Arabinofuranosylcytosine triphosphate
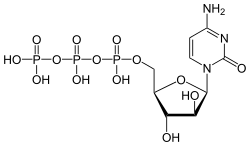
Arabinofuranosylcytosine triphosphate is a nucleotide that inhibits the synthesis of DNA by acting as an antimetabolic agent against deoxycytidine (a component of DNA). It is the biologically active form of cytarabine.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-1-deoxy-β-D-arabinofuranose 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} tetrahydrogen triphosphate | |
| Other names
Ara-CTP, Cytarabine triphosphate, Cytosine arabinoside triphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Arabinofuranosylcytosine+triphosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16N3O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 483.156323 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.