Dongshan County
ⓘ (simplified Chinese: 东山县; traditional Chinese: 東山縣; pinyin: Dōngshān Xiàn; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Tang-soaⁿ-koān) is a county of far southern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China, located along the Taiwan Strait.[1] It comprises 44 islands for a total area of 194 square kilometres (75 sq mi) and is under the administration of Zhangzhou City. The total population was 200,000. Dongshan County has jurisdiction over seven towns, a nationally managed forest and an economic and technological development district.[2] It is an important port for international trade and trade with Taiwan.
Dongshan County
东山县 Tungshan; Tung shan | |
|---|---|
 Dongshan Guandi Temple | |
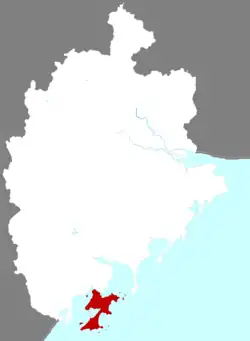 Location of Dongshan in Zhangzhou | |
 Dongshan Location in Fujian | |
| Coordinates: 23°41′58″N 117°25′13″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Fujian |
| Prefecture-level city | Zhangzhou |
| Area | |
| • Total | 194 km2 (75 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 200,000 |
| • Density | 1,000/km2 (2,700/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
History
On one of the islands, there are several ancient relics, including the 'Mountain of the Nine Immortals', and the Dongshan ancient city, where two famous Ming Dynasty generals, Qi Jiguang and Zheng Chenggong were based.
Tongling Town on Northeastern Dongshan Island has an ancient waterside castle. Tonghshan Castle was built of stone in 1387 by Zhou Dexing of the Ming Dynasty to protect against Japanese pirates. The gate tower still stands intact. Inside, a path is linked by corridors and the exquisite Temple of Guan Yu. The entrance to the temple is flanked by ancient houses, the birthplace of Huang Daozhou, an official of the Ming Dynasty.[3]
In 1950, at the end of the Chinese Civil War, the island was the scene of fighting between the nationalist Kuomintang and Chinese Communist forces, and again in 1953 during the so-called Dongshan Island Campaign, an unsuccessful attempt by the nationalists to retake the island.
Economy
Dongshan County is situated between two economically vibrant cities of Xiamen and Shantou. Both are Special Economic Zones which have spillover economic effects for Dongshan County, such as increased tourism. The total GDP of islands in 2003 was 3.62 billion yuan. The main industries are fishery, fish farming and asparagus farming.
Tourism
The tourism industry is based on rich ancient history, seaside resorts and breath taking scenery.[2]
Administration
There are seven towns (镇; zhèn) under the county's administration:
- Xibu (西埔镇), the county seat
- Tongling (铜陵镇), former county seat
- Qianlou (前楼镇)
- Chencheng (陈城镇)
- Kangmei (康美镇)
- Zhangtang (樟塘镇)
- Xingchen (杏陈镇)
The county has jurisdiction over a nationally managed forest and an economic and technological development district.[2]
Geography and climate
Dongshan is located in the southernmost part of the province, with Kaohsiung, Taiwan 110 nautical miles (200 km; 130 mi) to the east and Hong Kong 210 nautical miles (390 km; 240 mi) to the southwest.
The climate of the Dongshan Islands is humid subtropical (Köppen Cfa) and moderated by their coastal location, without frost through the year. In winter, north-east winds, and in summer south-east winds prevail. The annual average temperature is 20.9 °C (69.6 °F). The coolest month of the year is February with an average temperature of 13.1 °C (55.6 °F); the hottest, July, with an average temperature of 27.5 °C (81.5 °F). The annual average rainfall is only 1,256 millimetres (49.4 in), which causes a shortage of fresh water, especially from October to January. Additional water must be acquired from outside for both domestic and industrial use.[2]
| Climate data for Dongshan (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 24.8 (76.6) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
32.5 (90.5) |
34.1 (93.4) |
35.6 (96.1) |
35.5 (95.9) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.0 (95.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
35.6 (96.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) |
16.9 (62.4) |
19.0 (66.2) |
23.1 (73.6) |
26.8 (80.2) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.3 (86.5) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.6 (74.5) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.5 (76.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.8 (56.8) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
23.9 (75.0) |
26.7 (80.1) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
24.2 (75.6) |
20.5 (68.9) |
16.2 (61.2) |
21.5 (70.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 12.0 (53.6) |
12.0 (53.6) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.5 (67.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 4.6 (40.3) |
5.0 (41.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
14.5 (58.1) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.1 (57.4) |
9.0 (48.2) |
4.7 (40.5) |
4.6 (40.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 33.6 (1.32) |
52.5 (2.07) |
85.8 (3.38) |
112.9 (4.44) |
139.3 (5.48) |
217.3 (8.56) |
143.1 (5.63) |
230.0 (9.06) |
123.4 (4.86) |
41.6 (1.64) |
40.4 (1.59) |
37.8 (1.49) |
1,257.7 (49.52) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 5.6 | 8.8 | 10.6 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 8.8 | 11.1 | 7.5 | 2.9 | 4.2 | 5.6 | 102.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 79 | 81 | 82 | 84 | 87 | 83 | 83 | 77 | 70 | 73 | 73 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 153.7 | 119.8 | 123.4 | 140.1 | 163.2 | 193.2 | 271.2 | 243.0 | 222.0 | 223.3 | 183.3 | 166.4 | 2,202.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 46 | 37 | 33 | 37 | 40 | 48 | 66 | 61 | 61 | 63 | 56 | 51 | 50 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[4][5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[6] | |||||||||||||
Transport
Dongshan Port is one of the main ports in Fujian, open to foreign vessels since 2003 and very close to Taiwan and Hong Kong. The port has a large body of water, large hinterland, and a deep, sediment-free harbour. The harbour is big enough for twenty-two 10,000 tons berths. Currently, the port has two deep water harbours built to accommodate 3,000 tons berths. These facilities provide Dongshan Port an important commercial link between Xiamen and Shantou.[1]
References
- "Dongshan Island - A Natural Wonderland". Diedao.com. Archived from the original on 2013-05-10. Retrieved 2014-03-06.
- Case Study Reports 5 Global Environmental Forum (GEF), Japan, n.d.
- "Zhangzhou - Fujian Province travel guide - China travel guide, Fujian China travel services, Fujian tours". Chinaplanner.com. Retrieved 2014-03-06.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- 东山 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
External links
- Dongshan Island - A Natural Wonderland diedao.com