Demography of Liverpool
The demography of Liverpool is officially analysed by the Office for National Statistics. The Liverpool City Region is made up of Liverpool alongside the Metropolitan Boroughs of Halton, Knowsley, Sefton, St Helens, and the Wirral. With a population of around 496,784, Liverpool is the largest settlement in the region and the sixth largest in the United Kingdom.
| Demographics of Liverpool | |
|---|---|
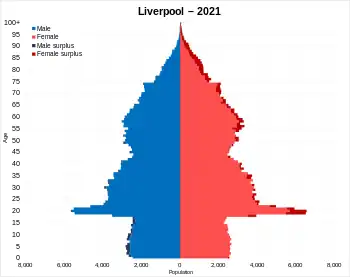 Population pyramid of Liverpool | |
| Population | 466,400 (2011) |
| Nationality | |
| Major ethnic | White: 88.9% |
Population change

As with other major British cities, Liverpool has a large and very diverse population. In the 2011 UK Census, the recorded population of Liverpool was 466,400,[1] a 5.5% increase from the 435,500 recorded in the 2001 census.[2] Liverpool's population peaked in the 1930s with 846,101 recorded in the 1931 census.[3] Until the recent increase, the city had experienced negative population growth every decade; at its peak, over 100,000 people had left the city between 1971 and 1981.[4] Between 2001 and 2006, the city experienced the ninth largest population percentage loss of any UK unitary authority.[5]
In common with many cities, Liverpool's population is younger than that of England as a whole, with 42.3% of its population under the age of 30, compared to an English average of 37.4%.[6] Those of working age make up 65.1% of the population.[6]
Urban and metropolitan area
The Liverpool Urban Area encompasses the city of Liverpool alongside Sefton, Knowsley, St. Helens and Ashton-in-Makerfield had a population of 864,122 in 2011, which ranks sixth out of all UK conurbations.[7] Liverpool City Region had an estimated population of 1,554,642 in 2019.
Ethnicity

While 84% of Liverpool's population is white, the city is one of the most important sites in the history of multiculturalism in the United Kingdom. Liverpool is home to Britain's oldest black community, dating to at least the 1730s, and some Liverpudlians are able to trace their black ancestors in the city back ten generations.[8] Early black settlers in the city included seamen, the children of traders sent to be educated, and freed slaves (since slaves entering the country after 1722 were deemed free men).[9]
The city is also home to the oldest Chinese community in Europe; the first residents of the city's Chinatown arrived as seamen in the 19th century.[10] The gateway in Chinatown is also the largest gateway outside of China.
The city is also historically known for its large Irish and Welsh populations.[11] The Liverpool accent (Scouse) is thought to have been influenced by the arrival of Irish and Welsh immigrants.[12] Today, up to 50% of Liverpool's population is believed to have Irish ancestry. The influences of Irish and Welsh culture have given Liverpool's people traits usually associated with the Celtic fringes of the British Isles.[13]
The vast majority of Liverpool's ethnic minorities live within the inner city area, particularly in and around Toxteth. According to the 2001 census, 38% of the population of Granby,[14] 37% of Princes Park,[15] and 27% of Central[16] were from ethnic groups other than White British.
