 100 railway carriages including 50 third class. India, Argentine Republic and South America as well as Home railway companies are ordering tyres, axles, springs, buffers and other railway items.[11]
A new Palace Car, a sleeping and dining car for the Buenos Ayres Great Southern Railway Company . . . largest of it kind ever constructed in this country . . . 60 feet long 9 feet 4inches wide and 9 feet 5 inches high . . . contains a saloon and a ladies saloon as well as lavatories, bathrooms and an attendant's room . . design and drawings by Mr T F Craven.[12]
Craven's built many diagrams of coaching stock for the pre-grouping Railway companies of Great Britain, the grouped companies and for British Railways itself. They also constructed coaches for many railway companies around the world. As well as surface running stock they also built vehicles for underground railways and especially noted are the London Underground A60 Stock. With modernisation the company adapted to build diesel multiple units and electric multiple units for British Railways. One of its last orders, in 1963, was of 55 mainline carriages, broadly similar to the British Railways Mark 1 design, for the Irish railway company Córas Iompair Éireann. Another of the orders received and completed before the absorption by Metro Cammell was a royal train for Peru.
Second World War
Craven's made airframe components and maintained supply of road and rail vehicles for the Admiralty and Ministry of Supply including: limbers, gun shields, gun mountings, gun turrets, rocket ammunition racks, ammunition boxes, and components for armoured vehicles.
Asbestos sound insulation
Many employees in the railway industry in general developed diseases related to asbestos, used during the locomotive and carriage building process. These diseases include peritoneal mesothelioma, lung cancer, asbestosis, diffuse pleural thickening and other pleural abnormalities.[13] Some ex Cravens employees have been awarded significant compensation in such cases but some families received relatively small amounts of compensation.[14]
One of the methods of working employed at Craven's was shooting a wet slurry of asbestos from a pressure gun. The operators would stand under a railway car supported on large trestles and spray the asbestos slurry in a 2-inch-thick (51 mm) layer onto the underside of the railway car. This was done to provide sound insulation to the floor of the railway car prior to final assembly.
Problems with asbestos in Craven's stock continued for many years. Craven's standard stock cars 4906 to 4909 were withdrawn from service in 1975 and 1976, and the schedule for their replacement suffered severe delays due to the discovery of asbestos in some of the Driving Motor cars. Because of this, it was 1983 before all the standard stock cars were replaced.[15]
Ireland
In spring 1961 CIÉ (National Railway Company of Ireland) sought tenders for the supply of 40 new Standard Class coaches, 10 to be delivered complete, the rest "part-finished" for assembly in Inchicore, Dublin, with technical assistance from the suppliers. The £500,000 contract was awarded to Cravens of Sheffield.[16] It was reported that these new vehicles "would set a pattern for future construction of CIÉ carriage stock." The first of the Sheffield-built coaches was unloaded at the North Wall, Dublin on 3 May 1963 and taken to Inchicore for acceptance. These saw long service, the last not being withdrawn from main line service until 2006 and some are preserved by the Railway Preservation Society of Ireland.
Preserved Craven's rolling stock
Craven's trains are preserved by the Craven Heritage Train group. One carriage built by Cravens for the Metropolitan Railway in 1892 (No353) is preserved by the London Transport Museum. Another built in 1900 is preserved on the Bluebell Railway in Sussex. Ex-Iarnród Éireann (which operated Ireland's railways after CIÉ was split up in 1987) Craven Carriage Numbers 1505, 1506, 1508, 1514, 1522, 1523, 1529, 1532, 1539 and 1541 have been preserved in regular use by the Railway Preservation Society of Ireland (RPSI).[17] They are used on their Dublin area excursions. The body of No.1558 is preserved at a pub in Naas County Kildare. Cravens also built four 40-tonne capacity steam cranes for the New Zealand Railways in the late 1930s. One of these, NO 200 (TMS EL 4007), was purchased for preservation by Euan McQueen of the Rail Heritage Trust in 1990 while it was in storage. The crane was transferred to Steam Incorporated's Paekakariki depot in 1993. The crane was being restored by the Craven Crane Group, although it is listed in a roster of preserved railway and tramway equipment as having been transferred to Steam Inc ownership in 2009. It is at present under overhaul, having last operated in the late 1980s. Two of Craven's Class 105 diesel multiple unit cars, numbers 51485 and 56121 are now owned by and have been restored to "as new" condition by the East Lancashire Railway.[18]
Gallery
 1907 Craven Brothers builders photo of a lathe.
1907 Craven Brothers builders photo of a lathe.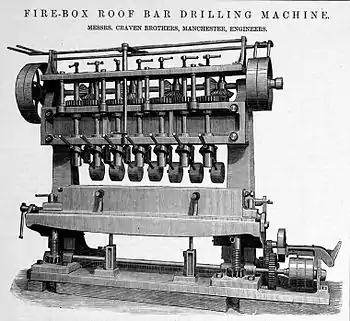 Craven Brothers catalogue illustration of a steam locomotive firebox drilling machine.
Craven Brothers catalogue illustration of a steam locomotive firebox drilling machine. Craven Brothers catalogue illustration of a 25 Ton railway breakdown crane.
Craven Brothers catalogue illustration of a 25 Ton railway breakdown crane. LMS Plough Brake Van Oyster, diagram 1805, nine built in 1932.
LMS Plough Brake Van Oyster, diagram 1805, nine built in 1932. The former general and drawing office of Craven Brothers in 1999.
The former general and drawing office of Craven Brothers in 1999.
See also
Notes
- Joseph Craven (c. 1828–6 December 1900) and Alfred Craven (c. 1835–28 March 1905) later joined by John Craven (c. 1831–3 December 1892). British Newspaper Collection and Census records, FindMyPast.
References
- John Brown And Company Limited. The Times, Monday, 4 October 1954; pg. 12; Issue 53053
- Obituaries, Mr Alfred Craven, page 7, Yorkshire and Leeds Intelligencer, 29 March 1905
- John Brown & Company (Limited). The Times, Wednesday, 1 October 1919; pg. 12; Issue 42219
- The Papers of Alfred Craven, The Royal Automobile Club Archives and Collections
- Three Leaks in John Brown, The Times, Friday, 20 August 1965; pg. 12; Issue 56405
- Tools to finish all jobs. The Times, Monday, 10 November 1969; pg. V; Issue 57713
- State Of Trade. Sheffield. The Times, Monday, 19 November 1883; pg. 11; Issue 30981
- State Of Trade. Sheffield. The Times, Monday, 20 April 1885; pg. 11; Issue 31425.
- Sheffield Trade for 1886. The Times, Friday, 7 January 1887; pg. 13; Issue 31963
- State Of Trade. Sheffield. The Times, Monday, 28 March 1887; pg. 11; Issue 3203
- State Of Trade. Sheffield. The Times, Monday, 6 August 1888; pg. 11; Issue 32457, Monday, 6 August 1888; pg. 11; Issue 32457
- New Palace Car. The Times, Monday, 7 January 1884; pg. 11; Issue 31023
- "Asbestos and railways". Archived from the original on 18 May 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Compensation: What Price On Your Life?". Archived from the original on 2 April 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Cravens Heritage Trains". Archived from the original on 7 August 2018. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- £½M. Railway Contract. The Times, Tuesday, 14 August 1962; pg. 13; Issue 55469
- "RPSI Carriage & Wagon Lists – Steel-bodied Carriages in the Dublin Area". Archived from the original on 22 April 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- "ELR Diesel Group - Fleet Information, DMU Diesel Multiple Units". www.elrdiesel.info. Retrieved 29 April 2020.