Distearoylphosphatidylcholine
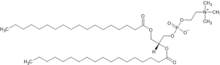
Distearoylphosphatidylcholine is a phosphatidylcholine, a kind of phospholipid. It is a natural constituent of cell membranes, eg. soybean phosphatidylcholines are mostly different 18-carbon phosphatidylcholines (including minority of saturated DSPC), and their hydrogenation results in 85% DSPC.[1] It can be used to prepare lipid nanoparticles which are used in mRNA vaccines,[2][3] In particular, it forms part of the drug delivery system for the Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines.[4][5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R)-2,3-Bis(octadecanoyloxy)propyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate | |
| Other names
1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, DSPC, 18:0 PC | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.309 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C44H88NO8P | |
| Molar mass | 790.161 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- Moderna COVID-19 vaccine nanoparticle ingredients
- Others
- Stearic acid, contributing stearoyl- group
- Phosphocholine
References
- van Hoogevest P, Wendel A (2014). "The use of natural and synthetic phospholipids as pharmaceutical excipients". The European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. 116 (9): 1088–1107. doi:10.1002/ejlt.201400219. PMC 4207189. PMID 25400504.
- Puri A, Loomis K, Smith B, Lee JH, Yavlovich A, Heldman E, Blumenthal R (2009). "Lipid-based nanoparticles as pharmaceutical drug carriers: from concepts to clinic". Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems. 26 (6): 523–80. doi:10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v26.i6.10. PMC 2885142. PMID 20402623.
- Salvatori G, Luberto L, and Marra E (2020). "SARS-CoV-2 SPIKE PROTEIN: an optimal immunological target for vaccines". Journal of Translational Medicine. 18 (1): 222. doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02392-y. PMC 7268185. PMID 32493510.
- "Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine Standing Orders for Administering Vaccine to Persons 18 Years of Age and Older" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- "Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine EUA Fact Sheet for Recipients and Caregivers". Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 June 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.