- Census data
| Ethnic Group | 1991[17] | 2001[18] | 2011[19] | 2021[20] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 435,404 | 96.23% | 414,526 | 94.32% | 414,671 | 88.91% | 408,443 | 84.03% |
| White: British | – | – | 403,625 | 91.84% | 395,485 | 84.79% | 375,785 | 77.31% |
| White: Irish | 5,813 | 1.28% | 5,349 | 1.21% | 6,729 | 1.44% | 6,826 | 1.40% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller[note 1] | – | – | – | – | 185 | 0.04% | 501 | 0.10% |
| White: Roma[note 2] | – | – | – | – | 1,169 | 0.24% | ||
| White: Other | – | – | 5,552 | 1.26% | 12,272 | 2.63% | 24,162 | 4.97% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | 6,358 | 1.41% | 9,962 | 2.26% | 19,403 | 4.16% | 27,767 | 5.71% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | 395 | 0.09% | 557 | 0.12% | 1,075 | 0.23% | 1,917 | 0.39% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese[note 3] | 3,337 | 0.73% | 5,143 | 1.17% | 7,978 | 1.71% | 8,841 | 1.82% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | 1,295 | 0.28% | 1,909 | 0.43% | 4,915 | 1.05% | 6,251 | 1.29% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | 630 | 0.14% | 1,050 | 0.23% | 1,999 | 0.42% | 3,673 | 0.76% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | 701 | 0.15% | 1,303 | 0.29% | 3,436 | 0.73% | 7,085 | 1.46% |
| Black or Black British: Total | 7,247 | 1.60% | 5,377 | 1.22% | 12,308 | 2.63% | 16,964 | 3.49% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | 1,495 | 0.33% | 1,083 | 0.24% | 1,467 | 0.31% | 1,493 | 0.31% |
| Black or Black British: African | 2,487 | 0.54% | 3,071 | 0.69% | 8,490 | 1.82% | 12,709 | 2.61% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | 3,265 | 0.72% | 1,223 | 0.27% | 2,351 | 0.50% | 2,762 | 0.57% |
| Mixed: Total | – | – | 7,907 | 1.79% | 11,756 | 2.52% | 16,880 | 3.47% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | – | – | 2,308 | 0.52% | 3,473 | 0.74% | 4,127 | 0.85% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | – | – | 2,207 | 0.50% | 3,164 | 0.67% | 4,157 | 0.86% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | 1,352 | 0.31% | 2,283 | 0.48% | 3,662 | 0.75% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | 2,040 | 0.46% | 2,836 | 0.61% | 4,934 | 1.02% |
| Other: Total | 3,441 | 0.76% | 1,701 | 0.38% | 8,277 | 1.77% | 16,034 | 3.30% |
| Other: Arab[note 1] | – | – | – | – | 5,629 | 1.21% | 8,312 | 1.71% |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | 3,441 | 0.76% | 1,701 | 0.38% | 2,648 | 0.56% | 7,722 | 1.59% |
| Total | 452,450 | 100% | 439,473 | 100% | 466,415 | 100% | 486,088 | 100% |
Per the above table, note that the census question regarding ethnicity was first asked in 1991.
Major ethnic and national groups
The largest and most significant non-English ethnic and national groups in Liverpool are listed in alphabetical order below.
Afro-Caribbeans

Historically, and even today, the Afro-Caribbean population of Liverpool has been largely outnumbered by Black Africans. In 2009, just under 5,000 Liverpudlians were of Afro-Caribbean origin (most of these being of mixed White and Black origins).[21] This is compared to the 6,900 plus individuals of full or partial Black African origin in the city.[21] The International Organization for Migration estimates that Liverpool is home to between 1,000 and 2,000 Jamaicans, with the vast majority of these residing in Toxteth and Granby.[22] Some Black Africans in Liverpool can trace their ancestry back to the city's links with the slave trade, whilst Afro-Caribbeans are a fairly recent and emerging ethnic group.[23] By far the largest wave of Afro-Caribbean immigrants to the UK occurred in the 1940s and 1950s, when the British government encouraged people to come over and help contribute to the economy by taking up empty job vacancies. Despite being a relatively small community, Afro-Caribbeans have made a significant contribution to the history and culture of the city. There are numerous Afro-Caribbean-owned businesses and community centres in and around Toxteth and the Smithdown Road area.
