DRAP1
Dr1-associated corepressor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRAP1 gene.[5][6]
| DRAP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DRAP1, NC2-alpha, DR1 associated protein 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602289 MGI: 1913806 HomoloGene: 4703 GeneCards: DRAP1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transcriptional repression is a general mechanism for regulating transcriptional initiation in organisms ranging from yeast to humans. Accurate initiation of transcription from eukaryotic protein-encoding genes requires the assembly of a large multiprotein complex consisting of RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors such as TFIIA, TFIIB, and TFIID. DR1 is a repressor that interacts with the TATA-binding protein (TBP) of TFIID and prevents the formation of an active transcription complex by precluding the entry of TFIIA and/or TFIIB into the preinitiation complex. The protein encoded by this gene is a corepressor of transcription that interacts with DR1 to enhance DR1-mediated repression. The interaction between this corepressor and DR1 is required for corepressor function and appears to stabilize the TBP-DR1-DNA complex.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000175550 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024914 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Mermelstein F, Yeung K, Cao J, Inostroza JA, Erdjument-Bromage H, Eagelson K, et al. (April 1996). "Requirement of a corepressor for Dr1-mediated repression of transcription". Genes & Development. 10 (8): 1033–48. doi:10.1101/gad.10.8.1033. PMID 8608938.
- "Entrez Gene: DRAP1 DR1-associated protein 1 (negative cofactor 2 alpha)".
- Iratni R, Yan YT, Chen C, Ding J, Zhang Y, Price SM, et al. (December 2002). "Inhibition of excess nodal signaling during mouse gastrulation by the transcriptional corepressor DRAP1". Science. 298 (5600): 1996–9. Bibcode:2002Sci...298.1996I. doi:10.1126/science.1073405. PMID 12471260. S2CID 22923124.
- Mermelstein F, Yeung K, Cao J, Inostroza JA, Erdjument-Bromage H, Eagelson K, et al. (April 1996). "Requirement of a corepressor for Dr1-mediated repression of transcription". Genes & Development. 10 (8): 1033–48. doi:10.1101/gad.10.8.1033. PMID 8608938.
- Yeung K, Kim S, Reinberg D (January 1997). "Functional dissection of a human Dr1-DRAP1 repressor complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 17 (1): 36–45. doi:10.1128/MCB.17.1.36. PMC 231727. PMID 8972183.
Further reading
- Goppelt A, Stelzer G, Lottspeich F, Meisterernst M (June 1996). "A mechanism for repression of class II gene transcription through specific binding of NC2 to TBP-promoter complexes via heterodimeric histone fold domains". The EMBO Journal. 15 (12): 3105–16. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00673.x. PMC 450253. PMID 8670811.
- Yeung K, Kim S, Reinberg D (January 1997). "Functional dissection of a human Dr1-DRAP1 repressor complex". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 17 (1): 36–45. doi:10.1128/MCB.17.1.36. PMC 231727. PMID 8972183.
- Ikeda K, Halle JP, Stelzer G, Meisterernst M, Kawakami K (January 1998). "Involvement of negative cofactor NC2 in active repression by zinc finger-homeodomain transcription factor AREB6". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (1): 10–8. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.1.10. PMC 121442. PMID 9418848.
- Castaño E, Gross P, Wang Z, Roeder RG, Oelgeschläger T (June 2000). "The C-terminal domain-phosphorylated IIO form of RNA polymerase II is associated with the transcription repressor NC2 (Dr1/DRAP1) and is required for transcription activation in human nuclear extracts". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (13): 7184–9. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.7184C. doi:10.1073/pnas.140202297. PMC 16520. PMID 10852970.
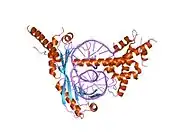
- Kamada K, Shu F, Chen H, Malik S, Stelzer G, Roeder RG, et al. (July 2001). "Crystal structure of negative cofactor 2 recognizing the TBP-DNA transcription complex". Cell. 106 (1): 71–81. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00417-2. PMID 11461703. S2CID 11064090.
- Iratni R, Yan YT, Chen C, Ding J, Zhang Y, Price SM, et al. (December 2002). "Inhibition of excess nodal signaling during mouse gastrulation by the transcriptional corepressor DRAP1". Science. 298 (5600): 1996–9. Bibcode:2002Sci...298.1996I. doi:10.1126/science.1073405. PMID 12471260. S2CID 22923124.
- Denko N, Wernke-Dollries K, Johnson AB, Hammond E, Chiang CM, Barton MC (February 2003). "Hypoxia actively represses transcription by inducing negative cofactor 2 (Dr1/DrAP1) and blocking preinitiation complex assembly". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (8): 5744–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212534200. PMID 12477712.
- Leonard D, Ajuh P, Lamond AI, Legerski RJ (September 2003). "hLodestar/HuF2 interacts with CDC5L and is involved in pre-mRNA splicing". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 308 (4): 793–801. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.539.8359. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01486-4. PMID 12927788.
- Klejman MP, Pereira LA, van Zeeburg HJ, Gilfillan S, Meisterernst M, Timmers HT (November 2004). "NC2alpha interacts with BTAF1 and stimulates its ATP-dependent association with TATA-binding protein". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (22): 10072–82. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.22.10072-10082.2004. PMC 525489. PMID 15509807.
- Lewis BA, Sims RJ, Lane WS, Reinberg D (May 2005). "Functional characterization of core promoter elements: DPE-specific transcription requires the protein kinase CK2 and the PC4 coactivator". Molecular Cell. 18 (4): 471–81. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.005. PMID 15893730.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C, Brembeck FH, Goehler H, et al. (September 2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. PMID 16169070. S2CID 8235923.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, et al. (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Assmann EM, Alborghetti MR, Camargo ME, Kobarg J (April 2006). "FEZ1 dimerization and interaction with transcription regulatory proteins involves its coiled-coil region". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (15): 9869–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513280200. PMID 16484223.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF, et al. (May 2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569. S2CID 13709685.
- Albert TK, Grote K, Boeing S, Stelzer G, Schepers A, Meisterernst M (June 2007). "Global distribution of negative cofactor 2 subunit-alpha on human promoters". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (24): 10000–5. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10410000A. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703490104. PMC 1891239. PMID 17548813.