Dornier Do 19
The Dornier Do 19 was a German four-engine heavy bomber that first flew on 28 October 1936. Only one prototype flew, and it was converted to a transport in 1938. The other two were scrapped.
| Do 19 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Dornier Do 19 | |
| Role | Heavy bomber |
| Manufacturer | Dornier-Werke GmbH |
| First flight | 28 October 1936 |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | 3 |
The Luftwaffe had a shortcoming in the lack of an efficient heavy bomber fleet. Generalleutnant Walther Wever, the Luftwaffe's first Chief of Staff, was the most persistent advocate of a German long-range strategic bomber fleet. It was built for the Luftwaffe's Ural bomber program under General Wever, competing against the Junkers Ju 89. The RLM Technisches Amt issued a specification for a four-engine heavy bomber. But after Wever's death in an airplane crash in June 1936, Wever's successor, Albert Kesselring, canceled Germany's long-range bomber projects to concentrate on tactical bombers.
Both Dornier and Junkers were competitors for the contract, and each received an order for three prototypes in late 1935. The Dornier design was given the project number Do 19, while the Junkers prototype became the Ju 89.
Design and development
The Dornier Do 19 was a mid-wing cantilever design, and was mostly metal in construction. It had a rectangular-section fuselage and the tail had braced twin fins and rudders, mounted on the upper surface of the tailplane, itself set low on the rear fuselage. This was quite similar to the tail of the contemporary British Armstrong Whitworth Whitley medium bomber. It also had retractable landing gear, including the tailwheel. The powerplant, according to some sources, was supposed to be four Bramo 322H-2 radial engines that were mounted in nacelles at the leading edges of the wings.
It had a crew of ten, which would have consisted of a pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, radio operator and five gunners. The V1 prototype flew on 28 October 1936. After Generalleutnant Wever died in an airplane crash on 3 June 1936, the heavy bomber program lost its momentum, and never recovered. When the Luftwaffe was given its heavy blow over the skies of England, the error of not having heavy bombers became apparent. By then, however, it was too late to develop the bombers required.
Albert Kesselring, Wever's successor, believed that what Germany required were more fighters and tactical bombers.
Also Kesselring and Jeschonnek had suggested to Göring that it would be better to drop heavy bomber projects due to material shortages. Around 2.5 tactical bombers could be built with the same material as one heavy bomber. In May 1937 Göring is reported as saying to Milch ‘The Führer does not ask me how big my bombers are, but how many there are’ [1]
Therefore, the V2 and V3 prototypes were scrapped. The original V1 became a transport in 1938. The Dornier Do 19 had a disappointing performance: it was slow, carried only a 1,600 kg bombload, and had only medium range. In fact, the whole Ural bomber concept had already been abandoned, not only because the required range was impossible, but also because existing navigation and bombsights were not up to the task.
Specifications (Do 19 V2)
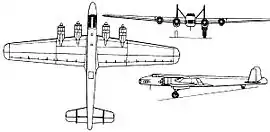
Data from Aircraft of the Third Reich Volume one.[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 10, pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, radio operator and five gunners
- Length: 25.45 m (83 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 35 m (114 ft 10 in)
- Height: 5.76 m (18 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 160.2 m2 (1,724 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 11,865 kg (26,158 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 18,500 kg (40,786 lb)
- Powerplant: 4 × Bramo 322H-2 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 533 kW (715 hp) each for take-off
- 447 kW (599 hp) maximum continuous power
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 315 km/h (196 mph, 170 kn) at sea level at 18,000 kg (40,000 lb)
- Cruise speed: 250 km/h (160 mph, 130 kn) at 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
- Range: 1,600 km (990 mi, 860 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 5,600 m (18,400 ft)
- Time to altitude: 2,000 m (6,600 ft) in 30 minutes 30 seconds
- Wing loading: 114 kg/m2 (23 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.13 kW/kg (0.079 hp/lb)
Armament
- 1 × 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 15 machine gun in nose
- 1 × 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 15 machine gun in tail
- 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) cannon in dorsal turret
- 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) cannon in ventral turret
- 16 × 100 kg (220 lb) bombs
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Boeing XB-15
- Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
- Handley Page H.P.54 Harrow
- Junkers Ju 89
- Petlyakov Pe-8
- Piaggio P.50
- Piaggio P.108
- Short Stirling
Related lists
References
- Irving, D (1973) The Rise and Fall of the Luftwaffe, P 54 London: Cox and Wyman ISBN 0 297 76532 9
- Green, William (2010). Aircraft of the Third Reich Volume one. London: Crecy. pp. 235–237. ISBN 9781900732062.