Chinese

Liverpool is home to the oldest Chinese community in Europe.[10] According to 2009 estimates, 1.1% of Liverpool's population are of Chinese ethnicity (some 5,000 people).[24] Despite this, the IOM has estimated that the true number of Chinese people in Liverpool could range between 25,000 and 35,000.[25] The first presence of Chinese people in Liverpool dated back to the early 19th century, with the main influx arriving at the end of the 19th century. This was in part due to Alfred Holt and Company establishing the first commercial shipping line to focus on the China trade. From the 1890s onwards, small numbers of Chinese began to set up businesses catering to the Chinese sailors working on Holt's lines and others. Some of these men married working class British women, resulting in a number of British-born Eurasian Chinese being born during World War II in Liverpool.[26] Although the Chinese population in Liverpool is much smaller than it was mid-20th century, the city's Chinatown district has spread significantly since its first establishment, now taking up much of Berry Street. The 2001 census showed 1,542 Liverpudlians were born in the People's Republic of China and 1,228 in Hong Kong.[27] Liverpool has been twinned with China's largest city, Shanghai since 1999.[28]
Ghanaians
There is a strong presence of Ghanaians in Liverpool, with an estimated 9,000 individuals originating in the African nation living in the city.[29] Liverpool is a stronghold for overseas Ghanaian students; significant numbers study at the city's three universities, particularly Hope University. Hope works alongside the Ghanaian High Commission and has set up the 'High Value Scholarship for Ghana', which alongside the university's other scholarships has helped draw a large number of potential students from the African nation.[30]
Greeks

The Liverpool Greek community dates back over 180 years, and a group named the Liverpool Greek Society was established in 1996.[31] The first large wave of Greeks to the city occurred in 1821 after massacres of Greeks by Turkish invaders on the island of Chios. Significant numbers also came to work for the Ralli Brothers, who recruited 40,000 Greeks in cities worldwide including New York City, Geneva and Liverpool.[31] The Greek Orthodox Church of St Nicholas in Toxteth was built in 1870 and serves the local Greek community. There are estimated to be 2,500 Greek Cypriots in the Merseyside area,[32] whilst 3,000 Greeks are estimated to live to the west of the River Mersey in the Wirral area, Chester and North Wales.[33]
Irish
Following the start of the Great Irish Famine, two million Irish people migrated to Liverpool in the space of one decade, many of them subsequently departing for the United States.[34] By 1851, more than 20% of the population of Liverpool was Irish.[35] At the 2001 Census, 0.75% of the population were born in the Republic of Ireland, while 0.54% were born in Northern Ireland,[36] but up to 50% of Liverpudlians are thought to have some form of Irish ancestry.
Italians
Significant numbers of Italians first arrived in Liverpool in the 19th century. The main reason for Italians coming to the city was to embark on a journey from the port of Liverpool to the 'New World' in hope of a better life than in their native Italy.[37] Despite this many failed to complete the journey and actually remained in Liverpool, the largest numbers settling on and around Scotland Road, which soon became nicknamed 'Little Italy'.[37] Currently, some 3,000 Italians reside in Liverpool, although little over 200 were actually born in Italy.[38][39] There is an Italian Consulate located on the west side of the Mersey in Birkenhead adjacent to the Queensway Tunnel.[40]
Latin Americans

Liverpool and the surrounding urban area is home to UK's largest Latin American community outside London.[41][42] Although significant migration from Latin America to the United Kingdom only began in the 1970s, at a time of much political turmoil and civil unrest in Latin America, Liverpool's Latin American community has seen a large increase in size during the mid-2000s.[41] The majority of these people originate from Bolivia, Colombia, Brazil and Peru.[41] Liverpool City Council and other local services offer information and help in Spanish and Portuguese due to the city's large Latin American population.[43] The University of Liverpool is one of the few educational facilities in the country that teaches Latin American studies.[44] Amongst the most famous Latin Americans in Liverpool are the numerous expatriate footballers who play for the city's professional football clubs. Liverpool F.C.'s current first team includes three Brazilians.[45] Liverpool has friendship links with Havana, Cuba, La Plata, Argentina and Valparaiso, Chile.[28] Brazilica Festival is the UK's largest celebration of Brazilian culture and has been held annually in Liverpool since 2008.[46]
