Demethylation
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule.[1][2] A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
The counterpart of demethylation is methylation.
In biochemistry
In biochemical systems, the process of demethylation is catalyzed by demethylases. These enzymes oxidize N-methyl groups, which occur in histones and some forms of DNA:
- R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O
One such oxidative enzyme family is the cytochrome P450.[3] Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar pathway. These reactions exploit the weak C-H bond adjacent to amines.
.jpg.webp)
In particular, 5-methylcytosines in DNA can be demethylated by TET enzymes as illustrated in the figure. TET enzymes are dioxygenases in the family of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. A TET enzyme is an alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG) dependent dioxygenase that catalyses an oxidation reaction by incorporating a single oxygen atom from molecular oxygen (O2) into its substrate, 5-methylcytosine in DNA (5mC), to produce the product 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA. This conversion is coupled with the oxidation of the co-substrate α-KG to succinate and carbon dioxide (see figure).
The first step involves the binding of α-KG and 5-methylcytosine to the TET enzyme active site. The TET enzymes each harbor a core catalytic domain with a double-stranded β-helix fold that contains the crucial metal-binding residues found in the family of Fe(II)/α-KG- dependent oxygenases.[4] α-KG coordinates as a bidentate ligand (connected at two points) to Fe(II) (see figure), while the 5mC is held by a noncovalent force in close proximity. The TET active site contains a highly conserved triad motif, in which the catalytically essential Fe(II) is held by two histidine residues and one aspartic acid residue (see figure). The triad binds to one face of the Fe center, leaving three labile sites available for binding α-KG and O2 (see figure). TET then acts to convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, while α-ketoglutarate is converted to succinate and CO2.
Demethylation of some sterols are steps in the biosynthesis of testosterone and cholesterol. Methyl groups are lost as formate.[5] During embryogenesis in the mouse, about 20 million 5-methylcytosines are demethylated in a six-hour period just after fertilization of an egg by a sperm to form a zygote.
In organic chemistry
Demethylation often refers to cleavage of ethers, especially aryl ethers, although there are some exceptions, such as N-demethylation of amines (e.g. imipramine to desipramine).
Cleaving methyl ethers
Aryl methyl ethers are pervasive in lignin and many derived compounds.[6] The demethylation of these materials has been the subject of much effort. The reaction typically requires harsh conditions or harsh reagents. For example, the methyl ether in vanillin can be removed by heating near 250 °C (482 °F) with strong base.[7] Stronger nucleophiles such as diorganophosphides (LiPPh2) also cleave aryl ethers under milder conditions.[8] Other strong nucleophiles that have been employed include thiolate salts like EtSNa.[9]
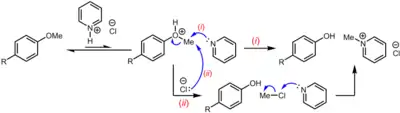
Acidic conditions can also be used. Historically, aryl methyl ethers, including natural products such as codeine (O-methylmorphine), have been demethylated by heating the substance in molten pyridine hydrochloride (melting point 144 °C (291 °F)) at 180 to 220 °C (356 to 428 °F), sometimes with excess hydrogen chloride, in a process known as the Zeisel–Prey ether cleavage.[10][11] Quantitative analysis for aromatic methyl ethers can be performed by argentometric determination of the N-methylpyridinium chloride formed.[12] The mechanism of this reaction starts with proton transfer from pyridinium ion to the aryl methyl ether, a highly unfavorable step (K < 10−11) that accounts for the harsh conditions required, given the much weaker acidity of pyridinium (pKa = 5.2) compared to the protonated aryl methyl ether (an arylmethyloxonium ion, pKa = –6.7 for aryl = Ph[13]). This is followed by SN2 attack of the arylmethyloxonium ion at the methyl group by either pyridine or chloride ion (depending on the substrate) to give the free phenol and, ultimately, N-methylpyridinium chloride, either directly or by subsequent methyl transfer from methyl chloride to pyridine.[12]
Another classical (but, again, harsh) method for the removal of the methyl group of an aryl methyl ether is to heat the ether to reflux in a solution of hydrogen bromide or hydrogen iodide in acetic acid (boiling point 118 °C (244 °F)) or concentrated hydrobromic or hydroiodic acid.[14] The cleavage of ethers by hydrobromic or hydroiodic acid proceeds by a very similar mechanism, in which the highly acidic HBr or HI serves to protonate the ether, followed by displacement by bromide or iodide, both of which are excellent nucleophiles. A slightly milder set of conditions uses cyclohexyl iodide (CyI, 10.0 equiv) in N,N-dimethylformamide to generate a small amount of hydrogen iodide in situ.[15]
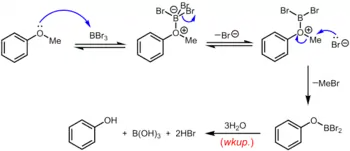
Boron tribromide, which can be used at room temperature or below, is a more specialized reagent for the demethylation of aryl methyl ethers. The mechanism of ether dealkylation proceeds via the initial reversible formation of a Lewis acid-base adduct between the strongly Lewis acidic BBr3 and the Lewis basic ether. This Lewis adduct can reversibly dissociate to give a dibromoboryl oxonium cation and Br–. Rupture of the ether linkage occurs through the subsequent nucleophilic attack on the oxonium species by Br– to yield an aryloxydibromoborane and methyl bromide. Upon completion of the reaction, the phenol is liberated along with boric acid (H3BO3) and hydrobromic acid (aq. HBr) upon hydrolysis of the dibromoborane derivative during aqueous workup.[16]
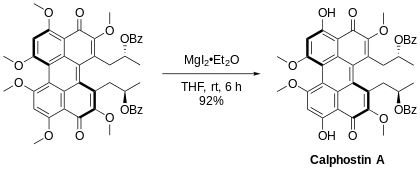
Aromatic methyl ethers, particularly those with an adjacent carbonyl group, can be regioselectively demethylated using magnesium iodide etherate.[17] An example of this being used is in the synthesis of the natural product Calphostin A,[18] as seen below.
