Cuanza River
The Kwanza River,[2] also known as the Coanza,[3] the Quanza,[3] and the Cuanza, is one of the longest rivers in Angola. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean just south of the national capital Luanda.
| Kwanza River Cuanza, Coanza, Quanza, | |
|---|---|
 | |
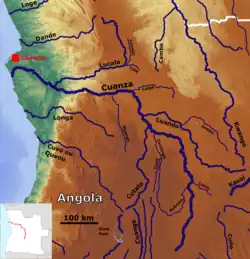 Kwanza River and tributaries | |
| Location | |
| Angola | Country |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Bie Plateau[1] |
| • location | Central Angola |
| • elevation | 1,234 m (4,049 ft) |
| Mouth | Atlantic Ocean |
• location | 60 km (37 mi) south of Luanda |
• coordinates | 9°21′S 13°9′E |
| Length | 960 km (600 mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 26.4km3/year |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Kukema, Cunhinga, Ngango, Cutato |
| • right | Cuiva, Luando, Cuige, Lucala |
| Waterbodies | Cambambe reservoir |
Geography
The river is navigable for about 150 miles (240 km) from its mouth, located 60 kilometers (37 mi) south of Luanda. Its tributaries include the Cutato and Lucala.
History
The river's navigable lower course was the original route of Portugal invasion into northern Angola.
The Capanda Dam in Malanje Province was finished in 2004, providing hydroelectric power to the region and assisting its irrigation. The Cambambe Dam and the Lauca Dam were also constructed on the river. The Caculo Cabaça Hydroelectric Power StationCaculo Cabaça Dam is under construction with estimated completion in 2024. The Barra do Kwanza, the mouth of the river is gradually being developed for tourism, including a golf course.
The Church of Nossa Senhora da Victoria stands near the banks of the Kwanza River in Massanganu, Province of Cuanza-Norte, Angola.[4]
Wildlife
Rich biodiversity has been found in the Angolan river, according to research reported on the Science and Development Network website. Angola's first biodiversity tally of the Kwanza River has so far found 50 fish species. Researchers from the National Fishing Research Institute and the South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity say genetic testing may reveal new species.[5] Sportfishing includes tarpon.
Legacy
Angola's currency, the kwanza, is named after the river.[2][6] The river is also the namesake of the provinces of Cuanza Norte ("Cuanza North") and Cuanza Sul ("Cuanza South").
See also
- Quissama National Park, to the south of the river
References
Citations
- "Source book for the inland fishery resources of Africa Vol. 1". www.fao.org. FAO. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- "O Perfil de Angola". Portal Official do Governo da República de Angola. Governo de Angola. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- EB (1878).
- Valdez, F. T. (1861), Six Years of a Traveller's Life in Western Africa, Vol. II, Hurst and Blackett.
- "Sub-Saharan Africa news in brief: 13–25 March, 2008". SciDev.Net (website). Accessed May 2010.
- Theroux, Paul (30 May 2013). The Last Train to Zona Verde: Overland from Cape Town to Angola. Penguin Books Limited. ISBN 9780241965139 – via Google Books.
Bibliography
- , 'Encyclopædia Britannica, 9th ed., Vol. VI, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1878, p. 81.