Malaysians
The IOM has stated that around 9,000 Malaysians live in the city which makes it one of the largest such communities in the country.[47] They are the second largest East Asian group in Liverpool. There are also an estimated 1,500 Vietnamese residing in the city.[48]
Somalis
Somalis number in the thousands in Liverpool, and are one of the city's longest established ethnic minority groups. According to the 2001 census, 678 Somali-born individuals were living in Liverpool,[49] but unofficial estimates place the figure between 4,000 and 9,000 inhabitants.[50][51] While many Somalis arrived in Liverpool seeking asylum after the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991, there has been a presence of Somalis in the city since the 19th century, when many came to Liverpool to work for the British Navy,[51] often by way of the former British Somaliland protectorate.[51] Today, Liverpool City Council and local services offer information and help in the Somali language (this is alongside information in English and 15 other common languages in Liverpool).[43] The majority of Liverpool's Somali community reside in Toxteth, where there are numerous Somali-run businesses and community groups. In 2004, a local social worker, Mohamed "Jimmy" Ali, became the UK's first Somali councillor, although he has since lost his seat.[52]
South Asians

Like most British cities, Liverpool has a strong presence of South Asians. 2007 estimates put the number of people of Indian origin in the city at 6,700, Pakistanis at 3,200, Bangladeshis at 1,100. Some 2,000 people belonged to other South Asian groups whilst a further 2,000 individuals were of mixed South Asian and European origin.[21] Bengali and Urdu are amongst the most common foreign languages spoken in Liverpool.[43] The South Asian population of Liverpool is one of the city's fastest growing ethnic groups; in 2001 some 5,000 South Asians were residing in the city (1.1% of the local population). Over the next eight years, the community more than doubled in size to 13,000 (3% of the local population, which is actually much lower than England's average of 6%).[21]
The Indian presence in Liverpool dates back to 1860s, although these people only tended to be sailors and tradesmen.[53] However, around 1910 a group of Indian males from the Punjab region of India moved to Liverpool and established the city's first fixed community. During World War I, many more came to Liverpool to look for work while numerous more came to the city after India was granted independence in 1947.[53] Two other significant waves of Indians to the city occurred when India was split into two separate countries (the other now known as Pakistan), the mass exodus of Indians from Kenya in the 1970s further added to Liverpool's long established South Asian community.[54] Historically, the first place Indians and fellow South Asians looked for work were the docks of Liverpool. It was a hard living with little pay and the fact that they spoke little to no English made it even harder.[53] They were proud people and working in oppressive conditions for people who were considered 'higher up', leading to many ending their jobs at the docks and seeking work elsewhere.[53] Eventually, large numbers of Indians in Liverpool set up their own businesses. Many began to work for themselves as street peddlers, entertainers and fortune tellers. The hours were long, but being their own boss appealed to many South Asians (a thought which is still maintained to this day).[53]
Welsh
In 1813, 10% of Liverpool's population was Welsh, leading to the city becoming known as "the capital of North Wales".[11][55] 120,000 Welsh people migrated from Wales to Liverpool between 1851 and 1911.[56] At the 2001 Census, 1.17% of the population were Welsh-born.[36]
.JPG.webp)
There are a number of people who use the Welsh language as their first language in Liverpool.
Yemenis
Liverpool, like several other port cities (such as South Shields, Cardiff and Kingston upon Hull), has had a strong presence of Yemeni people for centuries.[57] After the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, an increase of trade between Britain and the Far East meant that more men had to be recruited to work in ports and on ships.[57] Aden in Yemen was the main refuelling point for the vast majority of ships sailing this route, which led to many locals taking up jobs in the field. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries many of these seamen moved ashore and set up home in the likes of Liverpool.[57] Yemenis (who are most likely Liverpool's largest Arab group) alongside Somalis are the two largest Muslim groups in the city and worship at Liverpool's three main mosques (including the Al-Rahma mosque).[58] It is unknown exactly how many Yemenis and people of Yemeni descent live in Liverpool, due to the fact that Yemeni ethnic/national origin couldn't be stated in the 2001 census. Despite this, the 'Arab' ethnic option was added to the 2011 UK Census.[59] Many Yemenis in the city are noted for running newsagents and corner shops, the number of which is estimated to be approximately 400 in 2008.[60]