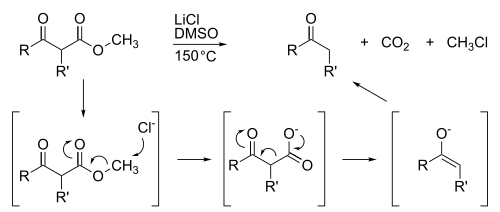
Methyl esters also are susceptible to demethylation, which is usually achieved by saponification. Highly specialized demethylations are abundant, such as the Krapcho decarboxylation:
A mixture of anethole, KOH, and alcohol was heated in an autoclave. Although the product of this reaction was the expected anol, a highly reactive dimerization product in the mother liquors called dianol was also discovered by Charles Dodds.
N-demethylation
N-demethylation of 3° amines is by the von Braun reaction, which uses BrCN as the reagent to give the corresponding nor- derivatives. A modern variation of the von Braun reaction was developed, where BrCN was superseded by ethyl chloroformate. The preparation of Paxil from arecoline is an application of this reaction, as well as the synthesis of GSK-372,475, for example.
See also
- Methylation, the addition of a methyl group to a substrate
References
- Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- Roland Sigel; Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut (2007). The Ubiquitous Roles of Cytochrome P450 Proteins: Metal Ions in Life Sciences. New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-01672-5.
- Kohli RM, Zhang Y (October 2013). "TET enzymes, TDG and the dynamics of DNA demethylation". Nature. 502 (7472): 472–9. Bibcode:2013Natur.502..472K. doi:10.1038/nature12750. PMC 4046508. PMID 24153300.
- Pietzke, Matthias; Meiser, Johannes; Vazquez, Alexei (2020). "Formate Metabolism in Health and Disease". Molecular Metabolism. 33: 23–37. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2019.05.012. PMC 7056922. PMID 31402327.
- W. Boerjan; J. Ralph; M. Baucher (June 2003). "Lignin biosynthesis". Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54 (1): 519–549. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134938. PMID 14503002.
- Irwin A. Pearl (1949). "Protocatechulic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 29: 85.; Collective Volume, vol. 3, p. 745
- Robert E. Ireland; David M. Walba (1977). Organic Syntheses. Vol. 56. p. 44. doi:10.1002/0471264180.os056.11. ISBN 978-0471264224.
- "ORCINOL MONOMETHYL ETHER". orgsyn.org. Retrieved 2019-02-23.
- Lawson, J. A.; DeGraw, J. I. (1977). "An improved method for O-demethylation of codeine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 20 (1): 165–166. doi:10.1021/jm00211a037. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 833817.
- Hassner, Alfred; Stumer, C. (2002). Organic syntheses based on name reactions (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Pergamon. ISBN 9780080513348. OCLC 190810761.
- Burwell, Robert L. (1954-08-01). "The Cleavage of Ethers". Chemical Reviews. 54 (4): 615–685. doi:10.1021/cr60170a003. ISSN 0009-2665.
- Vollhardt, Peter; Schore, Neil (2014-01-01). Organic chemistry : structure and function (Seventh ed.). New York, NY. ISBN 9781464120275. OCLC 866584251.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Streitwieser, Andrew; Heathcock, Clayton H.; Kosower, Edward M. (1992). Introduction to organic chemistry (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0139738500. OCLC 52836313.
- Zuo, Li; Yao, Shanyan; Wang, Wei; Duan, Wenhu (June 2008). "An efficient method for demethylation of aryl methyl ethers". Tetrahedron Letters. 49 (25): 4054–4056. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.04.070.
- J. F. W. McOmie, D. E. West (1969). "3,3'-Dihydroxybiphenyl". Organic Syntheses. 49: 13.; Collective Volume, vol. 5, p. 412
- Yamaguchi, Seiji; Nedachi, Masahiro; Yokoyama, Hajime; Hirai, Yoshiro (October 1999). "Regioselective demethylation of 2,6-dimethoxybenzaldehydes with magnesium iodide etherate". Tetrahedron Letters. 40 (41): 7363–7365. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(99)01411-2.
- Merlic, Craig A.; Aldrich, Courtney C.; Albaneze-Walker, Jennifer; Saghatelian, Alan (1 April 2000). "Carbene Complexes in the Synthesis of Complex Natural Products: Total Synthesis of the Calphostins". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 122 (13): 3224–3225. doi:10.1021/ja994313+. PMC 3548573. PMID 23335811.