Dibekacin
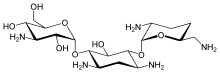
Dibekacin (3',4'-dideoxykanamycin B) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is a semisynthetic derivative of kanamycin developed by Hamao Umezawa and collaborators for Meiji Seika.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Panimycin, Tokocin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.316 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H37N5O8 |
| Molar mass | 451.521 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
It has been used in combination with sulbenicillin.[3]
References
- Umezawa H, Umezawa S, Tsuchiya T, Okazaki Y (July 1971). "3',4'-Dideoxy-Kanamycin B Active Against Kanamycin-Resistant Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa". The Journal of Antibiotics. 24 (7): 485–487. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.24.485. PMID 4998037.
- Umezawa H (November 1982). "Découverte de la dibékacine et de ses aspects chimiques [Discovery of dibekacin and its chemical aspects]". La Nouvelle Presse Médicale. 11 (46): 3379–84. PMID 7155844.
- Aonuma S, Ariji F, Oizumi K, Konno K (June 1987). "Electron microscopy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with sulbenicillin and dibekacin". Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 152 (2): 119–28. doi:10.1620/tjem.152.119. PMID 3114912.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.