Zimbabweans
People originating in Zimbabwe are another large Black African group in Liverpool; they are thought to number no fewer than 3,000.[61]
Country of birth
The 2001 Census showed that 92.79% of Liverpool's residents were born in England, 1.17% in Wales, 0.77% in Scotland, and 0.54% in Northern Ireland. 0.75% were born in the Republic of Ireland, 0.75% elsewhere in the European Union, and 3.27% elsewhere in the world.[36] Foreign nations where more than 500 Liverpool residents in 2001 were born included: the Republic of Ireland, the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong, Germany, India, Somalia and Nigeria.[62]
Religion
Overview
Due to thousands of migrants and sailors passing through Liverpool over the centuries, the city now has a religious diversity which is reflected in its equally diverse collection of religious buildings. At the time of the 2001 census, 79.5% of the city's population were Christian, 1.4% were Muslim, 0.6% were Jewish, 0.3% were Buddhist, 0.3% were Hindu, and 0.1% were Sikh. Just over 0.1% of individuals collectively belonged to other faiths whilst 9.7% claimed to be non-religious and 8.1% opted not to reveal their religion.[63]
- Census data
| Religion | 2001[64] | 2011[65] | 2021[66] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Buddhism | 1,198 | 0.27% | 2,017 | 0.43% | 2,128 | 0.44% |
| Christianity | 349,279 | 79.48% | 331,217 | 71.01% | 278,330 | 57.26% |
| Hinduism | 1,147 | 0.26% | 2,437 | 0.52% | 3,802 | 0.78% |
| Islam | 5,945 | 1.35% | 15,209 | 3.26% | 25,756 | 5.30% |
| Judaism | 2,698 | 0.61% | 2,157 | 0.46% | 1,807 | 0.37% |
| No Religion | 42,515 | 9.67% | 82,701 | 17.73% | 142,994 | 29.42% |
| Sikhism | 404 | 0.09% | 531 | 0.11% | 641 | 0.13% |
| Other Religion | 556 | 0.13% | 1,122 | 0.24% | 1,991 | 0.41% |
| Undeclared | 35,731 | 8.13% | 29,024 | 6.22% | 28,639 | 5.89% |
| Total | 439,473 | 100% | 466,415 | 100% | 486,088 | 100% |
Per the above table, note that the census question regarding religion was first asked in 2001 and response is voluntary.
Christianity
The parish church of Liverpool is the Church of Our Lady and Saint Nicholas, an Anglican church which has existed near the waterfront since 1257. Though it is Anglican, it regularly plays host to Catholic masses. Other notable Christian places of worship include the Church of St Nicholas (Greek Orthodox) and the Gustav Adolf Church (Lutheranism). The Church of St Luke was bombed by the Nazis in the Liverpool Blitz during World War II and has been abandoned ever since, though it has become a noted tourist attraction as its damage was never fixed and the roof is still missing entirely, earning it the local nickname of the "bombed-out church".[67]
Liverpool's wealth as a port city enabled the construction of two enormous cathedrals, both dating from the 20th century. The Anglican Cathedral, which was designed by Sir Giles Gilbert Scott and plays host to the annual Liverpool Shakespeare Festival, is the fifth largest cathedral in the world. The Catholic Metropolitan Cathedral was initially planned to be even larger. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, only the crypt was completed. The cathedral was eventually built to a simpler design by Sir Frederick Gibberd; while this is on a smaller scale than Lutyens' original design, it boasts the largest panel of stained glass in the world. The road running between the two cathedrals is called Hope Street, a coincidence which is often commented on positively by both Anglicans and Catholics.
Islam
Liverpool had one of the earliest mosques in Britain, founded in 1887 by William Abdullah Quilliam, a lawyer who had converted to Islam. This mosque, which was also the first in England, no longer exists.[68] Plans have been ongoing to re-convert the building where the mosque once stood into a museum.[69] Currently, there are four mosques in Liverpool: the largest and main one, Al-Rahma Mosque, in the Toxteth area of the city and a mosque recently opened in the Mossley Hill suburb. The third mosque was also opened in Toxteth. Multimillion-pound plans to refurbish and restore the city's first mosque were revealed in January 2010.[70] In 2018, the Bait-ul-Lateef Mosque opened on Breck Road in Everton, owned by the Ahmadiyya Muslim Association of Liverpool, making it the fourth mosque to be currently operating in the city.
