Dancing Links
In computer science, dancing links (DLX) is a technique for adding and deleting a node from a circular doubly linked list. It is particularly useful for efficiently implementing backtracking algorithms, such as Knuth's Algorithm X for the exact cover problem.[1] Algorithm X is a recursive, nondeterministic, depth-first, backtracking algorithm that finds all solutions to the exact cover problem. Some of the better-known exact cover problems include tiling, the n queens problem, and Sudoku.
The name dancing links, which was suggested by Donald Knuth, stems from the way the algorithm works, as iterations of the algorithm cause the links to "dance" with partner links so as to resemble an "exquisitely choreographed dance." Knuth credits Hiroshi Hitotsumatsu and Kōhei Noshita with having invented the idea in 1979,[2] but it is his paper which has popularized it.
Implementation
As the remainder of this article discusses the details of an implementation technique for Algorithm X, the reader is strongly encouraged to read the Algorithm X article first.
Main ideas
The idea of DLX is based on the observation that in a circular doubly linked list of nodes,
x.left.right ← x.right; x.right.left ← x.left;
will remove node x from the list, while
x.left.right ← x; x.right.left ← x;
will restore x's position in the list, assuming that x.right and x.left have been left unmodified. This works regardless of the number of elements in the list, even if that number is 1.
Knuth observed that a naive implementation of his Algorithm X would spend an inordinate amount of time searching for 1's. When selecting a column, the entire matrix had to be searched for 1's. When selecting a row, an entire column had to be searched for 1's. After selecting a row, that row and a number of columns had to be searched for 1's. To improve this search time from complexity O(n) to O(1), Knuth implemented a sparse matrix where only 1's are stored.
At all times, each node in the matrix will point to the adjacent nodes to the left and right (1's in the same row), above and below (1's in the same column), and the header for its column (described below). Each row and column in the matrix will consist of a circular doubly-linked list of nodes.
Header
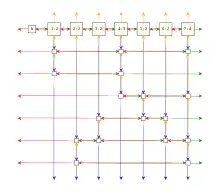
Each column will have a special node known as the "column header," which will be included in the column list, and will form a special row ("control row") consisting of all the columns which still exist in the matrix.
Finally, each column header may optionally track the number of nodes in its column, so that locating a column with the lowest number of nodes is of complexity O(n) rather than O(n×m) where n is the number of columns and m is the number of rows. Selecting a column with a low node count is a heuristic which improves performance in some cases, but is not essential to the algorithm.
Exploring
In Algorithm X, rows and columns are regularly eliminated from and restored to the matrix. Eliminations are determined by selecting a column and a row in that column. If a selected column doesn't have any rows, the current matrix is unsolvable and must be backtracked. When an elimination occurs, all columns for which the selected row contains a 1 are removed, along with all rows (including the selected row) that contain a 1 in any of the removed columns. The columns are removed because they have been filled, and the rows are removed because they conflict with the selected row. To remove a single column, first remove the selected column's header. Next, for each row where the selected column contains a 1, traverse the row and remove it from other columns (this makes those rows inaccessible and is how conflicts are prevented). Repeat this column removal for each column where the selected row contains a 1. This order ensures that any removed node is removed exactly once and in a predictable order, so it can be backtracked appropriately. If the resulting matrix has no columns, then they have all been filled and the selected rows form the solution.
Backtracking
To backtrack, the above process must be reversed using the second algorithm stated above. One requirement of using that algorithm is that backtracking must be done as an exact reversal of eliminations. Knuth's paper gives a clear picture of these relationships and how the node removal and reinsertion works, and provides a slight relaxation of this limitation.
Optional constraints
It is also possible to solve one-cover problems in which a particular constraint is optional, but can be satisfied no more than once. Dancing Links accommodates these with primary columns which must be filled and secondary columns which are optional. This alters the algorithm's solution test from a matrix having no columns to a matrix having no primary columns and if the heuristic of minimum one's in a column is being used then it needs to be checked only within primary columns. Knuth discusses optional constraints as applied to the n queens problem. The chessboard diagonals represent optional constraints, as some diagonals may not be occupied. If a diagonal is occupied, it can be occupied only once.
See also
References
- Knuth, Donald E. (2000). "Dancing links". Millennial Perspectives in Computer Science. P159. 187. arXiv:cs/0011047. Bibcode:2000cs.......11047K.
- Hitotumatu, Hirosi; Noshita, Kohei (30 April 1979). "A Technique for Implementing Backtrack Algorithms and its Application". Information Processing Letters. 8 (4): 174–175. doi:10.1016/0020-0190(79)90016-4.(subscription required)
- "Online tools for manipulating dancing links".
External links
- A distributed Dancing Links implementation as a Hadoop MapReduce example
- Free Software implementation of an Exact Cover solver in C - uses Algorithm X and Dancing Links. Includes examples for sudoku and logic grid puzzles.
- DlxLib NuGet package - a C# class library that implements DLX
- dlxlib npm package - a JavaScript library that implements DLX
- dancing-links-c++ - a C++ library that implements DLX
- go-dancing-links - a GoLang library that implements DLX
- Donald Knuth's original implementation of dancing links written in CWEB. (See also his frontend for solving sudoku puzzles.)
- Donald Knuth's 24th Annual Christmas Lecture: Dancing Links