Judaism
Records of Liverpool's Jewish community date back to the 1750s,[71] and it became the largest Jewish community in northern England during the 1800s.[72] It is believed that Jewish refugees were welcomed and accepted much more easily than in most other English cities, prompting them to encourage their descendants to remain in the city for generations.[72] The Jewish population reached up to 11,000 in the past, but this dwindled due to the common practice of moving elsewhere for work, and the current number is around 3,000.[72] Most Jews reside in the southern areas of the city, primarily in the suburbs of Allerton and Childwall, each of which has its own Orthodox synagogue.[72]
The most notable synagogue is the Orthodox Princes Road Synagogue in the Toxteth district, which is widely considered to be the best of the UK's Moorish Revival synagogues and one of the finest buildings in Liverpool.[73] Consecrated in 1874, its congregation also pioneered the use of the English language in Jewish services.[74] Another Orthodox synagogue, Greenbank Drive Synagogue in the Mossley Hill suburb, operated from 1937 until 2008.[75] The city's Reform Jews congregate at Liverpool Reform Synagogue in the Wavertree district, which was consecrated in 1962,[76] while there is also a Masorti community in the Woolton suburb.[77] Other Jewish institutions include the Lubavitch Foundation in Allerton,[78] King David High School in Wavertree,[79] and the Merseyside Jewish Community Care charity on Smithdown Road.[80]
Notable Liverpudlian Jews include entrepreneur Brian Epstein, who managed the Beatles;[81] actor Jason Isaacs, whose great-grandparents co-founded the Jewish community in Childwall;[82] businessman David Lewis, who founded the Lewis's department store chain and left much money after his death for the construction of what would become some of the city's most important hospitals and philanthropic institutions;[83] Lewis's chairman Harold Cohen, who funded the construction of the University of Liverpool's Harold Cohen Library;[72] and rabbi Isser Yehuda Unterman, who was Chief Rabbi of Liverpool for 22 years before becoming Chief Rabbi of Israel.[84]
Buddhism
The Duldzin Buddhist Centre and Kadampa Meditation Centre is located in the Aigburth suburb and focuses on Kadampa Buddhism.[74]
Notes
- New category created for the 2011 census
- New category created for the 2021 census
- In 2001, listed under the 'Chinese or other ethnic group' heading.
References
- "Resident Population Estimates Jun2001, All Persons". Office for National Statistics. 18 December 2007. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Resident Population Estimates, All Persons". Office for National Statistics. 1 October 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Liverpool District: Total Population". A Vision of Britain through Time. University of Portsmouth. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Liverpool District: Population Change". University of Portsmouth. Archived from the original on 25 July 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "UK population grows to 60,587,000 in mid-2006" (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 22 August 2007. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Neighbourhood Statistics: Resident Population Estimates by Broad Age Band". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Key Statistics for urban areas in the North – Contents, Introduction, Tables KS01 – KS08" (PDF). Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 July 2004. Retrieved 23 January 2010.
- Costello, Ray (2001). Black Liverpool: The Early History of Britain's Oldest Black Community 1730–1918. Liverpool: Picton Press. ISBN 1-873245-07-6.
- McIntyre-Brown, Arabella; Woodland, Guy (2001). Liverpool: The First 1,000 Years. Liverpool: Garlic Press. p. 57. ISBN 1-904099-00-9.
- "Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Chinese Community". Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – European Communities". Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 10 January 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- Coslett, Paul (11 January 2005). "The origins of Scouse". BBC Liverpool. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- "Why city is the real capital of Ireland..." Liverpool Echo. 17 March 2003. Archived from the original on 29 September 2012.
- "Area: Granby (Ward)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Area: Princes Park (Ward)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Area: Central (Ward)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- Data is taken from United Kingdom Casweb Data services of the United Kingdom 1991 Census on Ethnic Data for England, Scotland and Wales (Table 6)
- "Office of National Statistics; 2001 Census Key Statistics". webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- "2011 Census: Ethnic Group, local authorities in England and Wales". webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- "Figure 3: Population by ethnic group, 2021, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 29 November 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- "Neighbourhood Statistics: Resident Population Estimates by Ethnic Group (Percentages)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 20 May 2011.
- "Jamaica Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "Deconstructing the Liverpool black identity". iamcolourful.com. Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "China Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "Liverpool and its Chinese Seaman". halfandhalf.org.uk. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Twinning". Liverpool City Council. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010.
- "Ghana Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "New scholarship for Ghanaian students available at Liverpool Hope". Postgrad.com. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
- "History". Liverpool Greek Society. Archived from the original on 27 June 2011. Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- Bartlett, David (7 August 2007). "City Greek community to get its own centre at last". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 26 September 2012. Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- "Liverpool Greek Society needs £1m to build school and community centre". Wirral News. Retrieved 2 February 2010.
- "Coast Walk: Stage 5 – Steam Packet Company". BBC. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Leaving from Liverpool". National Museums Liverpool. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Neighbourhood Statistics: Country of Birth". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 20 January 2010.
- "Bringing Italy to Liverpool". Liverpool Echo. 16 June 2007. Retrieved 30 January 2010.
- "Italian Fans to turn out in force to cheer Liverpool". Liverpool Daily Post.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Italian Consulate". Yahoo!. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Liverpool's Latin quarter – just around the corner". Liverpool.com. Archived from the original on 11 October 2012. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- Key, Phil (21 December 2007). "Keep the culture real, keep it Latin". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 11 October 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- "Translation". Liverpool.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 26 February 2007. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- "University course search". Ucas. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- "First team". Liverpool F.C. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- "Brazilica samba festival in Liverpool this weekend". Click Liverpool. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- "Malaysia Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "Vietnam Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 April 2010. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Integration of the Somali Community into Europe". Federation of Adult Education Associations. Archived from the original on 16 December 2009. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- Casciani, Dominic (30 May 2006). "Somalis' struggle in the UK". BBC News. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- "Vilayat – Coming to Liverpool". liverpoolmuseums.org. Archived from the original on 21 November 2008. Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- "Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Indian Community". mersey-gateway.org. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- Morphy, Jim (22 October 2013). "The Welsh of Liverpool". Wales Art Review. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- http://new.wales.gov.uk/news/archivepress/officefirstminspress/firstminpress2004/706222/?lang=en
- "Islam and Britain". BBC. Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- "Islamic Cultural Centre and Al-Rahma Mosque". muslimsinbritain.org. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "2011 Census Questions Published". BBC News. 21 October 2009. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- "Tribute to newsagent gunned down in Huyton". 2 June 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- "Zimbabwe Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- "Area: Liverpool (Local Authority)". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- Data is taken from United Kingdom Casweb Data services of the United Kingdom 2001 Census on Religion Data for England, Scotland and Wales (Table 7)
- "QS210EW - Religion (detailed)". Nomis - Official Census and Labour Market Statistics. 2011. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- "Figure 2: Religion, 2021, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 29 November 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- Welcome, St Luke's Church, Liverpool, retrieved 9 April 2013
- Sardais, Louise. "Architectural Heritage – The 'little mosque'". BBC. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
- Sardais, Louise. "Architectural Heritage – The 'little mosque'". BBC. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
- Bartlett, David (15 January 2010). "Liverpool City Council's plans to restore Britain's first mosque". Liverpool Daily Post. Archived from the original on 30 September 2012.
- Miller, Colin (25 November 2006). "Liverpool's Jewish Heritage and Urban Regeneration". Archived from the original on 6 February 2007. Retrieved 13 May 2007.
- "Liverpool - jewish heritage, history, synagogues, museums, areas and sites to visit".
- Sharples, Joseph (2004). Pevsner Architectural guide to Liverpool. Yale University Press. p. 249.
- "Liverpool places of worship: Six religious buildings you probably don't know much about - Liverpool Echo". 22 June 2015.
- "Greenbank Drive Synagogue, Greenbank Drive, Sefton Park - Liverpool". Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- "Home". lrshul.org.
- "Liverpool Masorti Community".
- "Home". lubavitchliverpool.com.
- "Home". kingdavidliverpool.co.uk.
- "Home". mjccliverpool.com.
- The Beatles et al. (2000)
- Pfefferman, Naomi (14 July 2000). "Once a 'wimp,' Actor Thrives on Portraying Villains". Jewish News of Greater Phoenix. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 29 June 2008. Rpt. from Jewish Journal of Los Angeles, 14 July 2000.
- "The David Lewis Centre". Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- Isser Yehuda Unterman (1886 - 1976) biography, referenced to The Department for Jewish Zionist Education.




